* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2: Geography
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
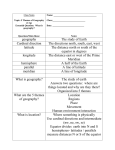
Unit 2: Geography Things to Remember… All items in RED will be on the test! Don’t forget the vocabulary list at the end! Be sure to study the PowerPoint presentations…they are your study guide for the test! What is Geography? Geography is the study of places and the relationships between people and their environments. The study of Earth and everything on it. Geography seeks to understand where things are found, why they are there, and how they develop and change over time. What do Geographers do? Geographers explore both the physical properties of Earth’s surface and the human societies spread across it. They also examine how human culture interacts with the natural environment and the way that locations and places can have an impact on people. Locations Locations can be broken down into continents, countries, states, provinces, counties, cities and towns. Example: Someone could live in North America, in the United States, in California, in Orange County and in the town of Newport Beach. Locations There are 7 continents on Earth: Africa Antarctica Asia Australia Europe North America South America Locations There are 5 major bodies of water on Earth: Atlantic Ocean Pacific Ocean Indian Ocean Arctic Ocean Southern Ocean The Continents and Major Bodies of Water on a Map You NEED to know all of these and where they are located on a map for Assessment 3! Hemispheres To find a place on the Earth, geographers use a system of imaginary lines that crisscross the globe. The equator divides the Earth into two halves: the north and south hemispheres. Everything north of the Equator is in the Northern Hemisphere Everything south of the equator is in the Southern Hemisphere Hemispheres Another imaginary line is the Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian splits the Earth into East and West Hemispheres. Everything East of the Prime Meridian is the Eastern Hemisphere Everything West of the Prime Meridian is the West Hemisphere North, South, East and West Hemispheres on a Map Finding Places on Earth So why do we use these different lines? The Equator and Prime Meridian are used by geographers to find places on Earth when using maps or globes. The Equator and Prime Meridian are only two of the many lines used to find places on Earth. All of the lines used are called latitude and longitude. Lines of latitude and longitude cross each other, forming a pattern called a grid system. Latitude and Longitude on a Map This is a Mercator Projection where land and distance are quite distorted but help to show the grid system. Maps vs. Globes A globe is a spherical scale model of the planet The most accurate way to show the Earth A globe best shows the sizes of continents and the shapes of landmasses and bodies of water Globes also show true distance and direction Maps vs. Globes Maps are flat drawings of all or part of the Earth’s surface Maps are more convenient to carry around than globes Maps can show small areas in great detail Maps can show political borders, population densities, area resources, etc. Maps cannot show true size, shape, distance and direction at the same time It is because of this that we use various projections Maps vs. Globes Projections are ways of showing the Earth on a flat sheet of paper. Each kind of projection shows the Earth’s surface in a slightly different way. We use different types of projections depending on the goal. If we want to compare land areas amongst continents, we would use a different projection than if we wanted to study the sizes and shapes of the continents. Maps vs. Globes Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Therefore, someone who makes various maps and projections would be a Cartographer. Physical Map: Shows land and water features Political Map: Shows names and borders of countries Special Purpose Map: a map that shows specific themes or patterns such as climate, natural resources or population. Cardinal Directions Cardinal directions are how we describe relative location of any place on Earth. The four cardinal directions are: North South East West This is a Compass Rose: It is used on a map to tell you the position of the cardinal directions. Hint: You need to know what a Compass Rose looks like for your test! Scale: a measuring line used to show distances on a map Hint: You need to know what a scale looks like! That is a scale! Population and Migration Population refers to how many people live in a specific area or place. Example: There is a population of over 65,000 people who live in Homestead, Florida! Populations don’t stay the same forever due to migration. Migration is the movement of people from one place to settle in another place. Throughout history there have been many migrations of human beings. Choropleth: a special-purpose map that uses color to show population density Culture What is culture? Culture is a set of beliefs, behaviors, and traits shared by the members of a group. What does culture have to do with geography? We can sometimes see on a map where specific cultures are more prevalent. However, with the passing of history, we have seen more and more cultural diffusion. Cultural diffusion means a group shares part of its culture with another group. An example of cultural diffusion would be the mixing of Christmas and Hanukkah. Fun Fact The oldest known map was found in 1993 by archaeologists in a cave in northern Spain. The small stone tablet only measures 7 inches by five inches. It is engraved with what appears to be symbolic representations of landscape features such as mountains and rivers. Scientists estimate that the map is almost 14,000 years old! The Five Themes of Geography The Five Themes of Geography 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Location Place Human-Environment Interaction Movement Regions 1. LOCATION: Where is it? Why is it located there? Absolute Location Is given in degrees of latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). Paris, France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. Relative Location Relative location depends upon point of reference. Eg. near, far, a short drive. Described by landmarks, time, direction or distance. From one place to another. You are here Where are you?! 2. PLACE: What is it like? Physical Characteristics Landforms (mountains, plains, etc.), bodies of water (oceans, lakes, bays, etc.), ecosystems (soil, plants, animals, and climate) Human Characteristics Bridges, roads, buildings, culture, languages, beliefs. All places have features that distinguish them from other places. 3. HUMAN-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION How do people interact with and change their environment? We depend on the environment. Ex. People depend on rivers for water and transportation. We adapt to the environment. Ex. We adapt to the environment by wearing clothing suitable for summer (shorts) and winter (coats), rain and shine. We modify the environment. Ex. People modify their environment by heating and cooling buildings for comfort. 4. MOVEMENT How are people and places linked by communication and the flow of people, products and information/ideas? Movement of People Cars, Trucks, Trains, Planes Movement of Products Cars, Trucks, Trains, Planes Movement of Information/ideas Phones, computer (email), mail TV, Radio, Magazines 5. REGIONS What are regions and how are they useful? Regions can be defined on the basis of physical and human characteristics Geographers divide the world into regions to help them interpret information. Need Help Remembering? If you can’t remember what they are just ask MR. HELP!!! M – Movement R – Regions HE – Human Environment interaction L – Location P - Place PRACTICE: Discuss the 5 THEMES in this picture. • Location • Place • Human Environment Interaction • Movement • Region PRACTICE: Discuss the 5 THEMES in this picture. Location Place Human Environment Interaction Movement Region Vocabulary Terms Hemisphere: used to refer to one-half of the globe when divided into North and South and East and West Latitude: Imaginary lines that circle the Earth parallel to the Equator Longitude: Imaginary lines that circle the earth from Pole to Pole, measuring distance east or west of the Prime Meridian Projection: a way of showing the round earth on a flat map Physical Map: a map that shows land a water features Political Map: a map that shows the names and borders of countries Special-Purpose Map: a map that shows themes or patterns such as climate, natural resources, or population. Scale: a measuring line that show the distances on a map Cardinal Directions: north, south, east and west Choropleth: a special-purpose map that uses color to show population density Migration: the movement of people from one place to settle in another place Culture: the set of beliefs, behaviors, and traits shared by a group of people Climate: the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period