* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular Services Study Guide
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
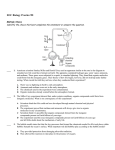
Allied Health and Medicine Study Guide Cardiovascular Services True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The period of ventricular contraction in the heart is called diastole. 2. The smallest branches of arteries are called arterioles. 3. Capillaries allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through to body cells. 4. Hypotension is high blood pressure. 5. Congestive Heart Failure occurs when the heart is weak and cannot pump blood efficiently. 6. The purpose of cardiac rehabilitation is to learn new things about the heart. 7. The red blood cells carry the oxygen in our blood. 8. During diastole, the atria are filling with blood and the ventricles contract. 9. The movement of the electrical impulse in the heart can be used to detect abnormal activity or disease. 10. Hemoglobin carries both oxygen and carbon dioxide. 11. Arteriosclerosis is a ballooning out of, or saclike formation on, an artery wall. 12. An embolus is a foreign substance circulating in the bloodstream. 13. Sickle cell anemia is a chronic, inherited anemia that occurs almost exclusively among African Americans. 14. Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms and can be mild to life threatening. 15. Angioplasty may be used to remove or compress deposits in arteries, or to insert a stent to allow blood flow. 16. If hypertension is not treated, it can cause permanent damage to the heart, blood vessels, and kidneys. Multiple Choice Choose the BEST answer of the choices given in each of the following questions. 1. The muscle layer of the heart is the ____. a. endocardium c. ectocardium b. pericardium d. myocardium 2. The chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood as it returns from body cells is the ____. a. right atrium c. left atrium b. right ventricle d. left ventricle 3. The chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood as it returns from the lungs is the ____. a. right atrium c. left atrium b. right ventricle d. left ventricle 4. The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle that prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium is the ____. a. tricuspid valve c. aortic valve b. pulmonary valve d. mitral valve 5. The valve between the left atrium and left ventricle that prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium is the ____. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. a. tricuspid valve c. aortic valve b. pulmonary valve d. mitral valve The blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are the ____. a. arteries c. venules b. veins d. capillaries The blood vessels that contain valves to prevent blood from flowing in a backward direction are the ____. a. arteries c. capillaries b. veins d. arterioles The blood vessels that are more muscular and elastic than are the other blood vessels are the ____. a. arterioles c. capillaries b. venules d. arteries The largest artery in the body is the ____. a. carotid c. aorta b. femoral d. coronary The blood cells that contain hemoglobin are the ____. a. leukocytes c. erythrocytes b. platelets d. thrombocytes The bright red color of blood indicates ____. a. anemia c. hemoglobin-carrying oxygen b. venous blood d. fibrinogen-carrying oxygen The blood cells that fight infection are the ____. a. erythrocytes c. thrombocytes b. leukocytes d. platelets An inherited disease that occurs almost exclusively in males and in which the blood is unable to clot is ____. a. anemia c. hemophilia b. leukemia d. aneurysm An inflammation of a vein with the formation of a clot is ____. a. phlebitis c. embolus b. thrombophlebitis d. varicose veins Which of the following is not a risk factor that increases the incidence of hypertension? a. race c. excessive exercise b. smoking d. obesity The build up of plague on the interior of the artery wall is called: a. anemia c. arteriosclerosis b. heart failure d. embolus Short Answer 1. Label the following diagram of the heart. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. 2. Trace a drop of blood through the heart, to the lungs, and back to the heart. Name the blood vessels carrying the blood, the valves, and all chambers of the heart. 3. Trace the pathway of the electrical impulse in the heart, listing all parts of the pathway in the correct order. 4. Name five things that blood transports through the body. 5. What is the disease that occurs when fatty plaques are deposited on the walls of arteries? 6. List three treatments that can be used to control hypertension. Allied Health and Medicine Study Guide Cardiovascular Services Answer Section TRUE/FALSE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: F T T F T F T F T T F T T T T T PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: D A C A D A B D C C C B C B C C SHORT ANSWER 1. ANS: A. pericardium, B. myocardium, C. endocardium, D. septum, E. superior vena cava, F. inferior vena cava, G. right atrium, H. tricuspid valve, I. right ventricle, J. pulmonary valve, K. pulmonary arteries, L. pulmonary veins, M. left atrium, N. mitral or bicuspid valve, O. left ventricle, P. aortic valve, Q. aorta PTS: 17 2. ANS: inferior and superior vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary arteries, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, body cells, venules, veins PTS: 20 3. ANS: sinoatrial (SA) node, pathways in atria, atrioventricular (AV) node, bundle of His, right and left bundle branch, Purkinje fibers PTS: 6 4. ANS: (Any 5 of the following) oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients (vitamins, carbohydrates, proteins, mineral salts or electrolytes), metabolic and waste products, heat, hormones PTS: 5 5. ANS: atherosclerosis PTS: 1 6. ANS: (Any 3 of the following) anti-hypertensive drugs, diuretics, limited stress, avoidance of tobacco, low-sodium and/or low-fat diet PTS: 3