* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Edith Hamilton Mythology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
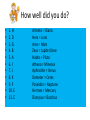
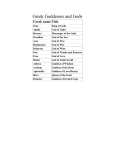
Edith Hamilton Mythology Chapter ONE Objectives • Students will identify characters through their distinguishing traits. • Students will recognize the chief Olympian gods and goddesses and their functions. • Students will identify and discuss the lesser Greek and Roman gods and goddesses. • Students will comment on two great gods of Earth: Dionysus and Demeter. Agenda • Bell ringer (Partners-matching game) • Power-point (add/check traits for the Olympian gods) • Gallery of the Gods (12 mins.) • Notes on mythological creatures • Collection of the crossword puzzle for a homework grade. Bell ringer INTRO. • Greek art and literature greatly influenced Roman culture and, as a result, the Olympian gods merged with the Roman deities. With a few exceptions, like Apollo and Pluto, the Greek gods were given Roman names. While the gods’ names were different, the duties and relationships were similar to their Greek counterparts. Bell ringer • • • • • • • • • • • 1. Artemis 2. Hera 3. Ares 4. Zeus 5. Hades 6. Athena 7. Aphrodite 8. Demeter 9. Poseidon 10. Hermes 11. Dionysus A. Pluto B. Jupiter C. Bacchus D. Juno E. Mercury F. Neptune G. Mars H. Diana I. Minerva J. Venus K. Ceres How well did you do? • • • • • • • • • • • 1. H 2. D 3. G 4. B 5. A 6. I 7. J 8. K 9. F 10. E 11. C Artemis = Diana Hera = Juno Ares = Mars Zeus = Jupiter/Jove Hades = Pluto Athena = Minerva Aphrodite = Venus Demeter = Ceres Poseidon = Neptune Hermes = Mercury Dionysus = Bacchus Best-Known writers of Greek and Roman mythology • Ovid-responsible for telling almost all of the mythological stories at great length; “a compendium of mythology” • Homer-writer of the Iliad and the Odyssey, the oldest of Greek writings “The best guides to a knowledge of Greek mythology are the Greek writers, who believed in what they wrote.” Zeus (Jupiter) • Lord of the Sky; he falls in love many times. • His power is greater than all the gods combined. Hera (Juno) • Wife of Zeus; her job is to protect marriage. • She often punishes Zeus and his female lovers. Poseidon (Neptune) • God of the Sea; he is second in power to Zeus. • He provides humans with the use of the horse. Hades (Pluto) • Ruler of the underworld; he marries Persephone. • The kingdom of the dead carries his name, Hades. Athena (Minerva) • The daughter of Zeus; she is Goddess of the City, Goddess of the strategy of war/wisdom. • Her job is to defend the city against any enemies. (Athens was named after her.) Phoebus Apollo (Apollo) • The god of light and truth and the healing arts. Artemis (Diana) • Apollo’s twin sister; she protects the young. • She is also the Goddess of the Hunt. Aphrodite (Venus) • The Goddess of Beauty and Love; she is usually surrounded by beautiful things. • She can entice men with her beauty. Hermes (Mercury) • The messenger of Zeus; he is graceful and swift. • He appears in more myths than any other god. Ares (Mars) • The God of War; he is found in many myths. • He is associated with fighting and destruction. Hephaestus (Vulcan) • The God of Fire and Artisans; he is ugly and crippled. • He is the most peace-loving and kind of the gods. Hestia (Vesta) • The sister of Zeus; she is not found in many myths. • She takes care of the gods’ home. Lesser Gods of Olympus • • • • Eros (Cupid) the God of Love Hebe- the Goddess of Youth Iris- the Goddess of the Rainbow The Graces- the triple incarnation of grace and beauty; the “queens of song” • The Muses- the nine daughters of Zeus and Mnemosyne (Memory) who inspire. Gods of the Waters • Poseidon (Neptune)- ruler of the seas • Ocean – Lord of the river Ocean which surrounds the Earth • Triton – the trumpeter of the sea who uses a large shell as his trumpet • Proteus – son of Poseidon who can foretell the future and change his shape • Naiads- water nymph Gods of the Underworld • Charon – the person who ferries the souls of the dead to the shores of Hades. • Cerberus- the three-headed, dragon-tailed dog that allows spirits to enter Hades but not to leave • Acheron, Cocytus, Styx- the three rivers of Hades • The Furies – punishers of evildoers Gods of the Earth • Demeter (Ceres) – associated with grain or harvest • Dionysus (Bacchus) – associated with wine Mythical Creatures • Pan (Faunus) – associated with the forest; goat-man • The Satyrs – goat-men found in the wild places of the earth • The Centaurs – half-men, half horse; savage beast-like creatures Mythical Creatures • The Nymphs – the lesser gods of nature; nymphs of the sea, of the waters, of the mountains, and of the trees • The Gorgons- dragon like creatures that can turn men to stone • The Sirens – creatures with enchanting voices that lure sailors to their death Clotho, Lachesis, Atropos • Associated with the fates: the spinner, the disposer of lots, and the cutter of the thread of life, respectively. Well-known lesser Roman gods • Saturn – the Protector of the Sowers and the Seed • Janus – the God with two faces in opposite directions; namesake of the month of January. Next Assignment: • Read Chapter TWO (pp. 50-75) • Your objective: visualization/characterization • You will have a constructed response on Demeter, the goddess of corn or Dionysus, the god of the vine. • Due Friday! Which two gods are found in this statue?