* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s Laws
Frictional contact mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
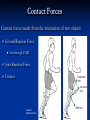
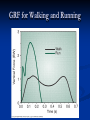
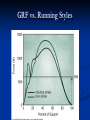
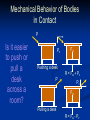
Physics 160 Biomechanics Newton’s Laws Questions to Think About Why does it take more force to cause an object to start sliding than it does to keep it sliding? Why is a ligament more likely to tear during rapid ankle inversion than during slow inversion? When spotting a bench press, why do you assist more on the way up than on the way down? Newton’s Laws Developed by Sir Isaac Newton (1642 – 1727) Define the mechanical basis of linear kinetics Newton’s First Law The Law of Inertia “A body will maintain a state of rest or constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force.” Mass is lazy Newton’s 2nd Law The Law of Acceleration A force applied to a body causes an acceleration of that body of a magnitude proportional to the force, in the direction of the force, and inversely proportional to the body’s mass. Fnet = ma Fnet = vector sum of all forces in [ N ] m = mass in [kg ] a = acceleration in [m / s ] 2 Example Lance Berkman swings his bat at a fastball. The impact of the bat on the ball gives it an acceleration of 9000 m/s2. What was the force exerted by the bat at impact if the ball has a mass of 0.25 kg Newton’s Third Law: The Law of Action & Reaction “When one body exerts a force an another, the second body exerts a reaction force on the first that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.” R OR A “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” Example Tonya crashes into Nancy while they are practicing their figure skating routines. Tonya’s mass is 60 kg, and Nancy’s mass is 50 kg. During the collision, Tonya exerts an average force of 1000 N against Nancy. How big is the average force Nancy exerts against Tonya during the collision? If this is the only horizontal force acting on each skater during the collision, what average horizontal acceleration does each skater experience during the collision? Force of Gravity The attractive force of the earth on an object. The force of gravity equals the weight of the object. Fw= mg Fua Fla Contact Forces Contact forces result from the interaction of two objects Ground Reaction Force Acts through COM Joint Reaction Force Friction Ground Reaction Force Ground Reaction Force (GRF) • The reaction force produced by individuals when walking, running, etc. As foot contacts the ground it produces a reaction force. A GRF Ground Reaction Force Vertical GRF during a landing from a jump GRF for Walking and Running GRF vs. Running Styles Magnitude of Vertical GRF Walking = 1 to 1.2 X Body Weight Running = 3 to 5 X Body Weight Squats = up to 7.6 X Body Weight at patello-femoral joint GRF Components GRF for walking Note the difference in magnitude between the vertical component and the shear components If stride length increases too much, the horizontal component (Fx) of the Ground Reaction Force (GRF) will tend to increase, retarding forward motion. Fx Fx GRF Fx x Fy GRF Fy Joint Forces Joint reaction forces will be different than the externally applied forces Muscle contraction also creates force across a joint Joint contact forces result from bone-on-bone contact Fig. 3.24 Resistance Friction Force to motion as a result of two bodies being in contact Static – force that must be overcome to initiate motion Kinetic – force that must be overcome to sustain motion Is Friction Good or Bad? Good… Feet on pavement while walking, running, or standing Bad… Skin against pavement while falling Frictional Coefficients Ff Friction force µ = Normal reaction force R µ k = Coefficient of Kinetic Friction µ s = Coefficient of Static Friction Ice on ice μk=0.03 (unitless) Cartilage on cartilage μk=0.002 Jogging shoes on artificial track μs=0.7-1.1 Normal Reaction Force Force due to the surface pushing on an object. It is always normal or perpendicular to the surface and points away from the surface applied force weight friction R=Normal reaction force Friction Force A theoretical representation of friction force as a function of the applied force. The applied force increases with the friction force until motion occurs. Mechanical Behavior of Bodies in Contact P Is it easier to push or pull a desk across a room? Pv Fw Pushing a desk R = Fw + Pv P Pv Fw Pulling a desk R = Fw - Pv Example A football player pushes a 590 N blocking sled. The coefficient of static friction between sled and grass is 0.73, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between sled and grass is 0.68. How much force must the player exert to start the sled in motion? How much force is required to keep the sled in motion? Repeat for a 100 kg coach on sled. Rolling Friction Between rolling object and surface bicycle tire and surface bowling ball and surface Rolling friction is 100 to 1000 times less than sliding friction Example Jay is gliding north on his crosscountry skis across a flat section of snow at 7 m/s. Jay’s mass is 100 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the skis and the snow is 0.10. What is Jay’s horizontal acceleration?