* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Component 4: Chemistry Oils, Earth and Atmosphere – Word Bank
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
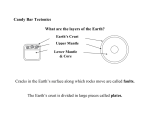
Component 4: Chemistry Oils, Earth and Atmosphere – Word Bank Outcome 1 Crude oil - a natural liquid product used as a raw material by oil refineriesMoulded means hat a material can be squeezed into different shapes. Polymer - polymers are chemical substances that are made up of many molecules all strung together to form really long chains. Polythene - chemical name poly(ethene), a common plastic which softens on heating and is unaffected by most chemicals. Outcome 2 Biodegradable - A biodegradable product has the ability to break down, safely and relatively quickly, by biological means, into the raw materials of nature and disappear into the nvironment. Incineration - this is a process of burning rubbish. It can be useful for getting rid of waste material, but it can often produce toxic gases or greenhouse gases. Landfill sites - these are sites where waste material can be buried in the ground. They are often used to dispose of household rubbish. Microbe - Microbe is another word for microorganism. This is a microscopic organism that is too small to be seen with the naked eye, but can be seen under a microscope. Microbes include bacteria, viruses and some fungi. Many microbes are very useful to us because they break down waste products. Recycling - as an alternative to burning or burying waste, sometimes it can be recycled. This may involve using the material again to make a new object. Outcome 3 Dissolve - if a substance dissolves in a liquid it will disappear so that it cannot be seen. For example, when you add sugar to your tea, the sugar dissolves in the water. Dissolving is a usually physical change and not a chemical change, as it can usually be easily reversed, for example by evaporating the liquid. Emulsion - this is a mixture of two liquids that do not dissolve in each other, for example oil and water. Oils - are certain types of liquids that do not mix with water. They may be vegetable or mineral. Solution - a mixture in which one substance is dissolved in another. For example, when you dissolve salt in water it makes a salt solution. Vegetable oil - this is oil which has been obtained from plant material, often the seed. Outcome 4 Boiling point -the temperature at which bubbles of gas start to form within a liquid that is being heated. Outcome 5 Core - This is the very centre of the Earth. Temperatures here are extremely hot. Crust - The Earth’s crust is like the skin of an apple, it is very thin compared to the thickness of the core and mantle. It is only a few miles thick. Mantle - The mantle makes up most of the volume of the Earth. Plates - These are large sections of the Earth’s crust that have cracked away from other parts. These plates are huge, the whole of the Earth’s surface being split into 8 plates. Outcome 6 Boundary - this is the ‘edge’ between two of the plates in the Earth’s crust. Convection currents - can only occur in liquids and gases. Warm fluid rises and cold fluid sinks. This circulation is called a convection current. Earthquake - this is a sudden release of energy in the Earth’s crust. It causes the whole area to shake violently. Volcanic eruption - this happens where an opening in the Earth’s crust allows hot, molten rocks from below the surface to be pushed violently upwards and released onto the surface of the Earth. Outcome 7 Atmosphere - The atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the surface of the Earth. Billion - a billion is a thousand million. ie 1,000,000,000. Outcome 8 Carbonates - these are chemical compounds. They are formed when carbon dioxide reacts with an acid. Fossil fuel - a fuel that has been made from the remains of plants and animals that died millions of years ago. Photosynthesis - is a process carried out by green plants. In the presence of sunlight, plants can use carbon dioxide and water to make food. This process also releases oxygen into the atmosphere. Outcome 9 Carbon dioxide - an invisible gas which is produced by burning fuels and by respiration. Oxygen - a gas found in the air. Water vapour - water which has evaporated into the air to form an invisible gas. Noble gas - gases such as helium and neon. They are very unreactive Helium - one of the noble gases. It has a very low density. Unreactive - does not take part easily in chemical reactions. Outcome 10 Burning - is sometimes called combustion. It is a chemical reaction in which a fuel combines with oxygen to release heat energy.










![c1b revision sheet 1[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016683336_1-baea0f7acdab057d50ded8ac95b62330-150x150.png)