* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biol 179 Study Guide Exam 1
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
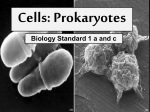
Biol 179 Study Guide Exam 1 - Classification, Viruses and Prokaryotes Spring 2009 To the student: This study guide contains sample questions for the first lecture exam. Your first exam will be based on such questions as well as any other material covered in class. Good luck! Part I: Fill-in-the-blanks 1. A species is the basic point of reference in ________ systems. 2. The biological specialty that deals with the classification and naming of organisms is t ___. 3. The Swedish biologist, Linnaeus, developed a two-part ____ naming system for organisms. 4. The name of an organism according to the binomial system developed by Linnaeus includes both the _____ and the _______. 5. The largest, most inclusive units of biological classification are called ______. 6. ______ organisms are divided into two kingdoms, Archaebacteria and Bacteria. 7. Systematists often use molecular data in a type of analysis called c__________, the study of the order of evolutionary events within a group sharing derived characters. 8. All viruses contain ___ and _____. 9. Nucleic acid of viruses is ___ or ____. 10. Outside the protein sheath, many viruses have a(n) __ made of protein, lipid, & carbohydrate. 11. The integration of a virus into a cellular genome is called _________. 12. The viruses that infect bacteria are called __________. 13. Viruses ___ only after they have entered the cells, and use the host cellular machinery. 14. The ______ virus infects the CD4+ T cells, which are required for normal immunity. 15. ___ are the oldest, structurally simplest, and the most abundant forms of life on earth. 16. Prokaryotes exhibit a great deal of ___ in terms of both structure and metabolism. 17. Prokaryotes split into two lines early in the history of life. The differences are so fundamental that they are assigned to two different domains, the _______ and the ________. 18. Genetic diversity in bacteria is influenced by ______ and ________ and ______. 19. Some species of photosynthetic, oxygenic prokaryotes play a vital role both in productivity. They are called ____ 20. Bacterial cell walls usually consist of ______________, a network of polysaccharide molecules connected by polypeptide cross-links. 21. Most bacteria that cause plant diseases are rod-shaped bacteria known as _____. 22. AIDS is caused by the _____. 23. Personal care products such as _____ will likely lead to bacteria immune to those antibiotics. Page 1 Part II: Matching: Match the taxon in Column A with characteristics given in Column B. ANSWER LETTER GOES HERE ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ Column A Taxon Column B Characteristic 1. Escherichia coli 2. Bacillus anthraxis 3. Clostridium 4. Streptomyces 5. Thermophiles, Halophiles 6. Chlamydia, Treponema 7. Mycobacteria 8. Cyanobacteria 9. Borrelia (Lyme disease) 10. Helicobacter pylori A. Archaebacteria B. photosynthetic oxygen producers C. bull’s-eye rash at infection site D. agent of biological warfare E. soil, dental plaque, erythromycin F. tuberculosis, leprosy G. enteric bacteria H. peptic ulcers I. sexually transmitted disease J. Tetanus, gangrene, botulism Part III: ONE of the following essay questions will be included on the exam. 1. Compare and contrast eukaryotes and prokaryotes. 2. Bacteria and Archaea are two very different domains, yet both contain only prokaryotic organisms. Do you think placing prokaryotic organisms in the domain Bacteria or the domain Archaea is justified? Explain. 3. Are viruses living or non-living? Explain. Page 2 Part IV: Multiple Choice Sample questions related to classification and systematics 1. In the taxonomic hierarchical system for grouping organisms, the next higher group to a family is A) genus B) order C) class D) species E) phylum 2. Characteristics between the branch points of a cladogram that are shared by all organisms above the branch point and are not present in any below it are called A) homologous characters B) analogous characters C) ancestral characters D) derived characters E) novel characters 3. Characteristics that have arisen in organisms as a result of common evolutionary descent are said to be A) homologous characteristics B) analogous characteristics C) adaptive characteristics D) derived characteristics E) novel characteristics 4. Most biologists now recognize and use a newer system for classification of all organisms that identify A) two kingdoms B) three kingdoms C) four kingdoms D) five kingdoms E) six kingdoms 5. Eukaryotic organisms are classified into a total of A) one kingdoms B) two kingdoms C) three kingdoms D) four kingdoms E) six kingdoms 6. Eukaryotic cells acquired mitochondria and chloroplasts by A) endosymbiosis B) exocytosis C) pinocytosis D) mutation E) natural selection 7. All living organisms share all of the following features in common except A) carry out metabolism Page 3 B) C) D) E) transfer energy with ATP