* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B3_Revision_Posters
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
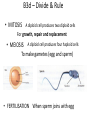
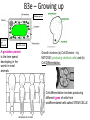
B3 Revision Posters B3a – Molecules of Life Controls movement in & out of cell Chemical reactions take place here – e.g. enzymes Site of respiration (provides energy) Site of Protein Synthesis DNA Fingerprinting Comparing samples of DNA to help identify samples B3b - Diffusion • The movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration FOR EXAMPLE: Leaves: Lungs: Placenta: Intestines: To INCREASE the rate of diffusion – have a LARGE surface area and GOOD blood supply B3c - Keep it Moving Plasma – yellow-ish fluid, carries glucose and CO2 Red Blood Cells – carry the oxygen Platelets – clot the blood White Blood Cells – fight off infection The Heart 4 chambers – ventricles - atrium Too much saturated fat and cholesterol – fatty deposits in blood vessels – coronary heart disease B3d – Divide & Rule • MITOSIS A diploid cell produces two diploid cells For growth, repair and replacement • MEIOSIS A diploid cell produces four haploid cells To make gametes (egg and sperm) • FERTILISATION When sperm joins with egg B3e – Growing up A gestation period is the time spend developing in the womb in most animals. Growth involves (a) Cell Division – by MITOSIS (producing identical cells) and (b) Cell Differentiation. Cell differentiation involves producing different types of cells from undifferentiated cells called STEM CELLS B3f – Controlling plant growth Plant hormones (also known as PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS or AUXINS) are chemicals that control growth of ROOTS and SHOOTS Leaves are positively phototropic, towards light Leaves are negatively geotrophic, away from gravity AUXINS are hormones which collect on the dark side of a shoot causing the cells to lengthen Roots are negatively phototropic, away from light Roots are positively geototropic, towards gravity B3g – New genes for old 1 – select the characteristic you want to improve – larger eggs 2 – cross breed the best hen with the best cockerel 3 –select the offspring which produce the largest eggs and mate that with your best cockerel 4. and repeat this over several generations The order of triplets in a gene determines the sequence of amino acids. GENETIC ENGINEERING Is when scientists transfer one gene from one living organism to another. The amino acids join together to form a protein molecule . If genes produce incorrect proteins, cells may not function properly. This is the cause of many inherited diseases. B3h – More of the same ADVANTAGES OF CLONING DISADVANTAGES OF Why clone animals? CLONING Animals or plants with special qualities could be mass produced to help in the manufacture of important drugs. •About 98% of cloning efforts fail. •Usually a cloned embryo dies before birth but sometimes afterwards too. Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into different sorts of cells – muscle, liver, bone, etc Cells lose this ability as the human gets older