* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Section 2
Sharing economy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Workers' self-management wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Social market economy wikipedia , lookup
Market socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
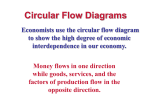
Chapter 2 Section 2 Features of the U.S. Economy Pages 29-35 Objectives • 1. Explain the basic principles of free enterprise in the United States. • 2. Name the two markets of the circular flow model. • 3. Explain how the circular flow model reflects exchange. Free Enterprise • Define the word free • Define the word enterprise Free Enterprise • The capitalist economy of the United States is called a free enterprise system because individuals in the United States have a great number of economic freedoms. Five Features of Free-Enterprise • The right to own private property and enter into contracts. • Make individual choices • Engage in economic competition • Make decisions based on self-interest • Participate in the economy with limited government involvement and regulation Collage • Choose a partner to work with on this project. • Using magazines create a collage illustrating the five basic principles of the free-enterprise system in the United States. • Write a caption the explains how the collage represents the features of a free-enterprise system. Activity • Consider a fast-food restaurant. Give examples of how a fast-food restaurant demonstrates each of the five features or benefits of a freeenterprise economy. Economic Actors in Free Enterprise • Producers-provide goods and services in the market. They rely on entrepreneurship to develop new products and production methods. • Consumers-influence production by purchasing goods and services. • Government-oversees and regulates the effects of decisions on the economy as a whole. Circular Flow Model • Markets-product market (green)-represents all of the exchange of goods and services in the economy. • Resource market (gold)-exchange of resources between households and business firms and the government. • Income-money paid to households by business firms and the government in exchange for the households’ resources. • Flows-Two different types of flows • 1. Flow of resources and products • 2. Flow of payments