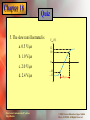
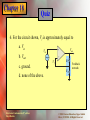
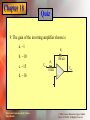
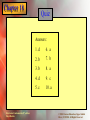
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download V out
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
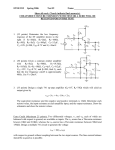
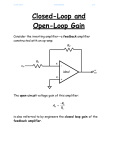
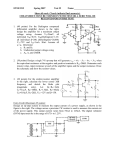
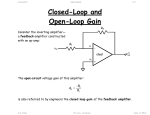
electronics fundamentals circuits, devices, and applications THOMAS L. FLOYD DAVID M. BUCHLA chapter 18 Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary The ideal op-amp The ideal op-amp is one with optimum characteristics, which cannot be attained in the real world. Nevertheless, actual op-amp circuits can often approach this ideal. The ideal op amp has infinite voltage gain, infinite input resistance (open), and zero output resistance. Rin= ∞ Vin AvVin Rout= 0 Vout + Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary The practical op-amp Practical op-amps have limitations including power and voltage limits. A practical op-amp has high voltage gain, high input resistance, and low output resistance. There are two inputs, labeled inverting and non inverting because of the phase relation of the input and output signals. inverting input Rin Vin AvVin Rout non inverting input Vout + Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary The differential amplifier Most op-amps have a differential amplifier (“diff-amp”) as the input stage. The differential amplifier has important advantages over other amplifiers; for example it can reject +VCC common-mode noise. The signal at the collector The signal at the collector of Q1 is inverted. of Q2 is not inverted. RC1 Q1 The input is in single-ended mode. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla RC2 Q2 RE -VEE At the emitters, the signal is ½ of the input. © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Differential and common-mode signals Signals can be applied to either or both inputs. If two input signals are out of phase, they are in differential-mode. If the signals are in phase, they are in common-mode. When the inputs are out of phase, the outputs are amplified and larger than with one input. When the inputs are in phase, the outputs tend to cancel and are near zero. Inputs Inputsout in phase of phase Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla +VCC RC1 Q1 RC2 Q2 RE -VEE © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) Many times, noise sources will induce an unwanted voltage in a signal line. When the noise is induced in commonmode, the differential amplifier tends to cancel it. (The diffamp cannot reject any signal that is in differential mode.) The ability to reject common-mode signals is measured with a parameter called the common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), which is defined as Av ( d ) CMRR Acm Av ( d ) A cm CMRR can be expressed in decibels as CMRR 20log Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) A certain diff-amp has a differential voltage gain of 500 and a common-mode gain of 0.1. What is the CMRR? From the defining equation for CMRR: Av ( d ) 500 CMRR 5000 Acm 0.1 Expressed in decibels, it is Av ( d ) CMRR 20log 20log 5000 74 dB Acm Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) A certain diff-amp has Ad = 100 and a CMRR of 90 dB. Describe the output if the input is a 50 mV differential signal and a common mode noise of 1.0 V is present. The differential signal is amplified by 100. Therefore, the signal output is Vout = Av(d) x Vin = 100 x 50 mV = 5.0 V The common-mode gain can be found by A 100 100 100 Acm v ( d ) 4.5 0.0032 CMRR 90 dB 10 31,600 The noise is amplified by 0.0032. Therefore, Vnoise = Acm x Vin = 0.0032 x 1.0 V = 3.2 mV Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Op-amp parameters Some important op-amp parameters are: Input bias Average of input currents required to bias current: the first stage of the amplifier: I BIAS I1 I 2 2 Differential input Total resistance between the inverting and resistance: non-inverting inputs Common-mode Total resistance between each input and input resistance: ground. Input offset Absolute difference between the two bias current: currents: IOS I1 - I 2 Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Op-amp parameters Output The resistance when viewed from the output resistance: terminal. Common-mode Range of input voltages, which, when applied input voltage to both inputs, will not cause clipping or other range: distortion. Common-mode Ratio of the differential gain to the commonrejection ratio mode gain. The differential gain for the op-amp by itself is the same as its open loop gain. CMRR Av ( d ) Acm Aol Acm Slew rate: The maximum rate of change of the output in response to a step input voltage. