* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stellar Evolution
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
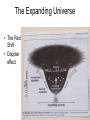
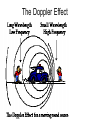
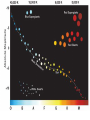
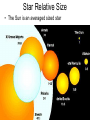
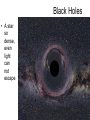
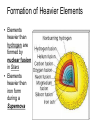
Stellar Evolution The Birth, Life, and Death of Stars The Universe • Everything – All matter, space, and time • The Universe is 13.72 billion years old Cosmology • The study of the origin of the Universe • An average sized Star • About 4.5 billion years old The Sun What is a Solar System? • A star and everything that revolves around it • Our Solar System is about ___ years old A light-year • A unit of distance, not time • The distance light travels in one year • 6 Trillion miles Distance to Sun • 93 million miles • 8.3 lightminutes Proxima Centauri • The closest star to our sun • About 4 lightyears away Galaxies • Stars are not evenly distributed in space. • They are in groups called Galaxies. Types and Sizes of Galaxies • Types: Elliptical, Spiral, Irregular • Two sizes – Giant – Dwarf • • 100,000 light years across • Has Hundreds of billions of stars The Milky Way Galaxy Galaxy Clusters •A Group of Galaxies •Local Group •2 mly across •3 large & about 2 dozen dwarf •Andromeda 2.2 mly Galaxy Superclusters • A cluster of clusters • The Local (Virgo) Supercluster • 100 clusters • 100 mly across Nearest Superclusters Galaxy Superclusters The Visible Universe How big is the Universe? • The visible universe is 28 billion light years in diameter. • Why is that all that is visible? • The entire universe may be much bigger How many Galaxies are there? • Hundreds of billions • Each has hundreds of billions of stars Edwin Hubble • 1920’s • Discovered other galaxies • Discovered the Universe is expanding The Expanding Universe • The Red Shift • Doppler effect The Doppler Effect The Big Bang • Tremendous explosion started the expansion of the universe • All of the matter and energy of the universe was contained at one point Characteristics of Stars Star Properties and Classification • • • • Color Temperature Age Apparent brightness • Distance from Earth Star Brightness • Apparent Magnitude – How bright it looks from Earth • Absolute Magnitude – How much light it actually produces Apparent Magnitude (Brightness) • Depends on actual brightness (luminosity) and distance away Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Compares a star’s Temperature (color) and its … • Absolute Magnitude (Brightness ) Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • Things to Know • Color depends on temperature – Blue, White, Yellow, Orange, Red • The higher the Temperature the Brighter the Star (if in the main sequence) – White Dwarfs and Red Giants are exceptions • The Sun is in the main sequence (90% of stars) Star Relative Size • The Sun is an averaged sized star Stellar Evolution The Formation and Life Cycle of Stars Star Formation • Originate in gas clouds in space called Nebula • Mostly Hydrogen • Gravity pulls it together Nebula • The contraction heats the gases • When it gets hot enough (27 million degrees) nuclear fusion starts Nuclear Fusion •Hydrogen nuclei are fused to make helium • The reaction produce s heat energy, which causes more fusion How big is a Nebula? • The Orion Nebula is about 2.5 light years across Old Age • When the hydrogen runs low • Contractions make more heat • Causes nuclear fusion to make heavier elements • Expansion results in a Red Giant White Dwarf • When energy is used, it shrinks to make a white dwarf Supernovas • Collapses abruptly then explodes • Billions of times brighter • Creates heavier elements • Occurs only in very massive stars After a Supernova • The outer layers are blasted into space to create a new nebula (starts the cycle over) • The core collapses to form a neutron star Neutron Star • Left over after a supernova • 1 teaspoon weighs billions of tons Black Holes • A star so dense, even light can not escape Formation of Heavier Elements • Elements heavier than hydrogen are formed by nuclear fusion in Stars • Elements heavier then iron form during a Supernova The End