* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Authentication Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Cellular network wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
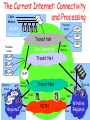
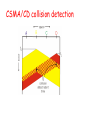
Wireless Security The Current Internet: Connectivity Cable and Processing Modem Premisesbased Access Networks Core Networks WLAN Transit Net WLAN Operatorbased Cell Cell Cell Regional LAN Transit Net Premisesbased WLAN LAN Analog NAP Public Peering Data Voice LAN Private Peering Transit Net H.323 RAS H.323 PSTN DSLAM Data Voice Wireline Regional How can it affect cell phones? Cabir worm can infect a cell phone Infect phones running Symbian OS Started in Philippines at the end of 2004, surfaced in Asia, Latin America, Europe, and recently in US Posing as a security management utility Once infected, propagate itself to other phones via Bluetooth wireless connections Symbian officials said security was a high priority of the latest software, Symbian OS Version 9. With ubiquitous Internet connections, more severe viruses/worms for mobile devices will happen soon … Outlines 802.11 Basics Mobile link access: CDMA/CA Security in 802.11b Example and more attacks Trend: 802.16 Wireless MAN IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN 802.11b 2.4-5 GHz unlicensed radio spectrum up to 11 Mbps widely deployed, using base stations 802.11a 5-6 GHz range up to 54 Mbps 802.11g 2.4-5 GHz range up to 54 Mbps All use CSMA/CA for multiple access All have base-station and ad-hoc network versions Base station approch Wireless host communicates with a base station base station = access point (AP) Basic Service Set (BSS) (a.k.a. “cell”) contains: wireless hosts access point (AP): base station BSS’s combined to form distribution system (DS) Ad Hoc Network approach No AP (i.e., base station) wireless hosts communicate with each other to get packet from wireless host A to B may need to route through wireless hosts X,Y,Z Applications: “laptop” meeting in conference room, car interconnection of “personal” devices battlefield CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) CSMA: listen before transmit: If channel sensed idle: transmit entire frame If channel sensed busy, defer transmission Human analogy: don’t interrupt others! CSMA collisions collisions can still occur: propagation delay means two nodes may not hear each other’s transmission collision: entire packet transmission time wasted note: role of distance & propagation delay in determining collision probability spatial layout of nodes CSMA/CD (Collision Detection) CSMA/CD: carrier sensing, deferral as in CSMA collisions detected within short time colliding transmissions aborted, reducing channel wastage collision detection: easy in wired LANs: measure signal strengths, compare transmitted, received signals difficult in wireless LANs: receiver shut off while transmitting human analogy: the polite conversationalist CSMA/CD collision detection IEEE 802.11: multiple access Collision if 2 or more nodes transmit at same time CSMA makes sense: get all the bandwidth if you’re the only one transmitting shouldn’t cause a collision if you sense another transmission Collision detection doesn’t work: hidden terminal problem IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol: CSMA/CA 802.11 CSMA: sender - if sense channel idle for DISF sec. then transmit entire frame (no collision detection) -if sense channel busy then binary backoff 802.11 CSMA receiver - if received OK return ACK after SIFS (ACK is needed due to hidden terminal problem) Collision avoidance mechanisms Problem: two nodes, hidden from each other, transmit complete frames to base station wasted bandwidth for long duration ! Solution: small reservation packets nodes track reservation interval with internal “network allocation vector” (NAV) Collision Avoidance: RTS-CTS exchange sender transmits short RTS (request to send) packet: indicates duration of transmission receiver replies with short CTS (clear to send) packet notifying (possibly hidden) nodes hidden nodes will not transmit for specified duration: NAV Collision Avoidance: RTS-CTS exchange RTS and CTS short: collisions less likely, of shorter duration end result similar to collision detection IEEE 802.11 allows: CSMA CSMA/CA: reservations polling from AP Outlines 802.11 Basics Mobile link access: CDMA/CA Security in 802.11b Example and more attacks Trend: 802.16 Wireless MAN 802.11b: Built in Security Features Service Set Identifier (SSID) Differentiates one access point from another SSID is cast in ‘beacon frames’ every few seconds. Beacon frames are in plain text! Associating with the AP Access points have two ways of initiating communication with a client Shared Key or Open Key authentication Open key: need to supply the correct SSID Allow anyone to start a conversation with the AP Shared Key is supposed to add an extra layer of security by requiring authentication info as soon as one associates How Shared Key Auth. works Client begins by sending an association request to the AP AP responds with a challenge text (unencrypted) Client, using the proper WEP key, encrypts text and sends it back to the AP If properly encrypted, AP allows communication with the client Wired Equivalent Protocol (WEP) Primary built security for 802.11 protocol Uses 40bit RC4 encryption Intended to make wireless as secure as a wired network Unfortunately, since ratification of the 802.11 standard, RC4 has been proven insecure, leaving the 802.11 protocol wide open for attack Case study of a non-trivial attack Target Network: a large, very active university based WLAN Tools used against network: Laptop running Red Hat Linux v.7.3, Orinoco chipset based 802.11b NIC card Patched Orinoco drivers Netstumbler • Netstumbler can not only monitor all active networks in the area, but it also integrates with a GPS to map AP’s Airsnort • Passively listen to the traffic NIC drivers MUST be patched to allow Monitor mode (listen to raw 802.11b packets) Assessing the Network Using Netstumbler, the attacker locates a strong signal on the target WLAN WLAN has no broadcasted SSID Multiple access points Many active users Open authentication method WLAN is encrypted with 40bit WEP Cracking the WEP key Attacker sets NIC drivers to Monitor Mode Begins capturing packets with Airsnort Airsnort quickly determines the SSID Sessions can be saved in Airsnort, and continued at a later date so you don’t have to stay in one place for hours A few 1.5 hour sessions yield the encryption key Once the WEP key is cracked and his NIC is configured appropriately, the attacker is assigned an IP, and can access the WLAN More Attacks in Wireless Networks Rogue Access Point Solution: Monitor the air space for unexpected AP Radio Frequency (RF) Interference AP Impersonation Rogue AP spoofs its MAC address to the identity of an authorized AP Man-in-the-middle attack Denial of service attack Outlines 802.11 Basics Mobile link access: CDMA/CA Security in 802.11b Example and more attacks Trend: 802.16 Wireless MAN IEEE 802.16 WirelessMAN Standard for Broadband Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks Broad bandwidth Up to 134 Mbps in 10-66 GHz band Comprehensive and modern security Packet data encryption • DES and AES used Key management protocol • Use RSA to set up a shared secret between subscriber station and base station • Use the secret for subsequent exchange of traffic encryption keys (TEK) Backup Slides Summary of MAC protocols What do you do with a shared media? Channel Partitioning, by time, frequency or code • Time Division,Code Division, Frequency Division Random partitioning (dynamic), • ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD • carrier sensing: easy in some technologies (wire), hard in others (wireless) • CSMA/CD used in Ethernet