* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 28 Animal Systems II
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
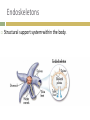
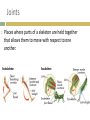
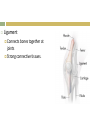
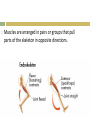
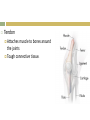
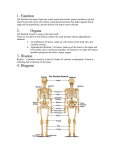
1. Apply Concepts How do muscles enable movement CH 28 ANIMAL SYSTEMS II 28.2 Movement and Support 1. 2. To move all animals must: Generate physical force Apply that force against air, water, or land in order to push or pull themselves around. Animals have three main kinds of skeletal systems: Hydrostatic skeletons Exoskeletons Endoskeletons. Hydrostatic Skeletons Consists of fluids held in a gastrovascular cavity Alters the body’s shape drastically by working with contractile cells in its body wall Cnidarians and annelids. Hydra closes its mouth and the cells encircling its body wall constrict Elongates and its tentacles extend Mouth opens, allowing water to flow out, and longitudinal cells in its body wall contract, shortening the body. Exoskeletons External skeleton usually made of chitin or calcium carbonate Many arthropods and most mollusks Jointed exoskeletons allow to swim, fly, burrow, walk, crawl, and leap May be water tight Offer protection from predators. Molting Breaking out of their exoskeleton and grow a new one to allow for growth Relatively heavy especially in large arthropods. Endoskeletons Structural support system within the body. Vertebrates have an endoskeleton made of cartilage or a combination of cartilage and bone Sharks and some other fishes have skeletons made entirely of cartilage Girdles Support limbs and allow for movement. Cannot protect an animal the way that an exoskeleton can Internal skeleton can grow as an animal grows, so the animal does not need to molt Lighter weight than exoskeleton. Joints Places where parts of a skeleton are held together that allows them to move with respect to one another. Ligament Connects bones together at joints Strong connective tissues. Muscles and Movement Specialized tissues that produce physical force by contracting when stimulated Muscles relax when they aren’t stimulated Generate force in only ONE direction. Muscles are arranged in pairs or groups that pull parts of the skeleton in opposite directions. Tendon Attaches muscle to bones around the joints Tough connective tissue. Exoskeleton Muscles are attached to the inside of the exoskeleton Endoskeleton Muscles are attached around the outside of bones. Vertebrate Muscular and Skeletal Systems The shapes and relative positions of bones, muscles, and joints are linked very closely to the functions they perform Many very different arrangements Many very different kinds of movement.