* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Effects of Illicit Drugs on the Heart and Brain
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
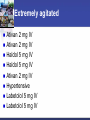
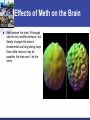
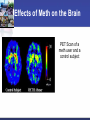
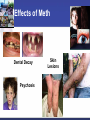
2014 Stroke/Cardiac System of Care Conference Effects of Illicit Drugs on the Heart and Brain Presented by: Jeffrey Sather, MD, FACEP Trinity Health Disclosures No Financial incentives No off label use of any drug or medical device to be discussed Case Study 21 Year old male presents to critical access hospital agitated and confused Possibly ingested 2 grams of Methamphetamine Extremely agitated Ativan 2 mg IV Ativan 2 mg IV Haldol 5 mg IV Haldol 5 mg IV Ativan 2 mg IV Hypertensive Labetolol 5 mg IV Labetolol 5 mg IV Extremely agitated Seizing Temperature reaches 104 All of the above happening over 30 minutes. Then intubated to be transferred by fixed wing aircraft. Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest while being loaded to airplane. Returned to CAH hospital for resuscitation About 10 minutes of CPR first arrest About 2 minutes of CPR second arrest Labs Labs Drugs of abuse screen Objectives What does a drug screen indicate? What are common drugs abused? What are the effects of drugs on the heart and brain? How does it effect treatment? North Dakota: Leader of the Pack North Dakota Ranks #1 in Binge Drinking Teen Alcohol Statistics 95% of the alcohol consumed by youth under the age of 21 in the U.S. is in the form of binge drinks. Binge drinking is associated with many health problems, including— Unintentional injuries (e.g., car crashes, falls, burns, drowning) Intentional injuries (e.g., firearm injuries, sexual assault, domestic violence) Alcohol poisoning Sexually transmitted diseases Unintended pregnancy Children born with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders High blood pressure, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases Liver disease Neurological damage Sexual dysfunction, and Poor control of diabetes. Drug Use - Study In 2009, the safety agency issued the National Roadside Survey of Drug and Alcohol Use by Drivers: Alcohol was the most likely intoxicant 8.6 percent of the total tested had used marijuana 3.9 percent had used cocaine 1.3 percent tested positive for methamphetamine Drug Use Two studies (44,000 collisions): One out of four drivers involved in crashes had marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, or some combination of those drugs in their system Approximately 14 percent of all drivers on the road have an illegal drug in their system Marijuana Marijuana Raises the heart rate 20-100% 4.8 fold increase in the risk of AMI in the first hour after smoking. This risk increases as other risk factors increase. Effects thinking and memory Stunts brain development Causes a decrease in IQ in subjects using through teens and twenties. Increased respiratory illness Marijuana Linked to increased mental illness such as: Depression Anxiety Suicide Psychosis Impairs judgment and contributes to increased risk of injury or death. Specific link to lung cancer not well established at this point Marijuana No Specific antidote Symptomatic Treatment Narcotics One of the oldest pharmacological substances Histamine releasing properties Produce bradycardia and hypotension by increasing parasympathetic and decreasing sympathetic response Strong respiratory depressant Can produce coma Infection from injection Narcotic Treatment Symptomatic treatment Antidote is Naloxone Half life can be shorter than the narcotic Cocaine Strong central nervous system stimulant that increases levels of dopamine Changes the short and long term reward system in the brain Cocaine Effects Constricts blood vessels Increases heart rate Increases blood pressure Increases body temperature Increased risk of AMI and Stroke Increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Cocaine Treatment No specific antidote Symptomatic Treatment Synthetic Drugs “Fake Substances . . . Real Dangers” K2, Spice, Bath Salts, Smiles . . . Synthetic Drugs What are they? Synthetic marijuana (often known as “K2” or “Spice”) and bath salts products are often sold in legal retail outlets as “herbal incense” and “plant food,” respectively, and labeled “not for human consumption” to mask their intended purpose and avoid FDA regulatory oversight of the manufacturing process. Synthetic Drugs How frequently is synthetic marijuana used? Use of synthetic marijuana is alarmingly high o 11.4 percent of 12th graders used Spice or K2 in the past year *second most commonly used illicit drug among seniors Synthetic Drugs What are they? Bath salts contain manmade chemicals related to amphetamines, also known as substituted cathinones. Cathinone derivatives are claimed to have effects similar to cocaine, amphetamine or MDMA (ecstasy). Smiles (not the good kind) “Designer Drug” – 2CI The drug, a hallucinogen, has been linked to two deaths in Grand Forks, North Dakota. Though little is known about this drug's dangers. Smile’s effects: combination of MDMA (ecstasy) and LSD “speedy charge along with intense visual and auditory hallucinations” Synthetic Treatment No specific antidote Symptomatic Treatment Methamphetamine 2012 0.4% of population or 1.2 million report using 103,000 ED visits directly related in 2011 4th most commonly mentioned abused drug by ED patients nationally behind Marijuana, Cocaine, and Heroin Methamphetamine effects Increased attention and decreased fatigue Increased activity and wakefulness Decreased appetite Euphoria and rush Rapid/irregular heartbeat Vasoconstriction Hypertension Hyperthermia Methamphetamine chronic effects Anxiety Confusion Insomnia Mood disturbances Violent behavior Psychosis Hallucinations visual and auditory Paranoia Effects of Meth on the Brain Meth rewires the brain. Prolonged use not only modifies behavior, but literally changes the brain in fundamental and long-lasting ways. Even while recovery may be possible, the brain won’t be the same. Effects of Meth on the Brain PET Scan of a meth user and a control subject Face lift courtesy of meth 2 months later 2 years, 5 months later 1 year, 5 months later 1 year, 5 months later Effects of Meth Dental Decay Psychosis Skin Lesions Unnecessary Deaths Teenage male collapses from unknown causes. Dies one day later. Dx: Sudden cardiac death secondary to “bad” meth. Unnecessary Deaths 17-year-old male and 23-year-old female with AMI. Both heavy meth users. 19-year-old presents with blood pressure of 290/160. Dies from a stroke after meth injection. Methamphetamine Treatment No specific antidote Symptomatic Treatment Drugs of Abuse Screen Screening test not a definitive test Must be metabolized and excreted to be present Metabolites present for variable periods Most 2-3 days Does not test for all abused substances For example fentanyl a synthetic opiate does not trigger positive for opiates. Pearls No specific antidote for most abused drugs except for Narcotics and Benzodiazepines. Pearls Flumazenil should not be given to benzodiazepine abusers and should only be used for iatrogenic overdose. Pearls Naloxone reverses narcotics Reversing narcotic overdose usually results in “bad behavior” Half life is shorter than many abused narcotics and repeated dosing may be needed. Pearls Gastric lavage has almost no utility Treatment is generally symptomatic Drug screen utility is to add evidence to clinical findings Case Study Case Study Arrives intubated with no neurologic response. In Rhabdomyolysis and has hyperkalemia. Case Study Case Study Case Study Hypothermia protocol for 24 hours Treated for Rhabdo and hyperklemia Rewarmed No neurologic recovery MRI shows diffuse edema and herniation Brain death testing protocol Support pulled and patient died Diagnosis: Death due to anoxic encephalopathy secondary to methamphetamine overdose