* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wireless LAN - People.vcu.edu
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum reallocation wikipedia , lookup
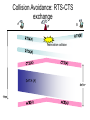
Wireless Access • avoid collisions: 2+ nodes transmitting at same time • CSMA - sense before transmitting – don’t collide with ongoing transmission by other node • no collision detection! – difficult to receive (sense collisions) when transmitting (what you hear is not he hear) – can’t sense all collisions in any case: hidden terminal, fading – The next best thing to do: avoid collisions CSMA/C(ollision)A(voidance) Collision Avoidance: RTS-CTS exchange A AP B reservation collision DATA (A) time defer IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN • 802.11b • 802.11a – 2.4-5 GHz unlicensed – 5-6 GHz range radio spectrum – up to 54 Mbps – up to 11 Mbps • 802.11g – direct sequence – 2.4-5 GHz range spread spectrum – up to 54 Mbps (DSSS) in physical • All use CSMA/CA for layer multiple access – widely deployed, using base stations • Base-station and ad-hoc network versions 802.11 LAN architecture Internet AP switch or router BSS 1 AP BSS 2 • wireless host communicates with base station – base station (BS) = access point (AP) 802.11 Operating Modes • DCF: Distributed Coordination Function – – – – – – aka Ad-hoc mode CSMA/CA RTS/CTS signaling Two stations can communicate All stations have the same logic No infrastructure, Suitable for small area • PCF: Point Coordination Function – – – – Infrastructure Based: Must have a base station (or access point) BS periodically broadcast a beacon MS can only transmit when it is being polled 802.11 Channels • 802.11b: Use 11 channels at different frequencies – AP admin select operating frequency for AP – interference possible: channel can be same as that chosen by neighboring AP! – Planning: decide which AP use which channels to provide good coverage. • host: must associate with an AP – scans channels, listening for beacon frames containing AP’s name (SSID) and MAC address – selects AP to associate with – may perform authentication – will typically run DHCP to get IP address in AP’s subnet