* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Note Sheet 4-8
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Covariance and contravariance of vectors wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Tensors in curvilinear coordinates wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Curvilinear coordinates wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
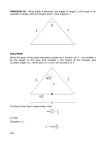
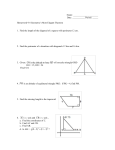
Geometry 4-8 Triangles and Coordinate Proof A coordinate proof uses figures drawn in the coordinate plane and algebra to prove geometric concepts. There are four basic rules for placing your figures in the coordinate plane: Use the origin as a vertex or center of the triangle. Place at least one side of a triangle on an axis . Keep the triangle in the first quadrant if possible. Use coordinates that make computations simple. Name the coordinates of isosceles triangle XYZ. Y(?,?) X(?,?) Z(a,?) X is at the origin, so X is (0,0). Z is on the x-axis, so Z is (a,0). Y is halfway between X and Z, so the x-coordinate is a/2. We don't know the y-coordinate, so we'll call it b. So Y is (a/2, b). Write a coordinate proof to show that a line segment joining the midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side. 2b + 0 2c + 0 M= = (b,c) 2 , 2 B(2b,2c) 2b + 2a 2c + 0 M N= = (b + a,c) N 2 , 2 c-c 0 m(MN) = b + a - b = a = 0 A C (0,0) (2a,0) m(AC) = 0 - 0 = 0 = 0 2a - 0 2a Since the slopes are equal, MN || AC. ( ( ) ) Position and label isosceles triangle JKL on the coordinate plane so that its base JL is a units long, vertex K is on the y-axis, and the height of the triangle is b units. K (0,b) (-1/2 a,0) J L(1/2 a,0) PAUSE HERE AND TRY THIS ONE. Name the coordinates of isosceles right triangle ABC. A(?,?) B(?,?) C(a,?) B is at the origin, so B is (0,0). C is on the x-axis, so C is (a,0). The triangle is isosceles, and A is on the y-axis, so A is (0,a).