* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sun Test Answers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
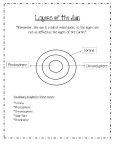
The Sun Name_______________________________ 1. The Sun is about _____________ times the diameter of the Earth a) 25 b) 100 c) 110 d) 125 2. The visible surface of the Sun is about ____________°F a) 5500 b) 10000 c) 28000 d) 60000 3. The core temperature of the Sun is about ____________°F a) 15 000 000 b) 27 000 000 c) 50 000 000 d) 100 000 000 4. The Sun is relatively rich in heavier elements. a) true b) false 5. The Sun was born about ___________years ago. a) 1.2 billion b) 4.6 billion c) 10 billion d) 15 billion 6. The life expectancy of our star is a) 1.2 billion b) 4.6 billion c) 10 billion d) 15 billion 7. Light from the core gets scattered in the ____________ zone, so that a single photon may take 100000+ years to pass through. a) convective b) corona c) chromosphere d) radiative 8. The lowest layer of the solar atmosphere from where light we see is emitted. a) chromosphere b) convective zone c) radiative zone d) photosphere 9. The chromosphere is made up of a) solar convection cells b) granulation cells c) spicules d) photons 10. The hottest layer of the solar atmosphere a) corona b) photosphere c) chromosphere d) transition region 11. The sun is made up of mostly a) hydrogen and oxygen b) hydrogen and helium c) carbon, hydrogen and oxygen d) helium and oxygen 12. Emerge where dense bundles of magnetic field lines break through the sun’s surface. a) spicules b) photons c) sunspots d) granulation cells 13. The number of sunspots is a constant number once the sunspot cycle begins. a) true b) false 14. Sunspots first appear at a) higher latitudes b) higher longitudes c) lower latitudes d) lower longitudes 15. Over the course of a sunspot cycle, the sunspots tend to move a) away from the equator b) toward the equator c) along the same east west path 16. The sunspot cycle last about a) 11 weeks b) 11 months c) 11 years d) 22 years 17. The polarity of sunspots is the same in both the northern and the southern solar hemispheres. a) true b) false 18. Shows the magnetic fields in the solar photosphere with black and white representing different polarities. a) Lasco C2 images b) Lasco C3 images c) SDO/HMI Continuum d) SDO/HMI Magnetogram 19. Shows the inner solar corona up to 5.25 million miles away from the sun. a) Lasco C2 images b) Lasco C3 images c) SDO/HMI Continuum d) SDO/HMI Magnetogram 20. The image produced by the Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT) of the hottest material is taken at ____________Angstroms. a) 171 b) 195 c) 284 d) 304 21. Looks very much like the sun in the visible spectrum. Sunspots are visible in this image. a) Lasco C2 images b) Lasco C3 images c) SDO/HMI Continuum d) SDO/HMI Magnetogram 22. By analyzing the sound waves that move through the sun’s interior, we are able to determine what’s happening inside the Sun. The study of these waves is called a) heliogeology b) heliocosmology c) heliotopology d) helioseismology 23. If the Sun produces a low frequency (low sounding) note, the information is coming from a) the surface of the sun b) slightly below the surface of the sun c) deep within the sun d) slightly above the surface of the sun 24. The core is made up of a gaseous soup of charged particles we call a) photons b) plasma c) spicules d) positrons 25. This same gaseous soup of charged particles is found in lightning. a) true b) false 26. In the core, protons fuse together and release small packets of heat and light called a) photons b) plasma c) spicules d) positrons 27. This gaseous soup of charged particles is made up of what two elementary particles? a) protons and electrons b) protons and neutrons c) neutrons and electrons d) positrons and electrons 28. The balance between the outward pressure of nuclear reactions in the core and inward pressure of gravity. a) stellar equilibrium b) hydromorpic equilibrium c) hydroponic equilibrium d) hydrostatic equilibrium 29. The second layer moving outward from the sun’s core. a) radiative zone b) chromosphere c) corona d) convective zone 30. The coolest of the regions listed a) corona b) core c)convective d) radiative 31. Photons take about ____________to move through the convective zone a) 100 000+ years b) 30 months c) 30 weeks d) 30 days 32. The “random walk” describes the movement of photons through the a) radiative zone b) convective zone c) transition zone d) core 33. The motion of matter in a lava lamp is similar to the motion of photons in the a) radiative zone b) convective zone c) transition zone d) core 34. The rising and sinking of plasma at the Sun’s surface produces the property known as a) granulation b) spicules c) coronal mass ejections d) solar flares 35. As the magnetic field lines emerge from the solar surface and twist, they may touch, short circuit, explode and produce a) granulation b) spicules c) coronal mass ejections d) solar flares 36. Crossing magnetic field lines can fling nets of plasma into space. These are known as a) granulation b) spicules c) coronal mass ejections d) solar flares 37. Needed for the sun to produce a magnetic field. a) movement of photons through the radiative zone b) movement of photons through the convective zone c) movement of plasma through the radiative zone d) movement of plasma through the convective zone 38. A second factor in the production of the sun’s magnetic field. a) differential rotation in the sun’s layers b) differential rotation in the sun’s corona c) differential rotation in the sun’s core 39. Light from the sun reaches earth in about a) 100 000+ years b) 30 weeks c) 30 days d) 8 minutes and 20 seconds 40. Label the diagram below solar flares photosphere convective zone corona radiative zone sunspots core chromosphere