* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
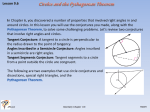
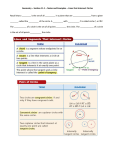
What You Need to Learn Understanding circle relationships is an important topic in Geometry. You can learn this material in a variety of ways. I’ve listed the pages in our Geometry textbook and provided links. There are certainly other links you can find. You can each individually study the lessons, or each person on your team can become an expert on specific topics then teach everyone else. Regardless of how you learn the topic, everyone is responsible for the practice problems and the test will be an individual test. 1. Know basic circle definitions (practice problems p. 687; 5-6, 14-17) Section 1 ● Radius ● Diameter ● Chord ● Secant ● Tangent ● Arc (minor and major) ● Sector ● Segment Definitions for these words can be found in your textbook or Math Is Fun https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/circle.html ❖ Central angle ❖ Inscribed angle ❖ Intercepted arc Definitions for these three words can be found in your textbook or these sites: http://hotmath.com/hotmath_help/topics/inscribed-angles.html http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Inscribed-Angles-in-Circles/lesson/Inscribed-Angles-in-Circles/ http://www.mathwarehouse.com/geometry/circle/inscribed-angle.php ❖ Radian (look at #3 for links for this word) 2. Compute area and circumference of a circle, length of an arc (p. 695), area of a sector (p. 783) (Practice problems p. 687 29, 31, 36; p. 697 36-37, 40, 45-47; p. 785 14, 16, 18, 23, 28, 32-34, 39) Section 2 Pay attention to the fact that the length of an arc and the area of a sector are just ratios. Textbook is your Geometry book (http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected/login.do). Any pages referenced are in the Geometry book. 3. Understand radians (Practice problems from IXL - link is below) Section 3 Be sure to know: ● what a radian is ● the relationship between a radian and the circumference of a unit circle ● how to convert radians to degrees and degrees to radians Look at YouTube Video: What is a Radian? Watch the interactive on Math Is Fun: http://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/radian.html Read how to convert on Hotmath and try the example problems: http://hotmath.com/hotmath_help/topics/radian-to-degree-measure.html http://hotmath.com/hotmath_help/topics/degree-to-radian-measure.html Practice problems from IXL (practice at least 5 where you convert radians to degrees and at least 5 where you convert degrees to radians - you can practice up to 20 problems for free) https://eu.ixl.com/math/grade-11/convert-between-radians-and-degrees 4. Understand how to find measures of arcs and angles in arcs (Practice problems p. 697; 1218) Section 4 Pages 692 – 694 http://hotmath.com/hotmath_help/topics/arcs.html 5. Learn properties of chords and radii (Practice problems p. 705 10, 12, 16-19, 22-24, 31, 33, 36) Section 5 Be sure to know about: ● the perpendicular bisector of a chord ● what happens with congruent arcs ● when two chords are congruent Pages 701 – 703 http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Chords-in-Circles/lesson/Chords-inCircles/?referrer=featured_content Textbook is your Geometry book (http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected/login.do). Any pages referenced are in the Geometry book. 6. Learn relationships between central angles and intercepted arc; inscribed angles and intercepted arcs (Practice problems p. 713 11-13, 17-20, 23-24, 27-28) Section 6 Be sure to know about: ● the Inscribed Angle Theorem ● what happens when two inscribed angles intercept the same arc ● what happens when an inscribed angle intercepts a diameter ● what is special about a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle Pages 709 – 712 https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/circle-theorems.html 7. Learn about tangent lines (Practice problems p. 722 13-14, 19, 21, 26, 30, 35, 40-43) Section 7 Be sure to know about: ● vocabulary of tangent lines ● what a line is tangent to a circle ● tangents from an exterior point ● circumscribed and inscribed polygons Pages 718 - 721 See a nice interactive at Math Is Fun (drag points F and G together to see what happens when you have a line tangent to a circle) http://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/tangent-line-.html 8. Know how to use the relationships between intersecting chords, secants, tangents and their intercepted arcs (Practice problems p. 731; 1-6, 8-16 [extra practice], 18-23, 26-27, 39b) Section 8 Be sure to know the relationships of angles and arcs when: ● two chords or secants intersect inside a circle ● a secant and a tangent intersect at the point of tangency ● two secants, a secant and a tangent, or two tangents intersect in the exterior of a circle Pages 727 – 730 – be sure to look at the concept summary on p. 731 See a summary of angle in the Regents Prep Center http://www.regentsprep.org/regents/math/geometry/gp15/circleangles.htm 9. Know the segment rules for intersecting chords, secants, tangents [used to be called the Power Theorems] (Practice problems p. 739; 1-4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 18, 19, 29) Section 9 Be sure to know the relationships of segments when: ● two chords intersect inside a circle ● two secants intersect outside a circle ● a secant and a tangent intersect on a circle Pages 736 - 738 Regents Prep Center has a summary Textbook is your Geometry book (http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected/login.do). Any pages referenced are in the Geometry book. http://www.regentsprep.org/regents/math/geometry/gp14/circlesegments.htm Textbook is your Geometry book (http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected/login.do). Any pages referenced are in the Geometry book.