* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Flash cards unit 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
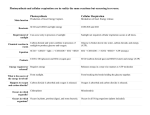
What is osmosis Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. Describe glycolysis Glycolysis is the break down of glucose to pyruvic acid (3Carbon atoms). It occurs in the cytoplasm. 2 molecules of ATP are produced. It occurs even when there is no oxygen present. Name the two types of respiration and the differences between them. What is a limiting factor? Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen and the pyruvic acid from glycolysis is broken down to Carbon dioxide, water and 36molecules of ATP. Anaerobic respiration happens in the absence of oxygen. Pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid (in animals) or alcohol and carbon dioxide (in plants) It is a factor which when in short supply prevents the reaction occurring at its maximum rate. Explain what optimum means in relation to enzymes Optimum is the condition at which an enzyme is most active. What happens to an enzyme when it is denatured and under what conditions? The enzymes active site changes shape so a substrate can no longer fit into it. What is the equation for photosynthesis Light energy Carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen pepsin Proteinpeptides catalase Hydrogen peroxidewater and oxygen Name as many break down enzymes as possible amylase Starchmaltose lipase Fatfatty acids and glycerol Describe what happens during photolysis Describe what happens during carbon fixation What is the importance for diffusion for cells? What types of molecules can diffuse? Water is broken down using light energy to produce ATP, oxygen gas (which is released) and hydrogen (which goes on to the carbon fixation stage). This stage relies on enzymes and carbon dioxide is converted into glucose by the addition of hydrogen. This process requires energy in the form of ATP So cells can obtain important useful substances required for survival and remove harmful waste products Small soluble molecules like carbon dioxide, water oxygen, glucose, urea, salts Yogurt produced when bacteria convert lactose sugar in milk to lactic acid which thickens and sours the milk. Bread produced by yeast fermenting Name two product produced by glucose to produce carbon dioxide which microorganisms and how they are produced makes bread rise. Alcohol produced by the fermentation of glucose by yeast to produce alcohol. Biogas produced by the fermentation of waste by bacteria to produce methane gas (a fuel) Gasohol when alcohol from the fermentation of glucose by yeast is added to petrol What do antibiotics destroy? What is resistance? Describe what happens to a plant cell when placed in hypertonic and hypotonic solution Describe what happens to an animal cell when placed in hypertonic and hypotonic solution Bacteria NOT VIRUSES When the antibiotic does not destroy the bacteria Hypotonic – water diffuses in = turgid (vacuole swells) Hypertonic – water diffuses out = plasmolysised/flaccid (cell membrane comes in from wall, vacuole and cytoplasm shrink) Hypotonic – water diffuses in = bursts Hypertonic – water diffuses out = shrinks Name the structure which are found in (i) a plant cells and (ii) an animal cell. What is the equation of the formation of ATP? How can plants be encouraged to grow to at their maximum rate( think limiting factors) Plant – cell wall Nucleus Cytoplasm Vacuole Chloroplast Cell membrane Animal – cell membrane Nucleus cytoplasm ADP + Pi ATP Use of extra lighting Increase temperature Enrich with carbon dioxide Ensure constant supply water. Glucose used as energy What are the three things which can happen stored as starch to glucose after it is produced in a leaf cell? converted to a structural carbohydrate cellulose