* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Classes with Mrs. Sheetz
Survey
Document related concepts
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
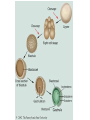
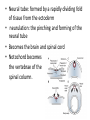
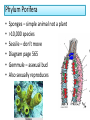
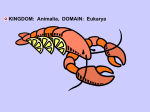
Chapter 26: Kingdom Animalia I Phylum Placozoa Phylum Porifera Overview • Vertebrate: -animal with a backbone -50,000 species • Invertebrate: -animal without a backbone -950,000 species • Classified according to similar structures and functions • Common characteristics for organisms in Animalia: -eukaryotes -reproduce sexually -multicellular -cells organized into tissues -heterotrophic -storage of carbohydrates as glycogen -no cell walls -extracellular matrix -mobile with specialized muscle and nerve tissue -needs oxygen Body Structure and Symmetry • Bilateral symmetry: right half looks like the left half • Radial symmetry: line drawn through middle in any plane results in symmetry (ex: jellyfish – aquatic animals) • Cephalization: high concentration of sensory tissues(eyes, ears, brain) in the anterior region • Directions: ventral/dorsal, anterior/posterior Tissues • A group of cells that all function in a similar way. • Examples in animals: connective, epithelial muscle, and nervous. Germ Layers • Fertilization: haploid egg fuses with haploid sperm and forms diploid zygote. • Mitosis occurs millions of times and the zygote forms an embryo. • Next form germ layers: 1. ectoderm 2. mesoderm 3. endoderm (note: Cnidarians and ctenophores form from only 2 germ layers) Gestation: the developmental period of an organism which begins after fertilization. Segments • Most animals show a repeating unit -called segmentation Coelom • Presence of a body cavity Multicellular with tissues in 2 layers: Placozoa and Porifera Multicellular, tissues in 2 layers, radial symmetry: Cnidaria, Ctenophora Embryonic Development • Morphogenesis: the study of the development of the embryos. • Cleavages: mitotic cell divisions • Zygote: diploid cell formed between sperm and egg • Blastula: the embryo consisting of 64 cells -cavity inside called blastocele • Gastrula: results from blastula growing and folding in on itself. -cavity inside called archenteron • Develops 2 distinct germ layers, endoderm & ectoderm, and most develop the mesoderm *see chart on page 561 for structures produced by germ layers • Neural tube: formed by a rapidly dividing fold of tissue from the ectoderm • neurulation: the pinching and forming of the neural tube • Becomes the brain and spinal cord • Notochord becomes the vertebrae of the spinal column. Development Patterns • Direct development: the immature form looks like a miniature version of the mature form. • Indirect development: has an intermediate stage between the immature and mature organisms. Do not look similar at this point. -see frog p.562 Vertebrates and Invertebrates • Main difference – vertebrates have a spinal column and invertebrates do not. • See chart on page 563 Phylum Placozoa • Smallest phylum in Animalia • One species • Multicellular in 3 layers Phylum Porifera • • • • • • Sponges – simple animal not a plant >10,000 species Sessile – don’t move Diagram page 565 Gemmule – asexual bud Also sexually reproduces