encode hereditary information in DNA are composed of one or more cells containing organelles 8. The binomial system of classification of organisms was developed by A) Darwin B) Linnaeus C) Wallace D) Griffith 9. The biological name of an organism in the binomial system contains two parts, the genus and the A) species B) phylum C) kingdom D) order E) family 10. In that any one group fits within a more inclusive group, the biological classification systems are A) evolutionary B) hierarchical C) inclusive D) numerical E) programmed 11. Complex characters A) evolve, fully formed in one step B) evolve through a series of evolutionary transitions C) show the same purpose throughout their evolutionary history D) evolve over a short period of time, involving few generations E) appear simultaneously with other complex characters 12. Of the following, the correct order from largest, most inclusive group to smallest, most specific group, is A) species, genus, family, class, order B) species, family, genus, class, order C) class, genus, order, family, species D) class, order, family, genus, species E) class, family, order, genus, species 13. The largest, most inclusive grouping in the classification scheme is A) genus B) family C) kingdom D) class E) order 14. The number of domains living organisms can be divided into is A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 15. The three multicellular eukaryotic kingdoms, animalia, plantae, and fungi differ in A) morphologies B) motility C) modes of nutrition D) a and c only Page 4 E) a, b, and c 16. The first eukaryotes appeared about A) 4.5 billion years ago B) 1.5 billion years ago C) 15 million years ago D) 1.5 million years ago E) 15,000 years ago 17. Kingdom ____________would include green algae and land plants. A) Chloroplantae B) Plantae C) Chloroprotista D) Virdiplantae E) Chlorophyta 18. Molecular data indicates that land plants belong in the same ________ as green algae. A) clade B) family C) kingdom D) order E) class 19. True multicellularity is a major characteristic of A) all eukaryotes and a few prokaryotes B) animals and plants only C) eukaryotes only D) protists, plants, and animals E) prokaryotes and protists 20. Pinus in the scientific name Pinus ponderosa is the A) phylum B) class C) family D) genus E) species 21. The phenomenon that probably gave rise to the organelles in eukaryotes and accepted by most scientists is A) recombination B) mutation C) syngamy D) endosymbiosis E) multicellularity Page 5 22. An organism has just been located and needs to be placed into one of the domains of life. The characteristics that have been reported are unicellular, phototrophic, oxygenic, nucleoid and a peptidoglycan cell wall. Based on your knowledge, which domain should this organism be placed? A) Bacteria B) Archaebacteria C) Bacteria D) Eukarya E) Protista 23. If two organisms are in the same phylum and the same order, then they also belong to the same A) class B) family C) genus D) species E) subspecies 24. A friend asks you the difference in kingdoms and domains. You respond. A) “Domains are larger and more inclusive than kingdoms. There are three domains into which the six kingdoms can be divided.” B) “Domains are within the six kingdoms and are not actually recognized by most biologists.” C) “Kingdoms have been around much longer and include all six domains.” D) “Kingdoms and domains are really the same thing since they both contain all life forms.” E) “The three domains and six kingdoms are important to a few taxonomists, but mainstream biologists stick with the more familiar five kingdom approach.” 25. One day after a biology class you have some confusion about the difference between phylogeny and systematics. Which friend is right? A) Friend A states that systematics and phylogenies are really the same, one is more recent than the other is, but basically they are the same. B) Friend B says that the way he remembers is that systematics is the same as cladistics and cladistics is reconstructing clades, which ultimately lead to the development of phylogenies. C) Friend C argues that systematics is the actual collecting and cataloguing of specimens into museums which can be used later by scientists to construct clades and phylogenies. D) Friend D says that the way she remembers is that systematics is the reconstruction and study of phylogenies. 26. A phylogenetically based taxonomy is important not only in creating a logical way to name organisms, but also in learning about ________ of organisms using information in related species. A) physiology B) behavior C) development D) a, b, and c E) none of the above 27. Which of the following statements is accurate about the chart of morphological data? The "1" in the box means the trait is present and the "0" indicates that the trait is absent. Page 6 A) All organisms in this chart share all of the derived characteristics. B) Only the gorilla and humans share all of the derived characteristics. C) The lamprey is the only outgroup since it shares none of the derived characteristics. D) The salamander and the tiger are outgroups because they only share two of the derived characteristics (jaws and lungs). E) The shark is an outgroup since it only has one of the derived characteristics (jaws). 