* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anterior Cerebral Artery
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
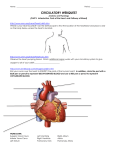
Anterior circulation: Carotid system Posterior circulation: Vertebrobasilar system (VB system) Circle of Willis CNS vessels 1 Anterior Circulation Common carotid artery (CCA) External carotid artery (ECA) Internal carotid artery (ICA) Anterior cerebral artery (ACA) Anterior communicating artery (Acom) Middle cerebral artery (MCA) Cortical branches Lenticulostriate artery CNS vessels 22 Posterior Circulation Posterior cerebral artery (PCA) Posterior communicating artery (Pcom) Vertebral artery (VA) Basilar artery (BA) Anterior spinal artery (ASA) CNS vessels 3 Internal Carotid Artery CNS vessels 4 Internal Carotid Artery (cavernous segment) CNS vessels 5 Meningohypophysial trunk from the cavernous & postclinoid segment of ICA Internal Carotid Artery Hypophysial arteries Posterior hypophysial arteries: posterior lobe of pituitary gland Anterior hypophysial arteries: medial eminence of hypothalamus; forming hypophysial portal system Ophthalmic artery Posterior communicating artery (Pcom) Anterior choroidal artery CNS vessels 6 Internal Carotid Artery 1: meningohypophyseal trunk 2: lateral mainstem CNS vessels 7 Middle Cerebral Artery CNS vessels 8 Middle Cerebral Artery CNS vessels 9 Middle Cerebral Artery 1: M1 2: lat. lenticulostriate 3: lat. fissure CNS vessels 10 Middle Cerebral Artery Terminal branches Cortical branches Lenticuostriate arteries (deep branch) Clinical note: depends on the site of occlusion Main trunk of MCA Branches of MCA: cortical vs. deep branches CNS vessels 11 Anterior Cerebral Artery CNS vessels 12 Anterior Cerebral Artery CNS vessels 13 Anterior Cerebral Artery CNS vessels 14 Anterior Cerebral Artery Branches: recurrent artery of Heubner (medial striate artery): proximal to Acom; penetrating anterior perforated substance; supplying head of caudate nucleus, putamen, anterior limb of internal capsule, corpus callosum Course: ascending in longitudinal fissure; bending backwards around corpus callosum; continuing as pericallosal artery and callosomarginal artery following the cingulate sulcus Territory: medial surface of cerebral hemisphere Clinical syndrome: motor and sensory deficits in contralateral leg; sometimes mental confusion. Why? CNS vessels 15 Anterior Cerebral Artery CNS vessels 16 Vertebrobasilar System Vertebral artery (VA): arising from the subclavian artery ascending in foramina of transverse processes of upper 6 C-vertebrae piercing posterior atlanto-occipital membrane on reaching skull base entering subarachnoid space at the level of foramen magnum; forming Basilar artery (BA) by joining of 2 VA at ponto-medullary junction; dividing into Posterior Cerebral Arteries (PCA) at midline of midbrain CNS vessels 17 Vertebral artery (VA) 1: Pcom 2-5: anastomosis between ICA and VB CNS vessels 18 VB system Spinal arteries: single Anterior Spinal Artery as continuation of VA Posterior Spinal Artery as a branch of either VA or PICA Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA) CNS vessels 19 VB system: PICA Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA) the largest branch of VA pursuing an irregular course between medulla and cerebellum supplying posterior part of cerebellar hemisphere, inferior vermis, nuclei of cerebellum and choroid plexus of 4th ventricle with medullary branches to dorsolateral region of medullla CNS vessels 1-7: br of PICA 8: AICA; 9: SCA 10: Ant spinal a. 20 VA system: Basilar Artery Basilar artery with branches: Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (AICA), Labyrinthine artery, Pontine Arteries, Superior Cerebellar Artery AICA: arising from caudal end of BA; supplying cortex of inferior surface of anterior cerebellum and underlying white matter and central nuclei; supplying upper medulla and tegmentum of lower pons by small branches Labyrithine artery: a branch of either BA or AICA; entering internal acoustic meatus and supplying membranous portion of internal ear CNS vessels 21 Pontine Arteries slender branches of variable length: Paramedian arteries: basal part of pons (corticospinal fibers, pontine nuclei and transverse pontocerebellar fibers) Circumferrential arteries: lateral part of pons and middle cerebellar peduncle; the floor of 4th ventricle and tegmentum by turning medially CNS vessels 22 Pontine arteries Paramedian branches Circumferential branches CNS vessels 23 Superior Cerebellar Artery branch immediately before terminal bifurcation of BA; Supply dorsal surface of cerebellum (cortex, white matter and central nuclei), rostral pontine tegmentum, superior cerebellar peduncle, and inferior colliculus CNS vessels 24 Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) curve around midbrain and reach medial surface of cerebral hemisphere beneath splenium of corpus callosum with temporal branches (inferior surface of temporal lobes: hippocampus), calcarine (primary and association cortex of vision), and parieto-occipital branches Posterior choroidal artery: from the splenium region beneath corpus callosum supplying choroid plexus of the lateral and 3rd ventricles, thalamus, fornix and tectum of midbrain anastomosing with anterior choroidal artery within choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle CNS vessels 25 Posterior Cerebral Artery CNS vessels 26 Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) 1-2: thala. A 3-4: post