* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rise of Europe 500 - 1300
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
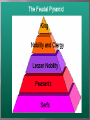
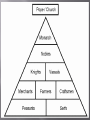
The Geography of Western Europe – •Second smallest in land area located on the western end of Eurasia. •Frontier land – forest, rich soil, ample access to waterways, mineral resources, many rivers and streams. The Germanic Kingdoms– •Germanic tribes were farmers and herders. •No cities or written laws. Much of their culture was governed by unwritten customs. •Warrior elected a king to lead them in war. These warriors swore allegiance to the king in return for certain privileges. Early form of Feudalism. The Germanic Kingdoms– •Strongest Germanic kingdom was the Franks. •Under the leadership of Clovis, the Franks conquered much of the old Western Roman Empire. •Clovis converted to Christianity and gained a powerful ally in the Church. •Charles Martel defeated the Muslims at the Battle of Tours and stop Muslim expansion. •United France, Germany, and parts of Italy. •Reunited most of the Old Roman Empire. •Declared “Emperor” by Pope Leo III after Charlemagne defeated rebellious Roman nobles. This revived the idea of a united Christian community. •This also widened the split between the East and the West. •Worked closely with the Church to spread Christianity. •Used powerful nobles known as Missi Domenici to control the provinces. •At the capital, Charlemagne set up school and has Alcuin establish a curriculum which included grammar, rhetoric, logic, arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy. •After his death, his heirs battled for power. The Treaty of Verdun split the empire into three regions. •Charlemagne extended Christian civilization, blended German, Roman, and Christian traditions. •Europe was still under attack from Muslims, Magyars, and Vikings. •Kings and emperors were too weak to maintain large kingdoms. •Feudalism – loosely organized system where land is divided in exchange for loyalty and service. Participants enter into a feudal contract. •Roles in society are determined. •Knights – intense training. •Development of castles. •The Manor was self-sufficient. Noblewomen – •managed the household •Rights were restricted – inheritance •Some women such as Eleanor of Aquitaine gained influence and political power. •Benefited from the code of Chivalry. Peasants – •Bound to the land - Majority of the population. •Obligations to the higher vassal or lord. •Received protection and land to farm. •Life was harsh – long hours, short life span. Everyday Life •Attend Mass – Administer Sacraments •Establish schools •Social center – Involved in ALL areas •Guide people – values and morality •All Christians pay taxes to the Church • Tithe •God – men & women •Earth – men & women •Anti-Semitism Power of the Church •Papal Supremacy – (power struggle) •Papal States •High government positions •Powerful secular force •Absolute power in religious matters •Church has its own laws and courts Canon law Excommunication Interdict Nuns and Monks •Missionary work •Preserve learning Establish schools Ancient works •Establish hospitals •Manual labor •Benedictine Rule Obedience Poverty Chastity Reforms •Church becomes rich and powerful •Some clergy become corrupt •Cluniac Reforms Benedictine Rule No outside interference Outlawed marriage for priests Prohibited Simony •Development of New Order Franciscan Order Dominican Order