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Op-amp parameters Vout (V) What is the slew rate for the output signal shown in response to a step input? 12 10 0 -10 -12 25 ms The output goes from -10 V to +10 V in 25 ms. Slew rate = Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Vout 20 V 0.8 V/ms t 25 ms © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Negative feedback In 1921, Harold S. Black was working on the problem of linearizing and stabilizing amplifiers. While traveling to work on the ferry, he suddenly realized that if he returned some of the output back to the input in opposite phase, he had a means of canceling distortion. One of the most important ideas in electronics was sketched out on his newspaper that morning. The op-amp has a differential amplifier as the input stage. When a feedback network returns a fraction of the output to the inverting input, only the difference signal (Vin – Vf) is amplified. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Vin Vout + Vf Feedback network © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Op amp circuits with negative feedback Negative feedback is used in almost all linear op-amp circuits because it stabilizes the gain and reduces distortion. It can also increase the input resistance. A basic configuration is a noninverting amplifier. The difference between Vin and Vf is very small due to feedback. Therefore, Vin V f . + Vin Vout Vf Rf Ri Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Feedback network The closed-loop gain for the noninverting amplifier can be derived from this idea; it is controlled by the feedback Rf resistors: A 1 cl (NI) Ri © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Op amp circuits with negative feedback The inverting amplifier is a basic configuration in which the noninverting input is grounded (sometimes through a resistor to balance the bias inputs). Again, the difference between Vin and Vf is very small due to feedback; this implies that the inverting input is nearly at ground. This is referred to as a virtual ground. The virtual ground looks like ground to voltage, but not to current! Rf Virtual ground Ri Vin + Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Vout The closed-loop gain for the inverting amplifier can be derived from this idea; again it is controlled by the feedback resistors: A - R f cl (I) Ri © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Input resistance for the noninverting amplifier The input resistance of an op-amp without feedback is Rin. For the 741C, the manufacturer’s specified value of Rin is 2 MW. Negative feedback increases this to Rin(NI) = (1 + AolB)Rin. This is so large that for all practical circuits it can be considered to be infinite. Vin + - Vout Rf Ri Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Keep in mind that, although Rin(NI) is extremely large, the opamp is a dc amplifier and still requires a dc bias path for the input. © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Output resistance for the noninverting amplifier The output resistance of an op-amp without feedback is Rout. Negative feedback decreases this by a factor of (1 + AolB). This is so small that for all practical circuits it can be considered to be zero. Vin + - Vout Rf Ri Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Rout Rout (NI) 1 Aol B The low output resistance implies that the output voltage is independent of the load resistance (as long as the current limit is not exceeded). © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary What are the input and output resistances and the gain of the noninverting amplifier? Assume the op amp has Aol = 100,000, Rin = 2 MW, and Rout = 75 W. The gain is Vin 36 kW Acl (I) 1 1 25 Ri 1.5 kW 1 The feedback fraction is B 0.040 25 Rf + - Vout Rf 36 kW Ri 1.5 kW The input resistance is Rin(NI) 1 Aol B Rin 1+ 100,000 0.040 2 MW = 8 GW Solution continued on next slide… Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary (continued) Vin The last result illustrates why it is rarely necessary to calculate an exact value for the input resistance of a noninverting amplifier. For practical circuits, you can assume it is ideal. + Vout - Rf 36 kW Ri 1.5 kW The output resistance is Rout 75 W Rout (NI) = 0.019 W 1 Aol B 1+ 100,000 0.040 This extremely small resistance is close to ideal. As in the case of the input resistance, it is rarely necessary to calculate an exact value for the noninverting amplifier. