* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the respiratory system
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
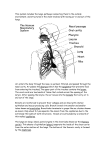
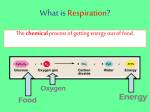
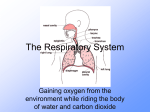
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM “Every Breath You Take” RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The four main functions: Controls blood pH Delivers oxygen to body and removes carbon dioxide as waste Defends the body against invading microbes Produces sounds RESPIRATORY SYSTEM THORACIC CAVITY: location of respiratory organs PLEURA: contains a lubricating fluid that allows lungs to expand and recoil smoothly NASAL and ORAL CAVITIES Warms air up to body temperature (37oC) Contains mucus producing cells that trap dirt, debris and microbes. Contains nose hairs and cells with cilia that also trap dirt and debris found in air. TRACHEA A long tube made up of cartilage that runs from the oral cavity to the lungs Contains mucus secreting cells and cells with cilia that trap dirt and debris and microbes. TRACHEA Contains the LARYNX which contains the vocal chords that allow us to make sounds. Protected by the EPIGLOTTIS; a structure that keeps food from entering the trachea. BRONCHI The two branches of the trachea Contains mucus secreting cells and cilia BRONCHIOLES Branches of the bronchi Also contains mucus secreting cells and cilia ALVEOLI The location of gas exchange between air and the blood Tiny air sacs that are very thin and are found at the end of the bronchioles Each cluster is surrounded by a network of capillaries Gas exchange occurs by DIFFUSION GAS EXCHANGE Deoxygenated blood flows form heart to lungs through capillaries Blood has large carbon dioxide concentration and small oxygen concentration while the alveoli is opposite Gas diffuses across its concentration gradient Oxygenated blood returns to heart to be circulated DIAPHRAGM A thin muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity INHALATION Diaphragm moves down Chest cavity moves up and out Volume in the cavity increases, as pressure in the cavity decreases INSPIRATION: air rushes in EXHALATION Diaphragm moves up Chest cavity moves down and in Volume in the cavity decreases, as pressure in the cavity increases EXPIRATION: air rushes out TERMS TO KNOW TIDAL VOLUME: amount of air that passes in and out of lungs with each breath TOTAL LUNG CAPACITY: maximum volume of air that can be held in lungs VITAL CAPACITY: maximum amount of air that can be moved into and out of the lungs DISEASES ASTHMA: a chronic disease characterized by inflammation and swelling of the bronchi and bronchioles that obstructs airflow CYSTIC FIBROSIS: an over production of unusually thick mucus that clogs the airways INFECTIONS INFLUENZA: caused by the flu virus TUBERCULOSIS: a bacterial infection that damages the tissues of the lungs and interferes with gas exchange PNEUMONIA: an infection of the lungs that causes the alveoli to fill with pus and mucus