28. Which statement is an accurate description of the characteristics found in the examples below that relate to the three Domains of life? A) Archaea and Eukarya share the characteristic of membrane bound organelles. B) Bacteria and Archaea share the characteristic of nuclear envelope. C) Eukarya and Bacteria share the characteristic of membrane bound organelles. D) Archaea and Eukarya share the characteristic of peptidoglycans in cell walls. E) Archaea and Bacteria share the characteristic of branched membrane lipid structure. 29. A scientist is studying endosymbiosis in cells. This means she is investigating A) how mitochondria and chloroplasts entered prokaryotic cells B) how mitochondria and chloroplasts entered eukaryotic cells C) how mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved into prokaryotic cells D) how mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved into eukaryotic cells E) how mitochondria but not chloroplasts entered prokaryotic cells Sample questions related to viruses 1. Which of the following statements about viruses is NOT accurate? A) Viruses are fragments of nucleic acids with associated proteins. B) Viruses can infect organisms at all taxonomic levels. C) Viruses can be placed in the Archaea Domain of life because of their similarities with these primitive organisms. D) Viruses cannot reproduce on their own. E) Viruses can invade cells and produce more copies of themselves. 2. Most viruses form a capsid around their nucleic acid core. This capsid is composed of A) a protein B) a monosaccharide Page 7 C) an antigen D) a glycoprotein E) a lipoprotein 3. Virulent viruses multiply within infected cells and eventually A) cause an alternation of generation in the host cell, releasing new viruses B) cause the transformation of the host cell, releasing new viruses C) cause lysis of the host cell, releasing new viruses D) cause the reduction of the host cell, releasing new viruses E) cause a transfer of material from the host cell, releasing new viruses 4. Lacking one of the criteria to be strictly classified as living units and containing fragments of eukaryotic genomes, the viruses are included in A) bacteria B) protists C) yeasts D) prokaryotes E) none of the kingdoms 5. The HIV virus is considered a ______ virus, because after getting integrated into the host cell chromosomes, it does not begin replicating immediately. A) phage B) latent C) transforming D) non-reproducing E) transfection 6. Each HIV particle possesses a ___________ on its surface that precisely fits a cell-surface marker protein called CD4 on the surfaces of the immune system cells called macrophages and T cells. A) nucleic acid B) phospholipid C) polysaccharide D) glycolipid E) glycoprotein 7. All of the following are diseases caused by viruses except A) strep throat B) AIDS C) polio D) small pox E) measles 8. Phages are viruses which can infect A) humans B) plants Page 8 C) insects D) farm animals E) bacteria 9. A layer of lipoprotein and glycoprotein that covers the outer surface of some viruses is the A) capsid B) casing C) envelope D) membrane E) coat 10. Viruses that cause lysis of their hosts are called A) lethal B) potent C) temperate D) virulent E) latent 11. Viruses that become established as stable parts of the host cell genome are called A) lethal B) potent C) temperate D) virulent E) latent 46. The infection cycle of HIV includes all of the following steps except A) attachment B) entry C) replication D) killing the host cell immediately with no exceptions E) viral DNA integrates into the host chromosome 12. HIV studies revealed that it is closely related to A) chicken sarcoma virus B) ebola virus C) herpes virus D) a chimpanzee virus E) mad cow disease 13. An example of an 'emerging virus' (a virus in a new host) with a lethality rate in excess of 50% is A) Influenza virus B) Ebola virus C) hepatitis B D) variola virus E) yellow fever 14. Activation of a latent herpes virus is responsible for A) fever blisters or cold sores B) AIDS C) syphilis Page 9 D) Alzheimer's disease E) dental caries 15. HIV infects cells by recognizing the cell-surface markers with its own A) DNA B) glycoproteins C) reverse transcriptase D) capsid protein E) enzymes 16. All viruses are constructed of A) DNA with a protein wrapping, called a capsid B) RNA with a protein wrapping, called a capsid C) either DNA or RNA with a protein wrapping, called a capsid D) either DNA or RNA, however many do not have the capsid 17. A scientist is studying the lysogenic cycle of the lambda 1 bacteriophage of Escherichia coli. This means that he is investigating A) the integration and stabilizing of the lambda 1 phase into a host cell's genome B) the integration of the bacteria's genome with the viral genome outside of the bacteria's cell wall C) the integration of the viral genome into the