* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Ms. Nancy K. Ware`s US History Classes
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Sino-Vietnamese War wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
McCarthyism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Bay of Pigs Invasion wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Cuban Missile Crisis wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cuban Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
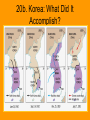
SSUSH 20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States a) b) c) d) Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U.S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine and the origins and implications of the containment policy. Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China, the outbreak of the Korean War, and how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy. Describe Cuban Revolution the Bay of Pigs and the Cuban missile crisis. Describe the Vietnam War, the Tet offensive, and growing opposition to the war. The U.S. & the U.S.S.R. Emerged as the Two Superpowers After WWII The Bi-Polarization of Europe: The Beginning of the Cold War The Iron Curtain: NATO vs. Warsaw Pact • The Iron Curtain symbolized the ideological fighting and physical boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. On either side of the Iron Curtain, states developed their own international economic and military alliances. • Physically, the Iron Curtain took the shape of border defenses between the countries of Europe in the middle of the continent. The most notable border was marked by the Berlin Wall, which served as a symbol of the Curtain as a whole. The Division of Germany: 1945 - 1990 20a. The Start of the Cold War • Marshall Plan~ a financial plan was developed by Secretary of State George C. Marshall to spark economic recovery in war torn Western Europe. The monetary aid helped to stop the USSR & communism from spreading into Western Europe. • The Truman Doctrine ~ the policy started by helping the countries of Greece and Turkey stop Soviet expansion into their countries. Truman’s foreign policy stated the United States would help any country that opposed communism (foreshadow!!) 20a. The Start of the Cold War • Addition to the Truman Doctrine was the Policy of Containment • Containment was a United States policy using military, economic, and diplomatic strategies to temper (stall or stop) the spread of Communism, enhance America’s security and influence abroad, and prevent a "domino effect”. • The policy was a response to a series of moves by the Soviet Union to expand Communist influence in Eastern Europe, China, and Korea • George F. Kennan- developed the philosophy of containment. 20b. Chinese Communist Revolution • The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang (KMT or Chinese Nationalist Party) led by Chiang Kai-shek (US backed) and the Communist Party of China led by Mao Zedong (USSR backed) (CPC). • The war began in April 1927, stopped during WWII, then resumed in 1946. • The war was fought over an ideological split between the Western-supported Nationalist KMT and the Sovietsupported Communist CPC. • The Communists took control and the People's Republic of China emerged after WWII around 1950. 20b. The Rise of Communism • The Korean War- the war started when communist troops from North Korea invaded democratic South Korea. • The United States and the UN aided South Korea, but China became involved when the allied forces invaded North Korea. • The war ended July 27, 1953, • with Korea being divided along the 38th parallel. • • This war accomplished nothing. • Video the Korean War Inside North Korea: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= loyw9eqkPjU&safety_mode=true& persist_safety_mode=1&safe=acti ve http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= 19RLKDfUPyY&feature=endscree n&NR=1&safety_mode=true&persi st_safety_mode=1&safe=active 20b. Korean Conflict (WAR) 1950-1953 20b. Korea: What Did It Accomplish? 20b. The Rise of Communism • Joseph McCarthy was an American politician who served as a Republican U.S. Senator from the state of Wisconsin from 1947 until his death in 1957. • Beginning in 1950, McCarthy became the most visible public face of a period in which Cold War tensions fueled fears of widespread Communist subversion. • He was noted for making claims that there were large numbers of Communists and Soviet spies and sympathizers inside the United States federal government and elsewhere. (especially Hollywood) • Ultimately, McCarthy's tactics and his inability to substantiate his claims led him to be censured by the United States Senate. The term McCarthyism, coined in 1950 in reference to McCarthy's practices, was soon applied to similar anti-communist pursuits. 20b. McCarthyism • Wisconsin Senator Joseph McCarthy was convinced that communist had infiltrated high levels of government and the US military • Eventually he had to defend his accusations in a series of televised hearings. • McCarthyism- ideas and fears of communism voiced by McCarthy and his supporters • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Po5 GlFba5Yg&safety_mode=true&persist _safety_mode=1&safe=active Confrontation with Cuba • In 1960, John F. Kennedy was elected the youngest President of the United States • Kennedy had to continue to deal with the Cold War in his Presidency – the first problem was with Cuba 20c. Cuban Revolution • The Cuban Revolution was an armed revolt that led to the overthrow of dictator Fulgencio Batista’s pro United States government of Cuba on January 1, 1959 by the 26th of July Movement led by Fidel Castro. • The United States, not wanting a Communist country in their backyard imposed economic sanctions • The United States embargo