* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry GRADE
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
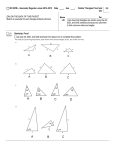
ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 2. Concepts of similarity are foundational to geometry and its applications a. Prove theorems involving similarity. i. Prove theorems about triangles. C We will prove theorems about triangles. ii. Prove that all circles are similar. C iii. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. C 2. Concepts of similarity are foundational to geometry and its applications b. Understand and apply theorems about circles. i. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. I ii. Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle. I iii. Prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. I 2. Concepts of similarity are foundational to geometry and its applications c. Find arc lengths and areas of sectors of circles. i. Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking TIMELINE: 3rd Quarter Resource Correlation Academic Vocabulary Ratios Evaluation We will prove that all circles are similar. We will use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Evaluation Evaluation Holt McDougal Geometry Teacher’s Edition pg 231 KUTA Geometry Software Radii Chords Inscribed angles Appl We will identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. We will construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle. Appl We will prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle Evaluation We will derive, the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian Synth Holt McDougal Geometry Teacher’s Edition pg 734 Arcs Sectors Page 1 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry Grade Level Expectation GRADE: High School Evidence Outcome and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality. I ii. 2. Concepts of similarity are foundational to geometry and its applications Derive the formula for the area of a sector. I d. Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations. i. Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor. 1. Show that a dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. C 2. ii. Show that the dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. C Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar. C iii. Explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Student-Friendly Learning Objective Level of Thinking measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality We will derive the formula for the area of a sector. TIMELINE: 3rd Quarter Resource Correlation Academic Vocabulary KUTA Geometry software Synth Scale factor We will verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor. We will show that a dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. We will demonstrate that the dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. We will describe why two figures are similar in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar. Appl Holt McDougal Geometry Teacher’s Edition pg 495 Appl Appl Appl Holt McDougal Geometry Teacher’s Edition pg 462-483 Similarity Similarity transformation Page 2 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry Grade Level Expectation GRADE: High School Evidence Outcome angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. C iv. Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. C Student-Friendly Learning Objective We will explain the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. We will use the properties of similarity transformations to prove the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking Appl TIMELINE: 3rd Quarter Resource Correlation Academic Vocabulary KUTA Geometry software Proportionality Corresponding parts Angle-Angle similarity Appl Page 3