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Input resistance for the inverting amplifier Recall that negative feedback forces the inverting input to be near ac ground for the inverting amplifier. For this reason, the input resistance of the inverting amplifier is equal to just the input resistor, Ri. That is, Rin(I) = Ri. Rf Vin Ri + Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Vout The low input resistance is usually a disadvantage of this circuit. However, because the Rin(I) is equal to Ri, it can easily be set by the user for those cases where a specific value is needed. © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Output resistance for the inverting amplifier The equation for the output resistance of the inverting amplifier is the essentially the same as the noninverting amplifier: Rout Rout (I) Rf Vin Ri + Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Vout 1 Aol B Although Rout(I) is very small, this does not imply that an opamp can drive any load. The maximum current that the opamp can supply is limited; for the 741C, it is typically 20 mA. © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Rf What is the input resistance and the gain of the inverting amplifier? Ri Vin 1.5 kW The gain is Acl (I) - Rf Ri - 36 kW -24 1.5 kW 36 kW - Vout + The input resistance = Ri = 1.5 kW The output resistance is nearly identical to the noninverting case, where it was shown to be negligible. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Summary Voltage-follower The voltage-follower is a special case of the noninverting amplifier in which Acl = 1. The input resistance is increased by negative feedback and the output resistance is decreased by negative feedback. This makes it an ideal circuit for interfacing a high-resistance source with a low resistance load. Vin + Vout - Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Selected Key Terms Operational amplifier A special type of amplifier exhibiting very high open-loop gain, very high input resistance, very low output resistance, and good rejection of common-mode signals. Differential amplifier An amplifier that produces an output proportional to the difference of two inputs. Common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla A measure of a diff-amp's or op-amp's ability to reject signals that appear the same on both inputs; the ratio of differential voltage gain or open-loop gain (for op-amps) to commonmode gain. © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Selected Key Terms Open-loop The internal voltage gain of an op-amp voltage gain without feedback. Closed-loop The overall voltage gain of an op-amp with voltage gain negative feedback. Noninverting An op-amp closed-loop configuration in amplifier which the input signal is applied to the noninverting input. Inverting An op-amp closed-loop configuration in amplifier which the input signal is applied to the inverting input. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 1. When two identical in-phase signals are applied to the inputs of a differential amplifier, they are said to be a. feedback signals. b. noninverting signals. c. differential-mode signals. d. common-mode signals. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 2. Assume a differential amplifier has an input signal applied to the base of Q1 as shown. An inverted replica of this signal will appear at the a. emitter terminals. RC1 RC2 b. collector of Q1 c. collector of Q2 d. all of the above. Q1 Q2 RE -VEE Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 3. A differential amplifier will tend to reject a. noise that is in differential-mode. b. noise that is in common-mode. c. only high frequency noise. d. all noise. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 4. The average of two input currents required to bias the first stage of an op-amp is called the a. input offset current. b. open-loop input current. c. feedback current. d. input bias current. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 5. The slew rate illustrated is a. 0.5 V/ms Vout (V) 12 10 b. 1.0 V/ms 0 c. 2.0 V/ms d. 2.4 V/ms Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla -10 -12 10 ms © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 6. For the circuit shown, Vf is approximately equal to a. Vin + Vin - b. Vout c. ground. d. none of the above. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Vout Vf Rf Ri Feedback network © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 7. For the inverting amplifier shown, the input resistance is closest to Rf a. zero b. 10 kW c. 2 MW Vin Ri 10 kW 150 kW - Vout + d. 8 GW Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 8. For the inverting amplifier shown, the output resistance is closest to Rf a. zero b. 10 kW c. 150 kW Vin Ri 10 kW 150 kW - Vout + d. 8 GW Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 9. The gain of the inverting amplifier shown is a. -1 Rf b. -10 c. -15 d. -16 Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla Vin Ri 10 kW 150 kW - Vout + © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz 10. A voltage follower has a. current gain. b. voltage gain. c. both of the above. d. none of the above. Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 18 Quiz Answers: Electronics Fundamentals 8th edition Floyd/Buchla 1. d 6. a 2. b 7. b 3. b 8. a 4. d 9. c 5. c 10. a © 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.