* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 1.6- Basic Constructions Essential Question: How can we
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
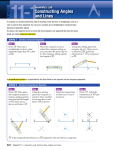
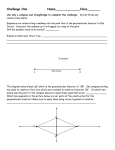
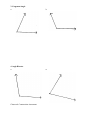
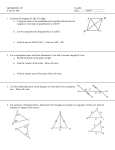
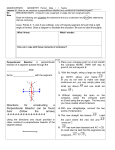
Section 1.6- Basic Constructions Essential Question: How can we use special geometric tools to make more accurate figures? Do Now: How is ̅̅̅ 𝐺𝐽 related to ∠ FGH? Vocabulary Review Perpendicular- two lines that intersect to form _________ angles Symbol Diagram of Perpendicular Lines Perpendicular bisector- bisects a line segment and forms two _____________ parts o Can be a ________, _____________, or _______ that is perpendicular to the segment at its __________ Circle the figure that correctly shows a perpendicular bisector. Construction- the making of a geometric figure using only a ________________ and a __________________ (no ruler or protractor) Construction #1- Congruent Segments Objective: To construct a segment congruent to the given segment. Steps: ̅̅̅̅ Given: 𝑨𝑩 1. Draw a ray with endpoint C. 2. Open the compass to the length of ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 . 3. With the same compass setting, put the compass point on C. Draw an arc that intersects the ray. Label the point of intersection D. Result: __________ ≅ __________ Construction #2- Congruent Angles Objective: To construct an angle congruent to a given angle. Steps: 1. Draw a ray with endpoint S. 2. With the compass point on A, draw an arc that intersects the sides of ∠A. Label the points of intersection B and C. 3. With the same compass setting, put the compass point on point S. Draw an arc that intersects the ray at point R. ̅̅̅̅ . 4. Open the compass to the length of 𝐵𝐶 Keeping the same compass setting, put the compass point on R. Draw an arc to determine point T. 5. Draw ⃗⃗⃗⃗ 𝑆𝑇. Result: ∠ ________ ≅ ∠ _________ Given: ∠A Construction #3: Perpendicular Bisector Objective: Construct the perpendicular bisector of a segment. Steps: Given: ̅̅̅̅ 𝑨𝑩 1. Put the compass point on point A and draw an arc greater than half the length of the segment given. 2. Keep the same compass setting, put the compass point on point B and draw an arc. Label the points where the two arcs intersect as X and Y. ̅̅̅̅ 3. Draw line XY. Label the intersection of 𝐴𝐵 and ⃡⃗⃗⃗⃗ 𝑋𝑌 as point M. Result: ________ is the perpendicular bisector of _______. Point M is the _____________ of the given segment. Construction #4: Angle Bisector Objective: Construct the bisector of an angle. Steps: 1. Put the compass point on vertex A. Draw an arc that intersects the sides of ∠A. Label the points of intersection B and C. 2. Put the compass point on point C and draw an arc. Keep the same compass setting and repeat with point B. Be sure the arcs intersect. Label the point where the two arcs intersect as point X. ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ . 3. Draw 𝐴𝑋 Result: ________ is the angle bisector of ∠CAB Given: ∠A Construction Practice 1. Congruent Segment a. b. 2. Segment Bisector a. b. 3. Congruent Angle a. b. 4. Angle Bisector a. Classwork: Construction Assessment b.







![PH_Geo_3-8_Constructing_parallel_lines[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001202465_1-91ca6e9d9e8948ba2229cefd106376ad-150x150.png)