* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Cloning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
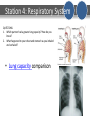
Cedillo DO NOW (Pg. 42 in journal) October 28th, 2013 Objective SWBAT explain possibilities for genetic engineering. Prompt Tape new Do Now to page 42. What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of human cloning? (Cloning: creating new, identical offspring from one organism’s DNA) Reminders: This week’s HW: Levels of Organization & Intro to Body Systems – Due FRIDAY --Write HW in agenda --Voice Level 0 --Tutorials Today: Make up Genetics Test if absent, other make up work ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What are the ethical issues involved in genetic engineering? OBJECTIVES: -Watch video on human cloning -Argue for or against a specific genetic engineering technology Human Cloning – page 43 Draw an outline of your hand to use to take notes on Through the Wormhole: Human Cloning On each finger, write 1 Interesting fact you hear In the video Genetic Engineering Topic 1 In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) • Treatment for infertility where sperm and egg are fertilized outside of the body in a laboratory. Successful offspring are sometimes called “Test Tube Babies” Genetic Engineering Topic 2 Gene Therapy • Medical treatment using DNA to treat disease. Most commonly uses a functional, therapeutic gene to replace a mutated gene. Example: HIV Genetic Engineering Topic 3 Human Cloning • The creating of a genetically identical copy of a human. Currently illegal in all countries, though some scientists have claimed to have completed experimental human cloning. Genetic Engineering Topic 4 Animal Cloning • Creating a genetically identical copy of an animal. The human consumption of meat and other animal products was approved by the FDA in 2006 with no special labels required. Gaur, to the right, was the first endangered species cloned in 2001. Assignment – page 44 • Choose 1 of the genetic engineering topics and decide if you are a proponent (you are for it) or if you are an opponent (you are against it) – – – – In vitro fertilization (IVF) Gene Therapy Human Cloning Animal Cloning • Make a flyer advertising your opinion on page 44 – Include 1-2 possible Advantages of your technology – Include 1-2 possible Consequences for not using your technology – Add color and make it neat, easy to read Genetic Engineering Technologies - Summary In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Treatment for infertility where sperm and egg are fertilized outside of the body in a laboratory. Successful offspring are sometimes called “Test Tube Babies” Gene Therapy Medical treatment using DNA to treat disease. Most commonly uses a functional, therapeutic gene to replace a mutated gene. Example: HIV Human Cloning The creating of a genetically identical copy of a human. Currently illegal in all countries, though some scientists have claimed to have completed experimental human cloning. Animal Cloning Creating a genetically identical copy of an animal. The human consumption of meat and other animal products was approved by the FDA in 2006 with no special labels required. Gaur, to the right, was the first endangered species cloned in 2001. Cedillo DO NOW (Pg. 42 in journal) October 29th, 2013 Objective SWBAT discover how much s/he already knows about the human body. Prompt The human body has over 7,500 named parts. Name as many as you can. (you can write on the notebook page underneath your Do Now if necessary) Reminders: --Voice Level 0 --Stow belongings under chair --Begin Do Now immediately This week’s HW: Levels of Organization & Intro to Body Systems – Due FRIDAY ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What are the structures and functions of the systems of the human body? OBJECTIVES: -Go over Genetics Test -Human Body Rally Table -Identify structures of Human Body Systems Genetics Test Bonus (Pre-AP) Grey Feathered Hawk (ff) + Heterozygous Blackfeathered Hawk (Ff) Go over test Key: 1. D 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. B 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. C 10. C 11. A 12. D 13. GL: B; Pre-AP: A 14. B 15. C 16. A 17. C 18. D 19. D 20. C Ff ff Ff ff Probabilities for Genotypes: FF = 0% Ff = 50% ff = 50% Human Body System • Intro to Human Body System Video Human Body System Rally Table Write down everything you know about your human body system in the time allotted. When your teacher calls “time”, you will pass the poster to the next table. Record all you know about the new body system on the next poster. Repeat for all body systems. Poster Set-Up Body System: ______________________ Structures Functions Record all of the structures, functions, and facts you know about your body system. Other Facts Let’s Rally! TABLE SYSTEM 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM RESPIRATORY SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM MUSCULAR SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXCRETORY SYSTEM Cedillo DO NOW (Pg. 42 in journal) October 30th/31st, 2013 Objective SWBAT investigate key functions of human body systems. Prompt What does