* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06 Control Methods
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
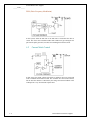
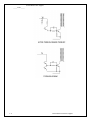
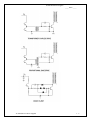
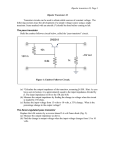
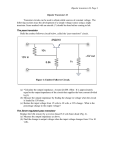
Table of Contents 6.0 Control Methods 6.1 Voltage Mode 6.2 Current Mode 6.3 Gated Oscillator Control 6.4 Bipolar Transistor Drive 6.5 MOSFET Drive Assignment Questions For Further Research An Introduction to Communications Systems i _____ Notes _____ 6.0 Control Methods Objectives The purpose: • • • The illustrations for this section come from Switchmode Power Supply Reference Manual rev 2 by ON Semiconductor. Most SMPS circuits use a form of PWM (pulse width modulation) or PFM (pulse frequency modulation) within a feedback loop to control the output voltage. 6.1 Voltage Mode Control PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) The output voltage is compared to a reference voltage. This in turn is compared to a ramp voltage. This effectively creates a pulse width modulator. If the output voltage has dropped below the reference level, the ramp signal turns ON the transistor switch. Since the turn ON point can occur anytime during the cycle, the ramp is effectively turned into a variable width pulse. An Introduction to Power Supplies 1-1 Switch Mode Power Supplies _____ Notes _____ PFM (Pulse Frequency Modulation) In this system, either the ON time or the OFF time is fixed while the other is varied. The circuit can be disabled under fault conditions by preventing the out put from the pulse generator (one-shot) from enabling the transistor switch. 6.2 Current Mode Control In this circuit, the output voltage and switch (or inductor) current is sensed and used to modulate the transistor switch. The oscillator fixes the turn ON instant, but the turn OFF instant is controlled by the voltage and current feedback. This technique has a very fast transient response time. 1-2 An Introduction to Power Supplies Switch Mode Power Supplies _____ Notes _____ 6.3 Gated Oscillator Control This circuit has two control mechanisms: PWM and PFM. The oscillator determines the ON instant while the feedback loop and reference determine the turn OFF instant thus creating PWM. However, the oscillator frequency can also change depending on the current flowing in the circuit thus creating PFM. The 78S40 chip used in the labs is of this type. 6.4 Bipolar Transistor Drive Bipolar transistors are current activated devices and can be driven in two modes: fixed and proportional base drive. In the fixed base drive mode, the transistor is normally biased OFF and provided with a large base current pulse sufficient to drive the transistor into saturation. This has the advantage of being simple but has the disadvantage of not being particularly fast because of the storage time associated with the transistor junction capacitance. In a proportional drive circuit, the transistor is never allowed to saturate, thus minimizing the stored junction capacitance charge and increasing the switching speed. Because of the increased circuit complexity, this technique is generally reserved for high power switching supplies. An Introduction to Power Supplies 1-3 Switch Mode Power Supplies _____ Notes _____ 1-4 An Introduction to Power Supplies Switch Mode Power Supplies _____ Notes _____ An Introduction to Power Supplies 1-5 Switch Mode Power Supplies _____ Notes _____ 6.5 MOSFET Drive MOS transistors are voltage controlled devices and can be 5 – 10 times faster than a bipolar transistor. However, the gate of a MOSFET has a relatively high capacitance, therefore the drive circuit must be capable of sourcing (and sinking) high surge currents. Bipolar totem pole drives are often used. 1-6 An Introduction to Power Supplies Switch Mode Power Supplies _____ Notes _____ Assignment Questions On-Line Test Quick Quiz 1. 2. Composition Questions To answer these questions, it will be necessary to do some research. 1. 2. 3. 4. An Introduction to Power Supplies 1-7 Switch Mode Power Supplies _____ Notes _____ For Further Research 1-8 An Introduction to Power Supplies