* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
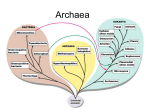
Download Domain Archaea Kingdom Archaebacteria Cell type Prokaryotic Cell
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Unique properties of hyperthermophilic archaea wikipedia , lookup
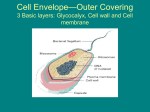
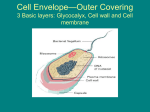
Domain Archaea Kingdom Archaebacteria Cell type Prokaryotic Cell structure Cell wall, no peptidoglycan Body type Unicellular Nutrition Autotrophic and heterotrophic Example 1. Thermoacidophiles *hot, acidic environments (sulfur hot springs, thermal vents on the ocean floor, and around volcanic vents) *thrive in temperatures above 80 degrees Celsius & pH of 1-2 * many die in presence of oxygen! 2. Halophiles *live in very salty environments (use salt to generate ATP) *Great Salt Lake, Dead Sea (15% or more of salt) *usually aerobic *carry out photosynthesis using a protein instead of chlorophyll 3. Methanogens *can not live in presence of oxygen (obligate anaerobes) * uses CO2 during respiration and give off methane gas as a waste product *found in: sewage treatment plants, swamps, bogs, and near volcanic vents... also responsible for gases release from digestive tract... A.K.A. farts! 1 Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Cell type Prokaryotic Cell structure Cell wall, peptidoglycan Body type Unicellular Nutrition Autotrophic and heterotrophic Example Streptococcus (strep throat) e-coli 2 pneumonia Staph infection meningitis MRSA gonorrhea E. coli Bacillus anthracis Strep throat Strep mutanscavities syphilis rod shape 2 round shape chain round bunch round spiral shape movement attachment and transfer DNA circular extra DNA that carries genes for toxins and resistance Antibiotic-disrupts the growth and development of bacteria Good Bacteria-fix nitrogen -help with decay -help with digestion -make cheese and yogurt -make medicines http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/videos/25296/pgr25296_700k.asf 3 --> Gram Staining: Hans Gram (1884) **Gram Positive: Thick layer of peptidoglycan, stains purple, can be treated with antibiotics Bacterial Examples: Lactobacilli (makes yogurt & buttermilk) Actinomycetes (make antibiotics) Clostridium (lockjaw bacteria) Streptococcus (strep throat) Staphylococcus (staph infections) ** Gram Negative: Thin layer of peptidoglycan, stains pink or reddish, hard to treat with antibiotics Bacterial Examples: -Rickettsiae are parasitic bacteria carried by ticks...Cause Lyme disease & Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever -cyanobacteria 4