the word function mean? Reminders: --HW Due on Friday --Genetics Test Retakes deadline: Tuesday 11/4 --Voice Level 0 This week’s HW: Levels of Organization & Intro to Body Systems – Due FRIDAY ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What are the structures and functions of the systems of the human body? OBJECTIVES: -Set up Human Body Notebook -Human Body Investigation New Unit Page – Page 45 Don’t forget! Add this to your unit table of contents page! (Page 2) MUSTANG MEDICAL SCHOOL HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS New Unit Page Mustang Medical School: Human Body System Unit We will learn about the 10 major body systems, the structures, functions and how these maintain balance and maintain life in an organism. We will… Complete Dissections Heart Chicken Wing Frog Create model of lungs Use Microscopes Case Studies xrays scenarios Lab Practical in December Human Body Investigation • 8 Stations – Structures, Data, Questions • Timed (8 minutes) 1. Voice Levels of 1-2 2. READ the station cards FIRST!! 3. Stay at your station and focus on the activity 4. Complete your station within the time frame LAB STATION EXPECTATIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. Voice Levels of 1-2 READ the station cards FIRST!! Stay at your station and focus on the activity Complete your station within the time frame Cedillo DO NOW (Pg. 42 in journal) November 1st, 2013 Objective SWBAT investigate key structures of human body systems. Prompt What does the word structure mean? Tape “Human Body Overview” to page 46. Reminders: --Get out HW, ready to turn in --Genetics Test Retakes deadline: Tuesday --Voice Level 0 This week’s HW: Levels of Organization & Intro to Body Systems – Due TODAY LAB STATION DEBRIEF • Add notes to your lab sheet as we go through each station! Station 1: Circulatory System QUESTIONS: 1. What happened to your heartbeat after you exercised? 2. Why do you predict that your heartbeat changed? How Lie Detectors Work Station 2: Integumentary System QUESTIONS: 1. Compare the graphs before running and after running. What happened to the temperature of your body? 2. What predictions can you make about the change in temperature? 3. What body systems do you predict control your temperature? Station 3: Skeletal System • Average length of Human humerus: 36.46 cm (14.3 in) • Average length of Human femur: 48 cm – What might cause these averages to vary (differ)? • Average length of Gorilla humerus: 40.5 cm • Average length of Gorilla femur: 33.1 cm – What might cause these average to vary (differ)? QUESTIONS: 1) What do you notice about the lengths of the human humerus compared to the femur? 2) What do you notice about the lengths of the gorilla humerus compared to the femur? How is that different that humans? 3) Gorillas are known as knuckle walkers (meaning they walk with their feet and the knuckles of their hands). Humans are bipedal (meaning we walk upright using only our legs). How does the structure of the Gorillas arms help the function of knuckle walking? Station 4: Respiratory System QUESTIONS: 1. Which partner had a greater lung capacity? How do you know? 2. What happened to your chest and stomach as you inhaled and exhaled? • Lung capacity comparison Station 5: Nervous System 1. A stimulus is something that causes a reaction. What was the stimulus in this station? 2. A reaction is what occurs because of the stimulus. What was the reaction in this station? 3. Why do you think our pupils do this? Crested Gecko Constriction/Dilation 4. Cameras are designed like a pupil. Can you think of how a camera might work in the same way? Station 6: Digestive System 1. What path is the water taking when it is swallowed? Where is it traveling the human body? 2. Do you think food would take the same path in the digestive system? Why or why not? 3. What does a stethoscope do? Station 7: Muscular System 1. What do you think happened? 2. Where does the muscle get the energy that it needs to perform this job? Station 8: Body Systems Overview • 1. I am the body system that is responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body. I am also in charge of transporting waste away from cells. Circulatory System • 2. I am the body system that controls the body. I respond to internal and external stimuli and cause responses that help the body. Nervous System • 3. I am the body system that obtains oxygen from the air for the body to use. I also get rid of carbon dioxide that is no longer needed by the cells of the body. Respiratory system • 4. I am the body system that provides support for the body. I am also in charge of making blood cells for the body. Skeletal System • 5. I am the body system that provides protection for the body. I perform a similar job to the cell membrane of a cell. I also help control the temperature of the body. Integumentary System • 6. I am the body system that takes in and breaks down nutrients for the body. Digestive System Human Body System Human Body Video






























![2 Exam paper_2006[1] - University of Leicester](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011309448_1-9178b6ca71e7ceae56a322cb94b06ba1-150x150.png)





