* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Mount Rainier wikipedia , lookup
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
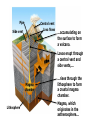
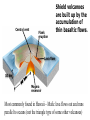
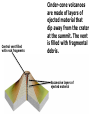
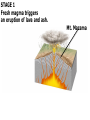
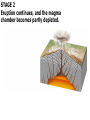
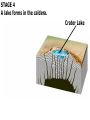
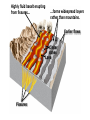
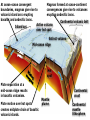
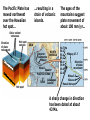
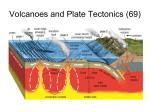
Video on Youtube: Volcano Eruption – The Eruption of Mount St Helens 1980 22 minutes VOLCANOES Pipe Central vent Lava flows Side vent ...accumulating on the surface to form a volcano. Lavas erupt through a central vent and side vents,... Magma chamber Lithosphere ...rises through the lithosphere to form a crustal magma chamber. Magma, which originates in the asthenosphere... Central vent Flank eruption Shield volcanoes are built up by the accumulation of thin basaltic flows. Lava flow 10 km Magma reservoir Most commonly found in Hawaii – Mafic lava flows out and runs parallel to oceans (not the triangle type of some other volcanoes) Mauna Loa (Hawaii) Lava dome Crater Volcanic domes are bulbous masses of felsic lava, which are so viscous that they pile up over the vent. Similar to Mt St Helens – The lava is so viscous that they end up piling up and then later blow all in one time. Mount St. Helens (Washington) Central vent filled with rock fragments Cinder-cone volcanoes are made of layers of ejected material that dip away from the crater at the summit. The vent is filled with fragmental debris. Successive layers of ejected material Cerro Negro (Nicaragua) Central vent filled from previous eruption Radiating dikes Stratovolcanoes are built from alternating layers of pyroclastic material and lava flows. Riblike dikes strengthen the cone. Pyroclastic layers Lava flows Alternating layers of pyroclastic and lava Mount Fuji (Japan) Craters are found at the summits of most volcanoes. Mt. Etna (Sicily, Italy) Mount Mazama created Crater Lake in Oregon Calderas result when a violent eruption empties a magma chamber, which collapses, leaving a large, steep-walled basin. Crater Lake (Oregon) STAGE 1 Fresh magma triggers an eruption of lava and ash. Mt. Mazama STAGE 2 Eruption continues, and the magma chamber becomes partly depleted. STAGE 3 The mountain summit collapses into the empty chamber. STAGE 4 A lake forms in the caldera. Crater Lake Highly fluid basalt erupting from fissures… …forms widespread layers rather than mountains. Earlier flows Cinder cones Lava Fissures At ocean-ocean convergent Magmas formed at ocean-continent boundaries, magmas give rise to convergences give rise to volcanoes volcanic island arcs erupting erupting andesitic lavas. basaltic and andesitic lavas. Continental volcanic belt Active volcano Island arc over hot spot Extinct volcano Mid-ocean ridge Hot spot Plate separation at a mid-ocean ridge results in basaltic volcanism. Plate motion over hot spots creates midplate chain of basaltic volcanic islands. Mantle plume Continental crust Continental mantle lithosphere The Pacific Plate has moved northwest over the Hawaiian hot spot… …resulting in a chain of volcanic islands. The ages of the mountains suggest plate movement of about 100 mm/yr… Older extinct volcanoes Direction of plate movement Hot-spot volcano ASIA Emperor Seamounts Midway NORTH AMERICA Hawaii Equator PACIFIC OCEAN Tahiti Hot-spot Galápagos Islands 64.7 Ma 56.2 Midway 27.7 55.4 55.2 Direction 48.1 of plate 39.9 movement 43.4 42.4 Nihau 5.5 Kilauea 0 Hawaii hot spot A sharp change in direction has been dated at about 43 Ma. 1.8 2.0 0.8 Ma PACIFIC OCEAN Montana Yellowstone Caldera Chain Washington Oregon California Idaho Nevada Hot spot 4.3 15.5 13.8 Wyoming Utah 13.7 16.1 13.8 12.5 15.6 14.7 11 Yellowstone National 6.6 Park 6.2 10.3 The North American Plate is moving southwest over the Yellowstone hot spot. 1.8 2.0 0.8 Ma Hot spot 4.3 15.5 13.8 13.7 16.1 13.8 12.5 15.6 14.7 11 Yellowstone National 6.6 Park 6.2 10.3 10 things you didn’t know about volcanoes (58:52) - Youtube Instability at the core-mantle boundary causes a mantle plume to arise. Basaltic magma penetrates the lithosphere and erupts as flood basalts. Flood basalts Lithosphere Mantle Outer core Plume head Core-mantle boundary The plume tail may form a hot-spot volcano. Continued plate movement creates a hotspot volcano chain. Hot-spot volcano Plate movement Plume tail Extinct volcano Active volcano