* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quadratic formula and complex numbers
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Numerical continuation wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic reciprocity wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Number theory wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic form wikipedia , lookup
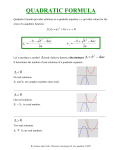
Simplifying a Radical Review Simplify each radical and leave the answer in exact form. 1. 48 16 3 4 3 2. 63 97 3 7 3. 72 36 2 6 2 How many Real Solutions? 2 Complex Solutions Two Real Solutions One Real Solutions How did you determine your answer? Looking at the number of times it touches or crosses the x axis Imaginary unit i • Not all Quadratic Equations have real-number solutions. •To overcome this problem, mathematicians created an expanded system of numbers using the imaginary unit i •The imaginary number i is use to write the square root of any negative number. Definition • For any positive real number b, b 2 b 2 1 b i bi • Modular 4 Pattern i 1 i , 1, i ,1 i 1 1 1 3 2 1 1 i i i 1 1 ( 1) 2 i 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 Example 1 Solve: x²+ 16 = 0 x 16 2 x 16 x 16 2 x 1 16 x i 4 x 4i, 4i Complex numbers Expression that contains a real number and a pure imaginary number in the form (a + bi) 5 + 2i 5 is the real number 2i is the imaginary part. Complex Number System Graphic Organizer Is every real number a complex number? Yes a bi Is every Complex number a real number? NO Rational #’s Irrational # Is every imaginary number a complex number? Yes b0 Imaginary # a=0 Pure Imaginary Non-pure a0 Imaginary Discriminant The expression b²- 4ac is called the Discriminant of the equation ax² + bx + c = 0 From the discriminant we can tell the nature and number of solutions for any given quadratic function. 2 Ex 11: x 4 x 5 2 0 x 4x 5 b 2 4ac a 1 2 ( 4) 4(1)(5) b 4 16 20 c5 4 2 imaginary Solutions Discriminant Graphic Organizer Type One Type Two Type Three Value of the Discriminant: b2- 4ac >0 b2- 4ac = 0 b2- 4ac < 0 Number and Type of Solutions: Two Real One Real Two Imaginary Solutions Solution Solutions Two One No x-intercept x-intercept x-intercept Number of Intercepts: Graph of y ax 2 bx c Example: Find the discriminant. Give the number and type of solutions of the equation. Ex 2: x 8 x 17 0 2 Disc b² - 4ac= (-8)²- 4(1)(17)= -4 -4<0 so Two imaginary solutions Ex 3: x 8 x 16 0 2 Disc (-8)²- 4(1)(16)= 0 0=0 so One real solutions Ex 4: x 8 x 15 0 2 Disc (-8)²-4(1)(15) = 4 4>0 so Two real solutions Quadratic Formula • Objective: – To use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. • Let a, b, and c be real numbers such that a ≠ 0. • Use the following formula to find the solutions of the equation ax² + bx+ c = 0 (Standard Form). b b 4ac x 2a 2 Can you Sing it? Yes you Can! Pop Goes The Weasel! • X equals the opposite of b plus or minus the square root of b squared minus four AC all over 2 A. Parts of the Quadratic Formula ax² + bx + c = 0 b b 4ac x 2a 2 Quadratic Formula Method to find solutions of a quadratic equation. b b 4ac x 2a x-value of the Vertex 2 Discriminant What kind of solutions and how many? Example 5 x 3x 2 2 • Solve using the Quadratic formula x 3x 2 0 2 a 1, b 3, c 2 3 32 4(1)(2) x 2(1) 3 9 8 x 2 3 17 x 2 3 17 3 17 x ,x 2 2 Example 6 25 x 2 18 x 12 x 9 • Solve using the Quadratic formula 25 x 30 x 9 0 2 Standard Form Identify the values of a, b and c a 25, b 30, c 9 Plug Values into the Quadratic Formula 30 (30) 4(25)(9) x 2(25) 2 Simplify under the radical 30 900 900 x 50 Simplify the formula 30 0 x 50 30 x 0 50 Write the Solution(s) 3 x 5 Example 7 • Solve using the Quadratic Formula x 4x 5 2 x 4x 5 0 2 4 16 20 x 2 4 4 x 2 imaginary a 1, b 4, c 5 4 2i x 2 4 (4)2 4(1)(5) x 2(1) 4 2i 4 2i x and 2 2 2 2 4 16 20 x 2 x 2 i, x 2 i Practice 8 • Solve using the Quadratic formula x 6 x 15 x 6 x 15 0 2 2 6 2i 6 x 2 6 62 4(1)(15) x 2(1) 6 36 60 x 2 6 24 x 2 6 2i 6 6 2i 6 x and x 2 2 2 2 x 3 i 6, x 3 i 6 imaginary