* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
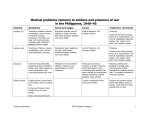
Medical problems common to soldiers and prisoners of war in the Philippines, 1940–45 Disease Symptoms Advanced stages Cause Treatment, comments Beriberi, dry Tiredness, irritation, nausea, constipation, poor memory, numb toes, burning sensation in the feet, sore legs, calf muscle cramps, unsteady walk, difficulty in getting up from a squat. Shrunken muscles, loss of reflexes in knees and feet, feet may hang limp. Disease can cause death. Lack of thiamine, a Bcomplex vitamin. Thiamine. Tiredness, irritation, nausea, constipation, poor memory, rapid heartbeat, sweating. Weakened heart, swelling in the legs, heart failure, extreme bloating. Disease can cause death. Lack of thiamine, a Bcomplex vitamin. Thiamine. Body lice Intense itching with deep scratches around shoulders, flanks, neck. Bites appear as small red pimples; may cause generalized skin rash. Headache, fever, bacterial infection. Body lice can spread typhus or other infections. Pediculosis humanus corposis, a small (1/16 inch) insect that feeds on skin. Associated with wearing the same clothes for long periods without laundering, shared bedding, close contact. Washing clothing and bedding in boiling water, ironing seams at high temperature, treating clothing with 1% malathion powder or 10% DDT powder. Broken bones Single fracture: bone breaks in one place, does not pierce skin. Trauma, weakened bones from poor nutrition. Support and protect broken bones with splints, casts, or braces. Limit motion to allow injured bone to heal. Beriberi, wet Compound fracture: bone breaks in two or more places. Thiamine rich foods include brown rice, whole grains, raw fruits & vegetables, legumes, seeds, nuts, yogurt, pork, beef, liver, brewer’s yeast. Thiamine rich foods include brown rice, whole grains, raw fruits & vegetables, legumes, seeds, nuts, yogurt, pork, beef, liver, brewer’s yeast. Open, compound fracture: Disease information RETA Battle for Bataan 1 Disease Symptoms Advanced stages Cause Treatment, comments Severe, life-threatening dehydration. Cholera is caused by the bacterium Vibro cholerae, which can be found in contaminated food or untreated water. Rehydration (replacing liquids through drinking or through an intra-venous [IV] drip) with a solution of water, sugar, and salt; antibiotics can hasten recovery. bone breaks and pierces skin. Can easily become infected. Cholera Watery diarrhea, vomiting. Prevented through cleanliness and wastewater treatment systems. Dengue fever Diphtheria Sudden high fever, chills, headache, eye pain, red eyes, enlarged lymph nodes, flushed face, lower back pain, extreme weakness, severe leg and joint pain. Most people infected with dengue fever are immune to further attacks. In some cases, however, extreme reaction to a second infection can cause fever, headache, coughing, purple spots on the skin, bruises from internal bleeding, abdominal pain, vomiting, shock. Dengue fever is caused by any of several mosquitoborne viruses. Symptoms vary with location of infection. Nasal, pharyngeal, and skin forms are milder forms. Nasal diphtheria produces a watery or bloody discharge; pharyngeal: sore throat, mild fever, rapid pulse, weakness; laryngeal: high fever, cough, difficulty breathing; skin: ulcer forms at infection site, wound is Advanced patients develop a swollen “bull neck”; complications from breathing problems can result in death. Diphtheria is caused by the body’s reaction to poisons from a virus that infects bacteria; the bacteria, in turn, infects humans. The poison destroys healthy tissue, and fluid from the cells forms a tell-tale gray to green film of diphtheria infection. Diphtheria is contagious. Disease information There is no known cure. Medicines may reduce fever and aches. Fluids can prevent dehydration. Blood transfusions may be needed. Dengue fever cannot be transmitted from person to person. RETA Battle for Bataan Treatment must be for both the poison and the bacterial infection. Hospital care is required for patients with breathing trouble. An antitoxin to counteract the poison must be given immediately, followed by antibiotics, to kill the bacteria. 2 Disease Symptoms Advanced stages Cause Treatment, comments Without treatment, dysentery can lead to death. Dysentery can be caused by infection with a parasitic amoeba or one of several bacteria. Dysentery from shigella is very contagious and can lead to widespread epidemics. Rehydration (replacing liquids through drinking or through an intra-venous [IV] drip) to replace lost fluids and antibiotics to control infection. slow to heal and may be numb to touch. Dysentery Bloody diarrhea, fever, stomach pain, rapid weight loss. Prevented through cleanliness, wastewater treatment, and hygiene and through boiling water. Gangrene, moist Red line surrounding the border of injury, sensation of heaviness in the affected area, severe pain, skin swollen and may be blistered, red, warm to touch before turning bronze, brown, or black. Pus is foulsmelling. Fever, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, loss of appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, vascular collapse. Moist gangrene may