* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rise of Islam
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
History of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
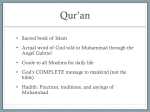
The Rise of Islam I. Daily life in early Arabia A. Much of the Arabian peninsula is desert, although there are mountains in the southwest. Oases are green areas fed by an underground water source. B. Early Arabs formed tribes that were headed by a sheikh. C. The Bedouins were desert herders who traveled from oasis to oasis to water their animals. Many Arabs lived in villages near oases. D. Merchants who transported goods across the desert formed caravans to protect themselves. Caravans are groups of traveling merchants and animals. E. Trade grew. Makkah (also known as Mecca) was the largest and wealthiest trade center and is an important religious site visited by pilgrims. F. In Makkah is the Kaaba, a low square building surrounded by statues of gods and goddesses. Inside the building is a large stone believed to come from heaven. G. Arabs consider Allah(Arabic for God) the creator. II. Muhammad: Islam’s prophet610 A.D. • A. Muhammad was accepted as a prophet to the people of Arabia. • B. Muhammad was dissatisfied with the ways of his town leaders and went into the hills to pray. There he was visited by an angel who told to preach Islam“surrendering to the will of Allah”. • C. Muhammad returned to Makkah and told the people to worship one god, Allah. Muhammad also preached that all people are equal and that the rich should share their wealth with the poor. • D. Many poor people began accepting Muhammad’s message and became Muslims, or followers of Islam. Wealthy people did not like the message of Muhammad. • E. Muhammad and his followers left Makkah for Yathrib. The journey is known as the Hijrah. • F. Yathrib welcomed the Muslims and renamed their city Madinah. G. Muhammad used the laws he believed he had received from God to rule the people of Madinah, creating an Islamic state, or a government that uses political power to uphold Islam. H. Muhammad built an army to defend his new government. The army conquered Makkah, and Muhammad returned to the holy city. I. Muhammad died two years after his return. III. Islam’s teaching • A. Islam, Judaism, and Christianity have some common beliefs. • B. The Quran is the holy book of Islam. Moral teachings in the Quran are similar to those in the Bible. • C. Many rules in the Quran apply to Muslim’s daily life. • D. The Five Pillars of Islam, or acts of worship, are to be followed by all Muslims. The Five Pillars are belief, prayer, charity, fasting, and pilgrimage. • E. The Sunna is the name given to the customs based on Muhammad’s words and deeds. • F. Islam’s law code is taken from the Quran and Sunna. Chapter 11 Section 1 Review questions • Write questions and answers pg. 378 (1-5) BELL RINGER • Have you ever tried to get someone to believe what you believe? Describe it.