ribosomes present in the bacteria to direct protein synthesis for the capsid formation D) the integration and stabilizing of a virus into its capsid, which provides protection until conditions are better for reproduction 18. If a virus enters the lytic phase in a host's cell, it will cause A) the host cell to reject the virus B) the host cell to shrink because of the loss of cytoplasm which has been used in the synthesis of viral DNA C) the host cell to burst because there will be so many viral particles present D) the host cell to replicate itself at a higher than normal frequency E) the host cell to initiate an attack on the virus 19. The specific white blood cells that HIV attaches to are the A) CD4-T cells B) gp120 -T cells C) CCR5-T cells D) CXCR4-T cells E) CD8-T cells 20. Viruses infect every organism that has been investigated for their presence. However, viruses can only replicate in A) very limited conditions, depending on their capsid type B) a very limited manner if they are a retrovirus C) a very limited manner depending on their envelope capability with the host's cell membrane or cell wall D) their lytic stage outside the host cell membrane E) a very limited number of the host's cells Page 10 Questions related to prokaryotes 1. Rocks dated to be 3.5-3.8 billion years old are most likely to contain fossils of A) Prokaryotes B) Eukaryotes C) Viruses D) Multicellular animals 2. Rocks called ___ contain the fossilized remains of prokaryotic organisms. A) impressions B) stromatolites C) inclusions D) replicas 3. Mutation is an important source of genetic variation in prokaryotes A) True B) False 4. Mutations are rarely found even in a sample of millions of bacteria. A) True B) False 5. Some bacteria have the ability to take up DNA directly from their environment in a type of horizontal gene transfer called A) Transformation B) Conjugation C) Transduction D) more than one answer is correct E) none of these 6. Some bacteria have the ability to take transfer DNA from one bacterial cell to another in a process called A) Transformation B) Conjugation C) Transduction D) more than one answer is correct E) none of these 7. Some bacteria have the ability to take transfer DNA from one bacterial cell to another in a process called A) Transformation B) Conjugation C) Transduction D) more than one answer is correct E) none of these 8. Some bacteria can be genetically transformed as a result of infection by a bacteriophage in a process called A) Transformation B) Conjugation C) Transduction D) more than one answer is correct E) none of these 9. In going from the external environment to the nucleoid of a bacterium, what structures would be observed in correct order A) cytoplasm, plasma membrane, cell wall, capsule B) cell wall, capsule, plasma membrane, cytoplasm C) capsule, cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm D) cytoplasm, plasma membrane, capsule, cell wall 10. Though a diverse group, all archaebacteria share certain characteristics which A) lack peptidoglycan cell walls B) possess very unusual lipids C) contain characteristic ribosomal RNA sequences D) some of their genes contain introns Page 11 E) all of the above are true 11. Which of the following cannot be included in the main categories of archaebacteria? A) methanogens B) extreme thermophiles C) extreme halophiles D) nitrogen fixers 12. Two principal organelles of eukaryotes that share features with one another and with bacteria from which they apparently were derived are the A) flagella and cilia B) microfilaments and microtubules C) mitochondria and chloroplasts D) rough ER and smooth ER E) plasma membrane and nuclear membrane 13. Current classification of prokaryotes is based on A) morphology of flagella B) sequencing of proteins, DNA and RNA C) occurrence of transverse binary fission D) type of colony formation E) ability to stain the cell wall with Gram stain 14. When bacteria are exposed to nutrient-poor conditions, they form thick-walled structures that contain the chromosome and a small amount of cytoplasm. These structures are called A) plasmids B) pseudomonads C) nucleoids D) endospores E) xospores 15. Certain bacteria are the only organisms that are capable of fixing atmospheric A) carbon dioxide B) oxygen C) hydrogen D) carbon E) nitrogen 16. Prokaryotes undergo a process that produces cells that are identical. This process is called A) mitosis B) meiosis C) conjugation D) binary fission E) syngamy 17. The prokaryotic DNA is located in the A) capsid region B) nucleoid region C) endospore region D) peptidoglycan region E) pili region 18. Which of the following is a characteristic of prokaryotes? Page 12 A) B) C) D) E) found in every habitat metabolically versatile contain enormous adaptability a and b a, b, and c 16. Prokaryotes are very important ecologically because they perform all of the following except A) carry out photosynthesis B) fix atmospheric nitrogen C) carry out decomposition D) all capable of causing diseases E) inhabit all types of habitats 20. Which of the following is not true