occur after an injury that stops or restricts blood flow to an area. Bacteria grows in the injured tissue and causes gangrene. First, infection is treated with antibiotics. Second, the affected tissue or limb is surgically removed. Other treatment includes pain medication, intravenous fluids, and blood transfusions. Good nutrition is critical to healing. Gangrene, gas Similar to symptoms of moist gangrene, but instead of foul smelling pus, discharge is sweet smelling and watery. Gas gangrene spreads rapidly through the bloodstream and may infect vital organs. Cause is similar to moist gangrene, but bacteria can live with little oxygen. Immediate antibiotics and surgery to remove affected tissue. Malaria All types of malaria: Uncontrollable chills followed by high fever, then sweating. Can include tiredness, severe headache, nausea, vomiting. Malaria symptoms follow a pattern of chills, fever, and sweats that can last for weeks or months. Malaria is caused by any of 4 species of Plasmodium, a parasite carried by mosquitoes. Treatment for all strains of malaria is the drug chloroquine. Falciparum malaria is treated in hospitals, and treatment depends on where malaria was contracted because some strains are not affected by some drugs. Disease information Falciparum malaria is more severe than other types of malaria and can kill people RETA Battle for Bataan 3 Disease Symptoms Advanced stages Cause within hours of infection. Treatment, comments Treatment may include IV (intra-venous) fluids, blood, transfusions, kidney dialysis, and breathing help. Malnutrition Anemia, diarrhea, disorientation, goiter, loss of reflexes, lack of coordination, muscle twitches, scaling or cracking of lips and mouth, thin hair that pulls out easily, night blindness, aching joints, sore bones, bleeding gums. Death by starvation. Poor diet: eating either too little food or food lacking in items the body needs. Change diet. Pellagra Redness and swelling of mouth and tongue, diarrhea, skin rash, memory loss. Thickened, pigmented skin may fall off, exposing patient to infection; abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, bloody diarrhea, insomnia, apathy, confusion, depression, hallucinations, stiffness in arms and legs, involuntary sucking and grasping motions. Niacin deficient, a B-complex vitamin. Common in areas with corn-based diets. Supplement with niacinamide (a form of niacin). Recurrent recollections or dreams about war, flashbacks, emotional numbing, distress following reminders of battle, and feeling on edge and alert for threats. Untreated PTSD can result in depression, with symptoms of sadness, poor concentration, lack of interest in others, appetite change, irritability, change in sleep patterns, apathy, lack of energy, and feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness. PTSD is caused by severe and often prolonged trauma. Counseling with a psychologist or psychiatrist. Treatment may include antidepressants, counseling. PostTraumatic Stress Disorder (battle fatigue, combat stress) Disease information RETA Battle for Bataan Complications: Many Bcomplex vitamin deficiencies occur together and need to be treated simultaneously. Niacin occurs in liver, yeast, meat, legumes, and whole cereals. 4 Disease Symptoms Advanced stages Cause Treatment, comments Tuberculosis Coughing, initially bringing up yellow-green stuff that becomes tinged with blood; low fever, chest pain, loss of appetite. Chronic illness, increasingly severe lung symptoms, severe weight loss, a wasted appearance. Can cause death. Tuberculosis is caused by bacterial infection. It is not highly contagious. Tuberculosis is treated by antibiotics, rest, and good nutrition. Lungs are sometimes collapsed surgically so they can rest and heal. Typhus Epidemic typhus: fever, headache, weakness, muscle aches, rash of spots or bumps. Epidemic typhus: swelling of the heart muscle or brain, can cause death. Epidemic typhus: caused by Rickettsia prowazekii, which is carried by body lice. Antibiotics such as tetracycline and chloramphenicol (all forms). Scrub typhus: encephalitis, pneumonia, swelling of the liver and spleen. Scrub typhus: caused by Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, which is carried by mites and chiggers. Prevented through good hygiene and avoiding insects. Drying of cornea, infection inside the eye, blindness. Lack of vitamin A. Vitamin A. Scrub typhus: fever, headache, muscle aches, cough, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash. Vitamin A deficiency Night blindness. Prevention: include in diet liver, meat, eggs, milk, red and orange vegetables such as peppers, carrots, pumpkins. Treatment notes: quinine (anti-malaria drug) and sulfa, an antibiotic, were sometimes smuggled into camp. Infected wounds were cleaned by maggots. Prison doctors mixed guava leaves, cornstarch, and charcoal from coconuts to treat diarrhea. Dr. Ralph Hibbs at Cabanuatuan Prison Camp invented a machine to collapse lungs of tuberculosis patients. Treatment notes from Ghost Soldiers by Hampton Sides (2001). Information from www.ahealthyme.com, accessed March 2003, sponsored by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts. Disease information RETA Battle for Bataan 5