* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solar System Formation
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
Near-Earth object wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
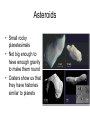
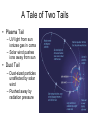
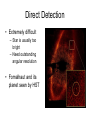
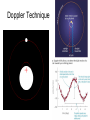
Solar System Formation And the Stuff that was Left Over Things we need to explain • The similarities in the motions and orbits of the objects in the solar system • Dichotomy in planetary morphology and composition • Asteroids and comets • Peculiarities Orbital Patterns • All planets orbit the sun in the same direction • Orbits nearly circular and in same plane • Nearly all rotate the same direction as sun • Satellites have properties similar to their host planets Morphology Dichotomy Terrestrial Planets Jovian Planets • Located in inner solar system • Small and dense • Rocks and metals • Few satellites • No rings • Located in outer solar system • Large and low density • Lots of H compounds • Lots of satellites • Rings Peculiarities • Uranus rotates on its side • Venus rotates opposite to its orbital motion • Earth has one of the largest satellites in inner solar system – Other inner planets don’t have satellites or very small ones What theory can explain all this? The Nebular Theory Orbital Motions • Heating – because of conservation of energy, as nebula contracts, it heats up • Spinning – because of conservation of angular momentum, as nebula contracts, it spins faster and faster • Flattening – due to collisions Making Planets • Start with some seed • Accretion – the process of more and more material being added to the seed • Gravity attracts more stuff – Inside frost line: all heavy elements – Outside frost line: Hydrogen compounds can condense Clearing out the Nebula • Young sun lights up and starts pouring out radiation and particles • Radiation and solar wind blow away the rest of the H and He • Clearing out the gas stops the planet from accreting more material • Planets are now stuck with what they’ve got Peculiarities When did the Solar System Form? • Radiometric dating shows us the solar system is about 4.5 billion years old • Look at ratios of radioactive isotopes • Half life – the length of time required for half of the material to decay Asteroids, Meteors, and Comets Oh My! What’s the Difference? • Asteroid – Rocky leftover planetesimals that never made it into a planet • Meteor – Flash of light in Earth’s atmosphere – (The weather person is a meteorologist) • Comet – Similar to asteroids but made of ice – Where were they formed • Dwarf Planet – Big enough to be round – Not big enough to clear its orbit Asteroids • Small rocky planetesimals • Not big enough to have enough gravity to make them round • Craters show us that they have histories similar to planets Asteroid Belt • Belt between Mars and Jupiter where most asteroids live • Why is it there? Asteroid Belt • Orbital Resonances with Jupiter – Creates Kirkwood gaps in belt – Prevented asteroids from ever coming together and forming a planet Meteors • Meteor – flash of light caused by something entering Earth’s atmosphere • Meteoroid – the object in Earth’s atmosphere • Meteorite – such objects once they have reached the ground Meteorites • Primitive Meteorites – Unchanged since the formation of the solar system • Processed Meteorites – From the core of a shattered asteroid – Often mostly Fe Comets Structure Interior • Nucleus – Main chunk of ice from which the comet is made • Coma – Cloud of gas around nucleus caused by sun’s heating of the ice A Tale of Two Tails • Plasma Tail – UV light from sun ionizes gas in coma – Solar wind pushes ions away from sun • Dust Tail – Dust-sized particles unaffected by solar wind – Pushed away by radiation pressure Origins • Oort Cloud – Goes out to 50,000 AU – Contains trillions of comets • Kuiper Belt – 30-50 AU • Heavy bombardment • Comets get flung way out by big things like Jupiter Kuiper Belt Objects Fate • Ice binds comet together • When all the ice is melted away, the comet might disintegrate Fate Tunguska Video Exoplanets Detection • Direct Detection – Images of the planet itself • Indirect Detection – precise measurements of the host star that tell us a planet must be orbiting it Direct Detection • Extremely difficult – Star is usually too bright – Need outstanding angular resolution • Fomalhaut and its planet seen by HST Indirect Methods Gravitational Wobble: Astrometric Technique Doppler Technique Transits • Planet travels in front of star, blocking some of stars light, which we can measure • Movie