* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
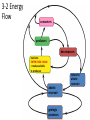
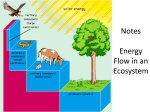
Chapter 3 Ecology • Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment Some of the levels at which life can be • cells studied include: • • • • • • organisms populations communities ecosystems biomes biosphere Population Individual Biosphere Biome Ecosystem Community • Cells are the smallest functional unit of life Nerve cell • Cells make up organisms. – Individual living things Species - individuals that can breed with one another and produce fertile offspring Population - all the individuals of the same species in an area A population is always composed of same-species organisms Community - all the populations that live together in an area Hawk, snake, bison, prairie dog, grass • Community and its nonliving surroundings are called an ecosystem. – Biotic factors: living things – Abiotic factors: nonliving things Hawk, snake, bison, prairie dog, grass, stream, rocks, air • A biome is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar communities. Tropical forest Savanna Desert Chaparral Temperate grassland Temperate broadleaf forest Northern coniferous forest Tundra High mountains Polar ice Biosphere - the part of the earth that supports life 1. A group of animals that live in the same area and can interbreed is called population a (n) _____________________ 2. The study of organisms and their interactions with the environment is ecology known as ___________________________ 3. A large area that has a particular climate and distinct plants and animals is biome called a ____________________________ 4. All of the different populations living in an area (plants, rabbits, coyotes...) community is called the _________________________ non-living (abiotic) factors in 5. An ecosystem includes all the living (biotic) and ___________ an area. biosphere 6. The portion of the planet that can sustain life is the ________ species 7. Animals that can interbreed are called a(n) _______________ 3-2 Energy Flow consumers producers decomposers nutrients ENTER FOOD CHAIN = made available to producers abiotic reservoir geologic processes return to abiotic reservoir Energy flows through ecosystems The Earth is not a closed system: It needs a constant input of energy sun secondary consumers (carnivores) primary consumers (herbivores) producers (plants) loss of energy loss of energy • Sun light – Sun light is the primary source of energy for our biosphere. • Autotrophs/prod ucers – Use energy from the environment to produce their own food • Photosynthesis – Use light – Plants, mosses, Algae • Chemosynthesis – Use chemicals – Bacteria Heterotrophs/Consumers: cannot make their own food. They must eat to get energy Carnivores Herbivores eat only meat eat only plants Omnivores eat both plants and meat Decomposers/Detritivores Breakdown plants and animals Level 4 Tertiary consumer Food chains • Trophic levels – energy from the sun by producers • 1st Sun top carnivore Level 3 captured Secondary consumer level of all food chains carnivore Level 2 Primary consumer – consumers make up the second, third, or higher levels – all levels connect to Level 1 Producer decomposers heterotrophs herbivore autotrophs Decomposers Bacteria Fungi Feeding Relationships A food chain is a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. • Arrows follow energy flow • All energy originates from the sun. Sun Bacteria Inefficiency of energy transfer • Loss of energy between levels of food chain – To where is the energy lost? The cost of living! 10% growth only this energy moves on to the next level in the food chain energy lost to daily living 40% cellular respiration 50% waste (feces) sun Ecological Pyramids • An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. Energy pyramid Biomass pyramid Pyramid of Numbers Shows the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level. Represents the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level. Shows the relative number of individual organisms at each trophic level Ecological pyramid • Loss of energy between levels of food chain – can feed fewer animals in each level sun Food webs • Food chains are linked together into food webs • Who eats whom? – a species may weave into web at more than one level • bears • humans – eating meat? – eating plants? Complete the Venn diagram about how organisms get energy using these terms: autotrophs heterotrophs both Carnivores Consumers Decomposers Herbivores Producers Are described by their energy source Form the base of all ecological pyramids Make organic molecules from inorganic molecules Part of food chains and food webs Some absorb their food from dead organisms Some eat other organisms