* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14 Respiratory system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
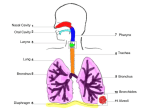
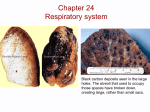
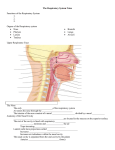
Chapter 24 Respiratory system Black carbon deposits seen in the large holes. The alveoli that used to occupy those spaces have broken down, creating large, rather than small sacs. Figure 24.1 Structures of the Respiratory System Frontal sinus Nasal cavity Nasal conchae Nose Sphenoidal sinus Internal nares Tongue Nasopharynx UPPER RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LOWER RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Hyoid bone Larynx Esophagus Trachea Bronchus Clavicle Bronchioles RIGHT LUNG Ribs LEFT LUNG Diaphragm Figure 24.4a Respiratory Structures in the Head and Neck, Part II Frontal sinus Nasal cavity Superior Middle Internal nares Inferior Nasal conchae Nasopharynx Nasal vestibule Pharyngeal tonsil External nares Entrance to auditory tube Hard palate Soft palate Palatine tonsil Oral cavity Oropharynx Tongue Epiglottis Mandible Aryepiglottic fold Lingual tonsil Hyoid bone Laryngopharynx Thyroid cartilage Glottis Cricoid cartilage Vocal fold Trachea Esophagus Thyroid gland A sagittal section of the head and neck © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 24.4b Respiratory Structures in the Head and Neck, Part II Ethmoidal air cell Medial rectus muscle Cranial cavity Frontal sinus Right eye Lens Lateral rectus muscle Superior nasal concha Superior meatus Middle nasal concha Nasal septum Perpendicular plate of ethmoid Vomer Hard palate Middle meatus Maxillary sinus Inferior nasal concha Inferior meatus Tongue Mandible A coronal (frontal) section of the head showing the positions of the paranasal sinuses and nasal structures Figure 24.2a Histology of the Respiratory Epithelium Movement of mucus to pharynx Ciliated columnar epithelial cell Mucous cell Stem cell Mucous layer Lamina propria Diagrammatic view of the respiratory epithelium Figure 24.5 Respiratory Structures in the Head and Neck, Part III (Part 1 of 1) Inferior nasal concha Hard palate Arbor vitae of cerebellum Choroid plexus Soft palate Foramen magnum External occipital crest Dens of axis (C2) Atlas (C1) (posterior arch) C3 Laryngopharynx Tongue Nasopharynx Uvula Atlas (C1) (anterior arch) Oropharynx Mandible Epiglottis C4 Spinal cord Hyoid bone C5 Ventricular fold C6 Spinous processes of vertebrae C7 Vocal fold Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage T1 Tracheal cartilages Esophagus T2 Trachea T3 External jugular vein Right common carotid artery Manubrium of sternum Aortic arch Pleural cavity Left brachiocephalic vein Body of sternum Figure 24.6a Anatomy of the Larynx Epiglottis Lesser cornu Hyoid bone Thyrohyoid ligament (extrinsic) Thyroid cartilage Larynx Laryngeal prominence Cricothyroid ligament (intrinsic) Cricoid cartilage Cricotracheal ligament (extrinsic) Trachea Tracheal cartilages Anterior view of the intact larynx © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 24.6d Anatomy of the Larynx Hyoid bone Thyrohyoid membrane Epiglottis Thyroid cartilage Vestibular ligament (false vocal cord) Corniculate cartilage Arytenoid cartilage Vocal ligament (true vocal cord) Cricothyroid ligament Cricoid cartilage Cricotracheal ligament Tracheal cartilages ANTERIOR POSTERIOR Sagittal section of the intact larynx Figure 24.7ab The Vocal Cords Corniculate cartilage POSTERIOR Corniculate cartilage Glottis (closed) Cuneiform cartilage Glottis (open) Aryepiglottic fold Vestibular fold Vocal fold Vocal fold Vestibular fold Epiglottis Epiglottis Root of tongue ANTERIOR Glottis in the open position See vocal cords in action!- endoscope NatGeographic- Aerosmith Glottis in the closed position Figure 24.7c The Vocal Cords POSTERIOR Corniculate cartilage Glottis (open) Cuneiform cartilage in aryepiglottic fold Vocal fold Vestibular fold Epiglottis Root of tongue ANTERIOR This photograph is a representative laryngoscopic view. For this view the camera is positioned within the oropharynx, just superior to the larynx. Trachea “windpipe” Figure 24.9a Anatomy of the Trachea and Primary Bronchi Hyoid bone Larynx Annular ligaments Trachea Tracheal cartilages Location of carina (internal ridge) Root of right lung Root of left lung Superior lobar bronchus Lung tissue Primary bronchi Superior lobar bronchus Secondary bronchi Middle lobar bronchus Inferior lobar bronchi RIGHT LUNG LEFT LUNG Anterior view showing the plane of section for part (b) Lower Respiratory tract- Bronchial Tree Figure 24.9b Anatomy of the Trachea and Primary Bronchi Esophagus Trachealis muscle Lumen of trachea Thyroid gland Respiratory epithelium Tracheal cartilage The trachea Histological cross-sectional view of the trachea showing its relationship to surrounding structures LM 3 Figure 24.13a Trachea Left primary bronchus Secondary bronchus Tertiary bronchi Smaller bronchi Bronchioles Terminal bronchiole Respiratory bronchiole Alveoli in a pulmonary lobule -Have alveolus The structure of one portion of a single pulmonary lobule Alveolar ducts & sacs • We have about 300 million alveoli within the lungs! Surface area for gas exchange is approx. 1500 ft2. • Alveolar sac= bunch of grapes; alveoli: one grape Figure 24.13c Bronchi and Bronchioles Alveolus Alveolar sac Hyaline cartilage plate Bronchiole Smooth muscle Arteriole Epithelial cells Alveolar duct Lumen of a small bronchus Histology of the lung LM 14 Histological section of the lung showing a small bronchus and bronchiole Pleura Figure 24.10a Superficial Anatomy of the Lungs Boundary between right and left pleural cavities Superior lobe LEFT LUNG RIGHT LUNG Superior lobe Oblique fissure Horizontal fissure Middle lobe Fibrous layer of pericardium Oblique fissure Inferior lobe Inferior lobe Anterior view of the opened chest, showing the relative positions of the left and right lungs and heart. Falciform ligament Liver, right lobe Liver, left lobe Cut edge of diaphragm Figure 24.10b Superficial Anatomy of the Lungs Lateral Surfaces Diagrammatic views of the lateral surfaces of the isolated right and left lungs Apex Apex Superior lobe Superior lobe Horizontal fissure Middle lobe Cardiac notch Inferior lobe Oblique fissure Base RIGHT LUNG Oblique fissure Inferior lobe Base LEFT LUNG Disorders of respiratory system Normal Emphysema Clinical Note 24.1 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (Part 2 of 3)