* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are blood types?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
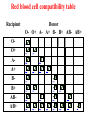
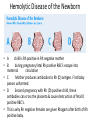
What are blood types? There are 3 alleles or genes for blood type: A, B, & O. Since we have 2 genes, there are 6 possible combinations. Blood Types AA or AO = Type A BB or BO = Type B OO = Type O AB = Type AB Average Percents… Type O—46% Type A—40% Type B—10% Type AB—4% • • • • Rh Factors • Scientists sometimes study Rhesus monkeys to learn more about the human anatomy because there are certain similarities between the two species. While studying Rhesus monkeys, a certain blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood contains the protein, your blood is said to be Rh positive (Rh+). If your blood does not contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh negative (Rh-). http://www.fi.edu/biosci/blood/rh.html A+ AB+ BAB+ ABO+ O- Blood Typing Test Determines blood type and compatibility • Figure 19–7 Red blood cell compatibility table Recipient OO+ AA+ BB+ ABAB+ Donor O- O+ A- A+ B- B+ AB- AB+ the AB+ blood type is referred to as the "universal recipient", as it possesses neither Anti-B or Anti-A antibodies in its plasma, and can receive both Rhpositive and Rh-negative blood. Similarly, the O− blood type is called the "universal donor"; since its red blood cells have no A or B antigens and are Rh-negative, no other blood type will reject it. Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn • A child is Rh positive in Rh negative mother • B during pregnancy fetal Rh positive RBC’s escape into maternal circulation • C Mother produces antibodies to Rh (D) antigen. First baby passes unharmed. • D Second pregnancy with Rh (D) positive child, these antibodies can cross the placenta & cause destruction of fetal D positive RBC’s. • This is why Rh negative females are given Rhogam after birth of Rh positive baby.