* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skills: To construct circles of a given radius, angle bisectors, and
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Rule of marteloio wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Cardinal direction wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
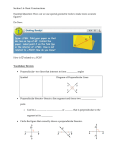
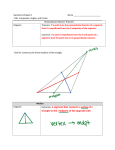
Constructions: angle bisector Skills: To construct circles of a given radius, angle bisectors, and equilateral triangles. Constructions are done only using a compass and a straight edge. A compass draws part of a circle - an arc Leave all the construction lines - they are the “working” Circles – Use a ruler to set the compass to the radius of the circle Angle bisector Definition: eg) Angle bisect angle FGH F G F G H H Constructing Startertriangles A 1) Construct an equilateral triangle with sides of 7cm. Label it ABC 2) Angle bisect angle ABC. Continue the angle bisector until it touches line AC. Label this point P 1 7 6 5 4 3 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3) Angle bisect angle APB and CPB. Continue the angle bisectors until they touches the sides of the triangle. Label these points Q and R 4) Measure the distance QR in mm. QR = ______ mm 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 5 4 3 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 Skills: Construct triangles given sides and angles. Given 3 sides lengths 1) Rule and measure the longest side 2) Set compass length of second side and arc. 3) Set compass to the length of the third side and arc again so the arc’s cross. Mark this point 4) Rule in the triangle sides Construct a triangle with side lengths 3cm, 4cm and 5cm 4cm 5cm 3cm 0 1 2 3 4 5 1 5 4 3 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 Constructing triangles B Given 2 sides and 1 angle 1) Rule the longest side (correct length) 0 2) Measure the angle with a protractor 3) Rule the second side (correct length) 4) Rule in the third side Construct a triangle with side lengths 5cm, 4cm and a 45° angle between them 4cm 45° 5cm 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 Constructing triangles C Given 1 side and 2 angles 1) Rule and measure the side length 0 1 2 3 4 5 2) Measure the angle to each of the other sides. Rule the sides in until they cross. Eg: 1) Construct a triangle with side length BC 5cm, and a 40° and 50° angles 2) Measure the sides AB = ____ AC = ____ 3) Measure the angle BAC = ____ Eg: 1) Construct a triangle with side length PQ 3cm, and a 30° and 120° angles 2) Measure the sides PR = ___ R QR = ____ 3) Measure the angle PRQ = ____ 30° P 120° 3cm Q Perpendicular bisector Skill: Construct perpendicular bisectors. Definition: ___________________________________ B A Construct the perpendicular bisector to the line AB B A Note that line AB is now cut in half at 90° B A Perpendicular line from point near a line Skills: Construct perpendicular lines from a point near a line. Construct a line passing through point P which is also perpendicular the line DE P . E D Put compass point at P Adjust the compass to reach just over line DE so the arc cuts the line twice Mark these points A and B P Now construct the perpendicular bisector of line AB as before. Note that line DE is now cut at 90° D . E Perpendicular line from point on a line Steps: Construct perpendicular lines from a point on a line. Construct a line passing through point P which is also perpendicular the line GH H P . G Put compass point at P Adjust the compass so the arc cuts the line GH twice. Mark these points A and B Now construct the perpendicular bisector of line AB as before. Note that line GH is now crossed at 90° H P G . Find the circumcircle Given any triangle construct a circle which will pass through all three corners of the triangle. Steps: 1) Rule a neat large triangle. 2) Perpendicular bisect all three sides 3) Continue the perpendicular bisectors until they intersect. Label this point P 4) Put compass point at P and construct a circle passing through the corners of the circle. Extension: Circumcircle Given any triangle construct a circle which will pass through all three corners of the triangle. Extension: Centre of gravity Given any triangle use construction to find the centre of gravity of the triangle. 1) Rule a neat large triangle. 2) Perpendicular bisect all three sides. Don’t rule in the perpendicular bisector, just mark the midpoint of the side. 3) Rule a line from a corner of the triangle to the middle of the opposite side found in step 2). 4) Repeat step 3) for the other two corners of the triangle. 5) Where the three lines meet mark point P. This is the centre of gravity (balance point of the triangle) 6) Repeat this on a piece of scrap paper. Carefully cut out the triangle. Put a pen point on point at P see if the triangle balances. Extension: The “altitude” is the line from a corner of a triangle which intersects the opposite side at 90° Do all 3 altitudes of a triangle meet? Construct a Square 1) Construct a circle. Mark the centre C 2) Use a ruler to mark two opposite points on the circle edge (mark A & B) Check AB passes through C C 3) Perpendicular bisect line AB . 4) Where the perpendicular bisector crosses the circle mark D & E 5) Join ADEB to make a square Extension: Can you find a different way to make a square only using a compass and straight edge? Construct an octagon Can you now make an octagon (8 sides) using the square as a starting point? Parallel Lines ARC METHOD 1) Put compass point at P Adjust the compass to reach JUST to line AB Keep the compass the same. 2) Now put the compass point on line AB and arc above the line. Repeat several times 3) Rule a line connecting the tops of the arc’s P . A Can you find another different way to construct parallel lines? Gamma p151 p153 Ex 9.1 Hw p71 Ex 17.01 B RHOMBUS METHOD 1) Put compass point at P Adjust the compass to reach OVER to line AB Mark this point E Keep the compass the same for all steps. P A . 2) Put compass point at E Arc across line AB again. Mark this point F B 3) Put compass point at P and arc into “space” roughly parallel to line AB A 4) Put compass point at F and arc To cross the arc in step 3) Mark this point Q P . 5) Rule a line through P and Q. This should be parallel to AB B Construct a Hexagon 1) Construct a circle Keep the compass the same. 2) Mark point P anywhere on the circle. Put compass point on P and arc on the circle point Q 3) Put compass point on Q and arc on the circle again. 4) Repeat until you go around the circle 5) Join the arc points to form a hexagon. Construct a dodecagon Can you now make an dodecagon (12 sides) using the hexagon as a starting construction? C . Extension: A pentagon 1) Construct a circle. Mark the centre C 2) Use a ruler to mark two opposite points on the circle edge (mark A & B) Check AB passes through C 3) Perpendicular bisect line AB. Where the perpendicular bisector crosses the circle mark D & E 4) Find the midpoint of BC, Label it N 5) Put the compass point on N. Adjust the compass to reach C. Construct a circle 6) Find the midpoint of AC, Label it M 7) Put the compass point on M. Adjust the compass to reach C. C. Construct a circle 8) Put the compass point on D. Adjust the compass just reach the circles in step 5) and 7) Construct a circle 9) Mark the two points where this circle cuts the original circle. Adjust the compass to this length. Keep the compass the same. 10) Arc around the original circle using this compass setting. Joining these points should form a regular pentagon NAME _______________________________ Angle bisect these angles Perpendicular bisect these lines





















![PH_Geo_3-8_Constructing_parallel_lines[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001202465_1-91ca6e9d9e8948ba2229cefd106376ad-150x150.png)