* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
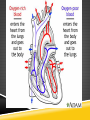
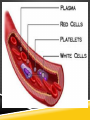
UNIT 2 Lesson 2 Big Idea HO DO THE CIRCULATORY AND RESPIRATORY SYSTE S W RK TOGET ER? Heart Rate Lower Class BPM: __________ Higher Field BPM: ___________ CALIFORNIA STANDARDS Science Standard 2.b: Blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2) are exchanged in the lungs and tissues. CALIFORNIA STANDARDS Investigation and Experimentation 6.c – Plan and conduct a simple investigation based on a student developed question and write instructions others can follow to carry out the procedure. Investigation and Experimentation 6.d - Identify the dependent and controlled variables in an investigation. INPUT Circulatory system – The body system that transports blood loaded with oxygen and nutrients to each cell of the body. Respiratory system – The body system that exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between your body and the environment. INPUT The Heart (Pg. 156) The heart is the pumping organ of the body. Some animal’s hearts are very simple and some are very complex. An earthworm’s heart is just a muscular part of a large blood vessel. A crayfish’s heart has two chambers A human heart is a double pump made up of four chambers INPUT INPUT Before your heart beats, two chambers fill with blood. The heart pumps this blood throughout the body creating a pulse. Blood travels in a certain path. INPUT Blood Path Blood from the right side of the body returns to the heart. The heart then pumps to the lungs. Carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen. Blood is then pumped to the left side of the heart. Then it is pumped to the entire body. INPUT The Circulatory System (Pg. 158) It transports blood loaded with oxygen to the cells and takes away waste from the cells. It is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. INPUT Blood is connective tissue: Plasma (liquid) is mostly water and carries dissolved food and waste Red blood cells (solid) carry oxygen White blood cells (solid) help fight infection Platelets (solid) help clot the blood to stop bleeding. INPUT Blood leaves the heart and travels through arteries. Arteries bring the blood to small vessels called capillaries. Here materials exchange between the blood and body cells. Capillaries have thin walls and touch every body cell. INPUT Materials cross through the walls of the capillaries and through the membranes of the cells. Capillaries then bring the old blood to large vessels called veins which return to the heart. INPUT The Respiratory System (Pg. 160) This system exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide. Your diaphragm is a muscle below your ribs that helps pull in air. Air flows in and travels down tubes to the lungs. The tubes end in tiny sacs in the air. INPUT Working Together (Pg. 162) Respiratory system brings air into the body. Oxygen passes from sacs in the lungs to the capillaries and into the bloodstream. Both systems are needed to do the job the body needs. SUMMARY In this lesson, you learned how the circulatory system and the respiratory system work together. They carry materials in the body and exchange gasses in the lungs. UNANSWERED QUESTIONS How does smoking affect the way the respiratory and circulatory system work? Why do you feel like you cannot breathe when you get the wind knocked out of you? Ask your own… WHERE WOULD YOU EXPECT TO SEE THE MOST CASES OF RESPIRATORY DISEASE? THE LEAST? MODELING 1) Where does gas exchange take place in the body? It takes place in tiny air sacs in the lungs. MODELING What are the four chambers in the heart? Right and left atrium and the right and left ventricle. CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING What carries blood away from the heart? Arteries CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING What is the name of the muscle that helps pull air into your body? Diaphragm