* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CP-CRE ISDH - APIC Indiana
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
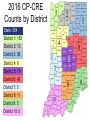
Carbapenemase-Producing Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae DJ Shannon Multidrug-Resistant Organism Epidemiologist Infectious Disease Epidemiology Epidemiology Resource Center Indiana State Department of Health Overview • Definitions • Antibiotic resistance – Spread – Mechanisms of action • CRE and CP-CRE – MDRO Reporting • Laboratory aspects • Infection control and prevention • IP Video Conference Series Definitions • Multidrug-resistant organism (MDRO): an organism that is resistant to one or more agent in at least three classes of antibiotics – or that exhibits a classification of resistance that is of epidemiological concern (e.g. MRSA, VRE, ESBL, CRE) • Extensively drug-resistant organism (XDRO): microorganisms that are resistant to nearly all antimicrobial agents that would be considered for treatment Definitions • Pan-resistant organism: microorganisms that are resistant to all antimicrobial agents that would be considered for treatment Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance • • • • • Penicillin-binding protein modifications Porin mutations Efflux pumps Antibiotic target changes Enzymatic inhibition Enzymatic Inhibition • ß-lactamases – AmpC cephalosporinases • Confers resistance to cephalosporins (and many penicillins) – Extended-spectrum ß-lactamases (ESBL) • Confers resistance to penicillins and cephalosporins • Can also exhibit coresistance to tetracyclines, sulfonamides, and aminoglycoside • Some ESBLs confer resistance to fluoroquinolones – Carbapenemases • Capable of inactivating all ß-lactam antibiotics (except Aztreonam) Carbapenemases • Class A Carbapenemases – Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) • Confers resistance to all ß-lactams • Susceptible to ß-lactamase inhibitors Carbapenemases • Class B Carbapenemases – Metallo-ß-lactamases (MBLs) – MBLs break down all ß-lactams, except aztreonam – High mobility poses an infection control threat – Examples: • New Delhi Metallo-ß-lactamase (NDM) • Imipenemase (IMP) • Verona Integron-mediated Metallo-ßlactamase (VIM) Carbapenemases • Class D Carbapenemases – Confers low-level resistance to carbapenems unless in the presence of other ß-lactamases – Not very efficient at breaking down 3rd generation cephalosporins – Example: • Oxacillinase-48 (OXA-48) Mobility of Carbapenemases – Carbapenemase genes are found on plasmids – Horizontal gene transfer • This occurs when a gene conferring resistance moves from one bacterial cell to another • Methods: • Conjugation • Transduction • Transformation CRE: A Public Health Threat • CP-CRE in the United States are an urgent threat • CP-CRE infections are associated with high mortality rates • CP-CRE confer high levels of resistance • CP-CRE have very mobile resistance genes that can easily be shared with other organisms (CP-CROs) Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae • Definition: Any Enterobacteriaceae that are not susceptible (i.e. intermediate or resistant) to a carbapenem antibiotic • Enterobacteriaceae can be resistant to carbapenems through several resistance mechanisms • Carbapenemase production is currently the most concerning Carbapenemase-Producing Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae • Enterobacteriaceae that are not susceptible (i.e. intermediate or resistant) to at least one carbapenem antibiotics – AND one of the following: • Positive for carbapenemase production by a phenotypic test • Not susceptible to at least three carbapenem antibiotics – OR: • Positive for a carbapenemase gene marker CRE vs. CP-CRE CarbapenemResistant Enterobacteriaceae NonCarbapenemases PBP mutation Efflux Pumps CP-CRE !!! Carbapenemases Porin Mutations KPC NDM, VIM, IMP Reportable OXA Risk Factors of CRE • Recent healthcare exposure – ACH, LTC, LTACH • Recent medical procedures • Recent invasive device use – Mechanical ventilator, PICC line, Foley catheter • Recent antibiotic use • Prior history of MDRO colonization or infection Laboratory Aspects • Culture • Antibiotic Susceptibility – Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) • Phenotypic Tests – Modified Hodge test, CarbaNP, Carbapenemase Inhibition method (CIM), modified CIM (mCIM) • Molecular Tests – PCR Infection Prevention Implications for CRE Facility-Level Prevention Strategies • Hand Hygiene • Contact Precautions • Healthcare Personnel Education • Use of Devices • Laboratory Notification • Inter-facility Communication • Antibiotic Stewardship • Environmental Cleaning • Patient and Staff Cohorting • Screening Contacts of CRE Patients • Active Surveillance Testing • Chlorhexidine Bathing Indiana CP-CRE 2016 Data 354 CP-CRE cases • • • • • • • • 281 Klebsiella pneumoniae 22 Serratia marcescens 21 Escherichia coli 20 Enterobacter cloacae complex 5 Citrobacter freundii 3 Proteus mirabilis 1 Citrobacter amalonaticus 1 Enterobacter aerogenes • • • • • • 334 KPC 4 NDM 4 VIM 2 OXA-48 1 SME 9 unknown 2016 CP-CRE Counts by District State: 354 District 1: 153 District 2: 13 District 3: 38 District 4: 8 District 5: 79 District 6: 42 District 7: 5 District 8: 11 District 9: 5 District 10: 0 I-NEDSS CDR Submission • Please attach the following: – History and physical – Associated antibiotic susceptibility labs – Medication history • Additional information: – Start date of contact precautions – Healthcare exposure history – Travel history Resources • Facility Guidance for Control of CRE – Google: CDC CRE Toolkit Resources • Guidance for a Health Response to Contain Novel or Targeted MDROs – Google: CDC contain novel MDRO New Video Conference Series • The ISDH Epidemiology Resource Center is launching a video conference series for infection preventionists in Indiana • Video conference will focus on HAIs, MDROs, antibiotic stewardship, and feature hot topics from other subject matter experts New Video Conference Series • The first IN-HASARD video conference will be held via WebEx on Friday, April 28th from 1-2 PM EST. • Need an invite? Email Janae Meyers, ISDH Antibiotic Stewardship Epidemiologist, at [email protected] Contact Information DJ Shannon Multidrug-Resistant Organism Epidemiologist Infection Disease Epidemiology Epidemiology Resource Center Indiana State Department of Health Work: 317-233-1306 Email: [email protected]