about prokaryotes? A) They are the oldest organisms on earth. B) They are the structurally simplest organisms. C) They are the most abundant life forms on earth. D) They contain organelles. E) They are found in fossils that are 3.0-3.5 billion years old. 21. Genetic engineering technology is being applied to adapt Bacillus thuringensis for the purpose of A) antibiotic production B) cheese manufacture C) insect control D) making human proteins E) toxic waste degradation 22. In all of the following characteristics, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes except in A) cell size B) multicellularity C) chromosomes D) plasma membrane E) organelles 23. In which of the following characteristics, prokaryotes and eukaryotes are similar? A) cell division B) internal compartmentalization C) flagella D) contain ribosomes E) enzymes localized in the plasma membrane 24. Which of the following is not a shape seen in prokaryotes? A) cocci B) bacilli C) spirals Page 13 D) helicals E) icosahedrals 25. Certain prokaryotes can withstand drying and hotter temperatures because of their ability to form A) cell walls B) endospores C) flagella D) organelles E) plasmids 26. Archaebacteria differ from bacteria in which of the following? A) cell wall B) plasma membrane make up C) gene translation machinery D) gene architecture E) all of the above 27. Heterotrophs that harvest energy from organic molecules are called A) photoautotrophs B) chemoautotrophs C) photoheterotrophs D) chemoheterotrophs E) nitrogen fixers 28. Bacterial cells can be shaped like A) circles, cubes and pyramids B) the letters S, T and U C) the letters O, L and T D) rods, spheres and spirals 29. Some prokaryotes attach to other substrates by hairlike outgrowths, which are shorter than flagella. These are called A) endospores B) flagellin C) pili D) plasmids E) fission products 30. Bacteria cause all of the following human diseases except A) cholera B) diphtheria C) mononucleosis D) tetanus E) malaria 31. Energy metabolism requiring organic compounds is A) heterotrophic B) autotrophic 32. Heterotrophic metabolism requiring energy (in part) from the sun is Page 14 A) chemoheterotrophic D) Chemolithotrophic B) Photoheterotrophic C) Phototrophic 33. A phototrophic bacterium will always A) use carbon dioxide as a carbon source B) produce oxygen C) use energy sources like ammonia or hydrogen sulfide E) more than one answer is correct 34. Autotrophic prokaryotes may A) use carbon dioxide as a carbon source B) produce oxygen C) use energy sources like ammonia or hydrogen sulfide D) use sunlight as an energy source E) more than one answer is correct 35. Which of the following must always occur during energy metabolism of autotrophic prokaryotes? A) use carbon dioxide as a carbon source B) use organic compounds as a carbon source C) use sunlight D) use energy sources like ammonia or hydrogen sulfide E) more than one answer is correct 36. Sexually transmitted diseases include which of the following? A) gonorrhea B) syphilis C) chlamydia D) a, b, and c E) a and b 37. Four of the five choices are characteristics of prokaryotic organisms. Select the exception. A) Most prokaryotic cell diameters are one micrometer or less. B) Most prokaryotic organisms are unicellular. C) Prokaryotic organisms use mitosis for their nuclear division. D) Prokaryotic organisms use binary fission to divide. E) Prokaryotic organisms do not have a membrane around their nuclear materials. 38. Which of the following differences between Archaebacteria and Bacteria is correct? A) Archaebacteria have peptidoglycans in their cell walls. Bacteria do not have peptidoglycans in their cell walls. B) Archaebacteria and Bacteria have different lipids in their bilipid layer of the plasma membranes. C) Archaebacteria and Bacteria have ribosomal proteins and an RNA polymerase that are distinctly different from eukaryotes, however bacteria ribosomal proteins are different from eukaryotes, while Archaebacteria ribosomal proteins are very similar. D) Genes of most Archaebacteria are not interrupted by introns, whereas interns interrupt bacteria genes. 39. A microbiologist is conducting a research project on chemoautotrophs. This means that the investigator is examining certain aspects of a bacterium that A) can oxidize sulfur Page 15 B) is a purple non-sulfur bacteria which depends on light C) obtains carbon from organic molecules D) can use the energy from sunlight to build organic molecules from carbon dioxide The following information will be provided on the exam. Genera of bacteria discussed in class: Be familiar with characteristics of each or their association with disease. Streptomyces Borrelia burdorferi Escherichia coli Aquifex Actinomyces Deinococcus Salmonella Mycobacterium tuberculosis Thermus aquaticus Gloeocapsa Vibrio cholerae Mycobacterium leprae Oscillatoria Rickettsia Spirulina Helicobacter Bacillus Clostridium Bacillus thuringensis Microcystis Myxobacteria Staphylococcus Bacillus anthraxis Bdellovibrio Clostridium Nitrosomonas Streptococcus Page 16 Page 17