* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Crust
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
3D fold evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Paleostress inversion wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
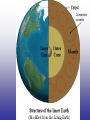
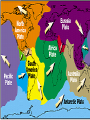
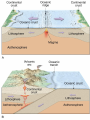
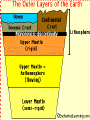
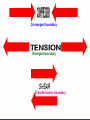
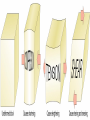
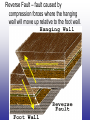
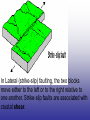
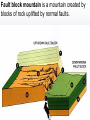
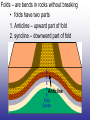
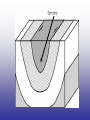
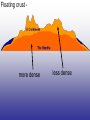
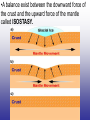
Earth’s Crust Convection currents Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. Ocean floor spreading – theory that hot less dense material below Earth’s crust rises toward the surface at the mid-ocean ridges. Then, it flows sideways, carrying the seafloor away from the ridge in both directions. http://geology.com/nsta/divergent-boundary-oceanic.gif Convection current – unequal distribution of heat in the mantel causes a net movement in a circular motion. The Earth’s CRUST is the outer most part of the Earth’s surface. • Average 32 km thick • Thickest point 70 km (in mountains) • Thinnest point 8 km (under ocean) Plate tectonic – theory that Earth’s crust and part of the upper mantle are broken into sections called plates. Lithosphere – all of the earth’s crust and part of the upper mantle. http://www.allaboutspace.com/subjects/astronom y/planets/earth/Inside.shtml Asthenosphere – plastic like layer below the lithosphere. The ridged plates of the lithosphere “float” on the more plastic layer called the asthenosphere. l Deformation – The breaking, tilting, and folding of crustal rock due to crustal movement. (three types of forces) 1. Compression – squeezing of earth’s crust that compacts the rock. Convergent boundary 2. Tension – is the pulling apart of the earth’s crust. Divergent boundary. 3. Shearing – pushes rocks side by side in opposite directions. Transform boundary. Convergent boundary Divergent boundary Transformation boundary Rift valley subduction FAULTS Normal Fault – fault caused by tension stress that moves the hanging wall down relative to the foot wall. Reverse Fault – fault caused by compression forces where the hanging wall will move up relative to the foot wall. In Lateral (strike-slip) faulting, the two blocks move either to the left or to the right relative to one another. Strike-slip faults are associated with crustal shear. Thrust Fault – is formed when compression causes the hanging wall to slide over the foot wall. (almost horizontal movement) Facts about folds/faults. 1. increased temp. =‘s fold 2. decreased temp =‘s fault 3. increased pressure =‘s fold 4. decreased pressure =‘s fault 5. rock type – brittle =‘s fault 6. rock type – ductile =‘s fold 7. time – greater the time =‘s fold 8. time – less time =‘s fault Fault block mountain is a mountain created by blocks of rock uplifted by normal faults. Rift Valley are valleys created when a block of land between two normal faults slide downward. • End of chapter 10 Folds – are bends in rocks without breaking • folds have two parts 1. Anticline – upward part of fold 2. syncline – downward part of fold Anticline Plateau – is a large area of flat land that is raised high above sea level. Usually bordered by cliffs or mountains. Domes – is the uprising area caused by magma Floating crust - more dense less dense •A balance exist between the downward force of the crust and the upward force of the mantle called ISOSTASY.