choroidal a 5-6: temp. a 7: parieo-occipital a 8: calcarine a 9: splenial a CNS vessels 27 Central Arteries slender, thin-walled vessels directly from the circle of Willis ganglionic, nuclear, striate or thalamic perforating arteries supply corpus striatum, internal capsule, diencephalon and midbrain recurrent artery of Heubner, anterior and posterior choroidal arteries groups: anteriomedial, anteriolateral, posteromedial, posterolateral CNS vessels 28 Central Arteries (1/2) Anteriomedial group: from ACA; penetrating anterior perforated substance; to hypothalamus (preoptic and suprachiasmatic) Anteriolateral group (striate arteries; lateral striate arteries): from MCA; penetrating anterior perforated substance; to supply corpus striatum CNS vessels 29 Central Arteries (2/2) Posteromedial group: from PCA and Pcom ; penetrating posterior perforated substance (the floor of interpeduncular fossa); to diencephalon & midbrain (medial portion of cerebral peduncle) Posterolateral group: from PCA; curving around midbrain; to portion of thalamus and midbrain (tectum, lateral portion of cerebral peduncle) CNS vessels 30 CNS vessels 31 CNS vessels 32 CNS vessels 33 CNS vessels 34 Clinical Notes of Stroke Vasomotor Control Autoregulation: to ensure constant rate of blood flow depending on local vasodialtor metabolites Stroke syndromes example: visual pathway and cerebral circulation CNS vessels 35 Visual pathway and cerebral circulation CNS vessels 36 Visual pathway and stroke CNS vessels 37 Venous Drainage Brainstem and cerebellum: drained by unnamed veins into dural venous sinuses of posterior cranial fossa Cerebrum: by external cerebral veins (surface) and internal cerebral veins (central core, beneath corpus callosum in transverse fissure); both systems finally draining into dural venous sinuses CNS vessels 38 Venous Drainage: External Cerebral Venous System Superior cerebral veins: over lateral surface of hemisphere into superior sagittal sinus Superficial middle cerebral vein: downward along lateral sulcus and into cavernous sinus; with anastomotic channels: superior anastamotic vein (of Trolard) into superior sagittal sinus inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbé) into transverse sinus Deep middle cerebral vein: anterior cerebral vein and basal vein (of Rosenthal) CNS vessels 39 Eexternal Cerebral Venous System CNS vessels 40 Internal cerebral venous system Thalamostriate vein (vena terminalis) Choroidal vein Internal cerebral vein Great cerebral vein (of Galen) CNS vessels 41 Cerebral Venous System CNS vessels 42 CNS vessels 43 Spinal Arteries Anterior spinal artery: from VA Posterior spinal arteries: paired; from VA or PICA running longitudinally throughout the length of spinal cord Spinal arteries from VA: only sufficient for upper cervical cord Segmental spinal arteries CNS vessels 44 Segmental spinal arteries from VA of cervical segment, posterior intercostal branches of thoracic aorta and lumbar branches of abdominal aorta; enter vertebral canal through intervertebral foramina; give anterior and posterior radicular arteries running along the ventral and dorsal roots of spinal nerves; of small caliber, only for nerve roots and vascular plexus in pia; join the anterior and posterior spinal arteries in lower cervical, lower thoracic and upper lumbar regions; with the largest one (spinal artery of Adamkiewicz) for upper lumbar region CNS vessels 45 CNS vessels 46 Segmental Spinal Arteries Anterior spinal artery ventral horn portion of dorsal horn ventral and lateral white funiculi Posterior spinal artery dorsal funiculi the remaining part of dorsal horn CNS vessels 47 Segmental Spinal Arteries CNS vessels 48 Spinal Veins Variable in course Anterior spinal vein: along midline and ventral rootlets Posterior spinal vein: along the midline and dorsal rootlets Drained by anterior radicular veins and posterior radicular veins into epidural venous plexus, further into external vertebral plexus via intervertebral foramina and finally into vertebral, intercostal and lumbar veins CNS vessels 49 Imaging of brain in vascular disorders Computed tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Cerebral angiography Regular angiography Computed tomography angiography (CTA) Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) Ultrasound CNS vessels 50 CT and MRI CNS vessels 51 Vascular territories on neuroimaging: border zone (watershed) infarct (cortical border zone infarct JNNP) CNS vessels 52 Clinical-Neuroanatomical correlations CNS vessels 53 Clinical-Neuroanatomical correlations CNS vessels Somatosensory Motor 54 Cerebral angiography CNS vessels 55 Cerebral angiography CNS vessels 56 CNS vessels 57 Case report A 47-year-old male was sent to Emergency Department (ER) due to acute onset of right hemiplegia, right facial plasy (central type), and global aphasia (motor + sensory aphasia). Neurological examinations showed upper motor neuron signs on the right side. You are the VS in charge of ER: Localization of lesion: where is the lesion according to clinical neuroanatomical correlations? Underlying pathophysiology: which vessel is occluded? 58 CNS vessels Localization of lesion CNS vessels 59 Underlying pathophysiology: Magnetic resonance angiography CNS vessels 60 CNS vasculature Brain Circle of Willis, Carotid system, VB system Territory of vessels and functional correlations Spinal cord Anterior and Posterior spinal artery Venous system Internal cerebral venous system Dural sinuses CNS vessels 61