* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
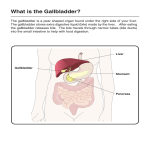
Liver Protocol (Hepatic or RUQ) This protocol includes images of several organs and structures. It has been divided into sections to assist in determining diagnostic images that should be stored for the physician. o Pancreas o Liver o Gallbladder and Common Bile Duct You must always evaluate the entire organ first before you store an image You should understand completely why you stored the image and identify everything in the image Multiple breathing techniques and patient positions will be required Organ/ Order Pancreas Organ/ Order Scan Plane Transverse plane on the body Key Landmarks Identified PANCREAS PANCREAS PANCREAS Pancreas head Portal splenic confluence CBD o If CBD is enlarged, measure internal AP diameter Pancreas body Aorta Measurement o If pancreatic duct is seen measure internal AP diameter Pancreas tail Splenic vein Scan Plane Label Sagittal LIVER SAG Left lobe with inferior tip The transducer is placed sagittal in the mid portion of the patient’s body LIVER SAG Left lobe Caudate lobe IVC Right lobe Diaphragm Right lobe superior Right hemidiaphragm Right pleural space Right lobe mid Main portal vein Right lobe inferior o Demonstrating largest superior to inferior area o Measure liver length from superior to inferior Right kidney Left lobe Caudate lobe IVC Right lobe Left lobe Right hepatic vein Left hepatic vein LIVER SAG LIVER Sagittal LIVER SAG SUP Sagittal The transducer is placed sagittal and lateral on the patient’s body LIVER Transverse Label LIVER SAG MPV LIVER SAG INF Transverse LIVER TX The transducer is placed transverse in the mid portion of the patient’s body LIVER TX HV Angulation of the AK\backup\Abdomen I\Protocols Key Landmarks Identified probe is used for right lobe images LIVER TX LIVER TX SUP LIVER TX MPV LIVER Transverse Transverse The transducer is placed transverse and lateral on the patient’s body LIVER TX MPV LIVER TX MPV LIVER TX INF Organ/ Order Scan Plane Gallbladder Sagittal plane of the GB Patient in Supine position Transverse plane of the GB GB SUPINE SAG GB SUPINE SAG GB SUPINE TX Patient in Left lateral decubitus position Gallbladder Patient in Right lateral decubitus position GB LLD SAG Sagittal plane of the GB Transverse plane of the GB Sagittal plane of the GB level of the porta hepatis GB LLD SAG GB LLD TX GB RLD SAG GB RLD SAG Transverse plane of the GB GB RLD TX Transverse plane of the CBD CBD TX Common Bile Duct CBD SAG Sagittal plane of the CBD CBD SAG CBD SAG AK\backup\Abdomen I\Protocols Middle hepatic vein Right lobe-most anterior portion Diaphragm Right lobe superior Right hemidiaphragm Right pleural space Right lobe mid Main portal vein Right lobe mid Main portal vein with color Doppler Right lobe mid Main portal vein with color & spectral Doppler o Normal waveform will demonstrate slight phasic flow toward the liver Right lobe-inferior Right kidney Label GB SUPINE TX Gallbladder Key Landmarks Identified Gallbladder body Gallbladder fundus Gallbladder body Gallbladder neck Gallbladder mid body with clear delineation of anterior wall Gallbladder mid body with clear delineation of anterior wall Measurement o measure anterior wall thickness Gallbladder body Gallbladder fundus Gallbladder body Gallbladder neck Gallbladder mid body Gallbladder body Gallbladder fundus Gallbladder body Gallbladder neck Gallbladder mid body Portal vein CBD Hepatic artery Portal vein CBD Enlarged image Portal vein CBD Enlarged image Portal vein CBD Measurement o Internal AP diameter Anatomical/ Image Correlation CBD Hepatic artery CBD measurement Inner wall to inner wall Where it enters the liver Portal vein Transverse Portal triad Mickey Mouse sign Anterior GB wall measurement Outer wall to inner wall Normal Measurement Ranges Structure Common Bile Duct Area of Interest Level of Porta Hepatis Plane Long Axis Measurement <7-8 mm Gallbladder wall Anterior Wall Transverse <3 mm Liver Pancreas RT Lobe Inferior Head 15-17 cm Head 2-3.5 cm Pancreatic Duct Body of the pancreas Sagittal Transverse on the body Transverse on the body 2 mm or less Transverse on the body/ long axis on the vessel Normal AP measurement is <13 mm Normal flow velocity is 20-40 cm/s Main Portal Vein Porta Hepatis AK\backup\Abdomen I\Protocols Comments Measure inner wall to inner wall If duct is enlarged: o Look for and document any intrahepatic ductal dilatation o Follow CBD to pancreatic head If GB removed, CBD may be enlarged (up to 11 mm) Calipers are placed outside to inside of the anterior wall Measure superior to inferior Only performed if abnormalities are suspected Only performed if duct is visualized Measure internal duct diameter anterior to posterior Internal AP diameter where MPV crosses the IVC o Only performed if abnormalities are suspected Flow should be phasic and toward the liver Liver Protocol Common Laboratory Values to be Reviewed prior to Examination Lab Value Amylase Lipase AST (SGOT) Organ Pancreas Pancreas Liver Level Increased Increased Increased Indication or Association Pancreatitis or other pancreatic disease Pancreatitis or other pancreatic disease Hepatitis, fatty liver, cirrhosis other liver disease ALT (SGPT) Liver Increased Jaundice or hepatitis Alkaline phosphatase Liver Gallbladder Liver Gallbladder Increased Biliary obstruction or metastases Increased Jaundice, liver damage or obstruction Bilirubin Tips Patient should be NPO for this study to reduce the amount of gas present and to prevent contraction of the GB Have patient poke out their abdomen or take in a deep breath if having trouble seeing the pancreas Pancreatic tail may be evaluated using the spleen as a window Sit the patient erect for scanning if suspicious for stones stuck in the neck that weren’t confirmed in LLD or RLD Watch your gain settings: o Making the GB lumen too dark with TGC can mask pathology o Using too much gain can give the appearance of pathology If the GB appears to have artifacts, change to a higher frequency, use harmonics, use a different window, or have the patient poke out their abdomen If the GB is enlarged make sure to evaluate the ducts for signs of stones. These can obstruct the ducts To find the CBD: o Scan from the GB in transverse and follow it to the neck and cystic duct, you will see CBD o Follow the portal vein from the portal confluence. The CBD will be anterior to the vein If the GB has been surgically removed (postcholecystectomy), document a “GB FOSSA” image (main lobar fissure near porta hepatis) instead of the gallbladder images Pathology Seen o Gray scale sagittal and transverse images o Gray scale sagittal and transverse images with 3 measurements (length, width, and height) o Color Doppler image to document the presence of blood flow o Spectral Doppler image to document the type and velocity of blood flow o If the wall measures greater than 3 mm, color Doppler can be used to confirm increased flow in the wall due to cholecystitis. o If the patient has gallstones and/or gallbladder wall thickening, they should be evaluated for a positive Murphy’s sign (extreme tenderness upon transducer or manual pressure in the RUQ). This needs to be reported to the interpreting physician as it indicates acute cholecystitis. o Must attempt to demonstrate movement of any pathology seen in the GB – sludge and stones will move – masses will not!! o If the CBD is enlarged at the porta hepatis, it should be followed to the pancreatic head to evaluate for stones or an obstructive lesion AK\backup\Abdomen I\Protocols