against Cuba (described in Cuba as el bloqueo, Spanish for "the blockade") is a commercial, economic, and financial embargo partially imposed on Cuba in October 1960. It was enacted after Cuba expropriated (confiscated & redistributed) the properties of United States citizens and corporations and it was strengthened to a near-total embargo since February 7, 1962. • Watch the video Confrontation with Cuba • In 1959, Fidel Castro overthrew the Cuban government and became head of the Communist government in Cuba • Castro was receiving aid from the Soviet Union • When Kennedy became President, he learned of a plan, approved by Eisenhower, to overthrow Castro via the CIA 20c. Bay of Pigs Invasion • An unsuccessful attempt by an United States CIA -trained force of Cuban exiles to invade southern Cuba, with support from US government armed forces, to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro and the newly established Communist government. • The plan was launched in April 1961, less than three months after John F. Kennedy assumed the presidency. The Cuban armed forces, trained and equipped by the Soviet Union, defeated the exile combatants in three days. • The failure of this operation was an embarrassment to the Kennedy administration and led to the Cuban Missile Crisis. 20c. Cuban Missile Crisis http://www.cas.sc.edu/hist/Oval OfficeTapes/Cuban%20Missile %20Crisis.htm 20c. Cuban Missile Crisis • The Cuban Missile Crisis was a confrontation between the United States, the Soviet Union, and Cuba in October 1962, during the Cold War. • In September 1962, the Cuban and Soviet governments placed nuclear missiles in Cuba. When United States military intelligence discovered the weapons, the U.S. government did all it could to ensure the removal of the missiles. • The crisis ranks with the Berlin Blockade as one of the major confrontations of the Cold War, and is generally regarded as the moment in which the Cold War came closest to a nuclear war. • Cuban Missile Crisis Video 20c. Cuban Missile Crisis • The US saw this as a direct threat that must be responded to • Kennedy had 4 options: negotiate with Stalin’s successor, Nikita Khrushchev, invade Cuba, blockade Cuba, or bomb the missile sights • Kennedy had a difficult decision to make – the wrong decision could easily lead to nuclear war and possibly even nuclear holocaust • Kennedy decided to blockade Cuba • No one knew what would happen, but as Soviet ships headed for Cuba, they suddenly turned back • However, construction on the bases continued • Khrushchev sent Kennedy a note saying he would remove the missiles if Kennedy would end the blockade 20d. Vietnam War ~ Another Domino • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5KBPgqSgku0&safety _mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active • http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=tGvLGfxaz7Y& feature=endscreen&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_ mode=1&safe=active • http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=endscreen&v=jkNG_8HuUI&NR=1&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_ mode=1&safe=active • http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=endscreen&v=m K0qZuZOT0E&NR=1&safety_mode=true&persist_safety _mode=1&safe=active 20d. Vietnam War ~ the 10,000 day War • The Vietnam War was fought from 1957-1975. • The US backed the democratic forces of South Vietnam • Communist North Vietnam (NLF, or Viet Cong), supported by the Soviet Union. • The Tet Offensive was a military campaign during the Vietnam War that began on January 31, 1968. • The purpose of the offensive was to strike military and civilian command and control centers throughout South Vietnam and to spark a general uprising among the population that would then topple the Saigon government, thus ending the war in a single blow. This turned the tide of public opinion against the war. Opposition to Vietnam http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=endscreen&v=KnnLrmboOYE&NR=1&safety_mo de=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active The United States became deeply divided on the Vietnam War. This was the 1st war in the history of the United States that was so openly protested by so many. • 50,000 anti-war demonstrators who marched on Washington • firing on students at Kent State by the National Guardsmen • Daniel Ellsberg leaking a secret study on the war to the press. Vietnam War Memorial, Washington DC Mini Assessment Questions President Truman issued the Truman Doctrine in response to a. Soviet aggression in Poland b. Pressure by communist in Greece and Turkey c. Churchill’s Iron Curtain Speech d. Stalin’s demands at Potsdam Conference 1. 2. a. b. c. d. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? To help the United States buy its way into European Affairs. To create stable democracies that could resist communism. To establish strong trading partners in Asia. To force the Soviet Union to allow more emigration. 3. a. b. c. d. What was the final resolution of the Korean War? North gained control South gained control Dividing line moved north Dividing line stayed about the same Mini Assessment Answers President Truman issued the Truman Doctrine in response to a. Soviet aggression in Poland b. Pressure by communists in Greece and Turkey c. Churchill’s Iron Curtain Speech d. Stalin’s demands at Potsdam Conference 2. a. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? To help the United States buy its way into European Affairs. b. To create stable democracies that could resist communism. c. d. To establish strong trading partners in Asia. To force the Soviet Union to allow more emigration. 3. a. b. c. What was the final resolution of the Korean War? North gained control South gained control Dividing line moved north d. Dividing line stayed about the same