* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jovial Planets
Eight Worlds wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Juno (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
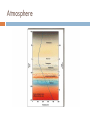
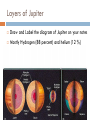
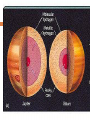
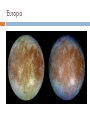
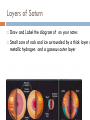
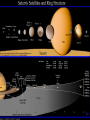
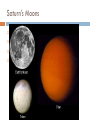
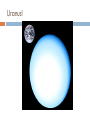
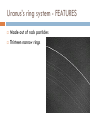
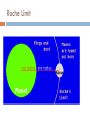
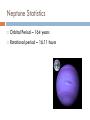
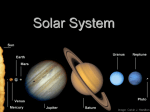
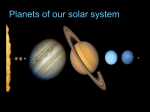
JOVIAL PLANETS Outer Solar system Outer system Jupiter Jupiters Facts Mythology – Roman god Jupiter Facts 5th planet from the sun Largest planet in our solar system Gas Giant Oblate Spheriod shape – Bulge in the middle! Jupiter’s Statistics Orbital Period – 4331. 5 days Size = 121 Earths Gravity – 24 m/s Surface Temp – 165 K (more than 200 C below 0) Jupiter’s Atmosphere Atmospheric Data comes from Galileo Probe that crashed into the atmosphere of Jupiter Atmosphere divided into distinct bands Atmosphere Layers of Jupiter Draw and Label the diagram of Jupiter on your notes Mostly Hydrogen (88 percent) and helium (12 %) Magnetosphere 14 times as strong as earths Aurora Magnetic Flux Tubes Three bright dots connect to Ion, Ganymede and Europa Aurora Jupiter’s Red Spot Longest Lasting Storm in history (Discovered in the 1600) Rotates counterclockwise every 6 days Slowly fading Jupiter’s Ring System Jupiters ring System Jupiter’s ring system Jupiters rings are very difficult to see. Jupiter's rings were first found by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979 Three main sections comprise Jupiter's ring system. Halo ring -The innermost, cloud-like Main Ring -is quite narrow and thin. Gossamer Ring-wispy, nearly transparent http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moons_o f_Jupiter Jupiter’s Shepherd Moons Metis Thebe Adrastea Amalthea INNER MOONS! Jupiters 4 galilean Satellites Io Europa Callisto Ganymede BASIC FACTS = discovered by Galileo in 1610 He spotted the four large moons and realized that they were orbiting Jupiter, Not EARTH!!! Io Images of Io Image Io http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KXeIll6YYQs Has a large iron Core (may be molten) SO2 Atmosphere (Thin) Closest to jupiter 4th largest moon Most volcanically active body in the solar sustem 400 active volcanoes blue./white spots are volcanoes erupting Europa Water? Life? http://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=xEtf5lh3 SEw Europa is an Icy satellite Below Europa’s frozen exterior of ice, there is liquid water Vast sea could hold microorganisms Heat generated by planet flexing, keeps water liquid Europa europa Ganymede Largest Moon in the solar system Has a magnetosphere http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=64oBWEsMq 2Y Sounds http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=6PPEwGJy6P I Callisto 2nd largest moon of jupiter Tidally locked Thin CO2 Atmospere Subsurface ocean Could be a “human” base for research Saturn Saturn’s Facts Mythology – names after roman god Saturnus (Saturday!). Facts 6th planet from the sun 2nd largest planet in the solar system Gas Giant Oblate Spheriod Less dense then water! Saturn’s Statistics Orbital Period – 10759 days (29.5 years) Size = Gravity= Surface Temp – Saturn’s Atmosphere Atmosphere 93.2 % molecular hydrogen, 6.7 %helium Faint atmosphere bands (lighter than jupiter) Cloud patterns observed by voyager (hexagonal) Surface Has a planetary magnetic field, strength in between earth and jupiter Wind speeds of 1800 km/h Saturn’s Great White spot Giant storm hat happens every 30 years (once a saturian year) Will be another one in 2020 Layers of Saturn Draw and Label the diagram of on your notes Small core of rock and ice surrounded by a thick layer o metallic hydrogen and a gaseous outer layer Saturn’s ring System Saturns’s ring system First discovered by Galileo in 1610 Rings consist mostly of ice with small amounts of debris and dust Theories: Roche - Rings were once a moon of saturn that was ripped apart by tidal forces Secondary – Rings are left over from original nebular material from which saturn formed Saturns’s ring system - FEATURES Features: Cassini division Enckle Gap Possess own atmosphere of molecular O2 different from saturn Roche Limit Moons 61 moons 52 with names 6 unconfirmed moons Jupiter’s Shepherd Moons Metis Thebe Adrastea Amalthea INNER MOONS! Saturn’s Moons Io Europa Callisto Ganymede Titan Images of Io Image Titan Only moon in the solar system to have its own atmosphere atmosphere is impenetrable to visible waves 2nd largest moon in the solar system Resembles early earth Atmosphere of nitrogen and methane Surface – False Color Cassini Missions Voyager Arrived: 1980 Studies: close fly by of Titon, Achieves: images of rings Missions Cassini Arrived: 2004 Studies: saturn orbit insertion, flyby of titan. lightning Huygen Insertion – Huygens descended onto the surface of Titan on January 14, 2005, Missions – Cassini Orbit Uranus! Uranus’s Facts Mythology – Named after the greek god of the sky 7th planet from the sun 3nd largest planet in the solar system Ice Giant Tilted sideways (north and south lay where other planets have their equators) Uranus’s Statistics Orbital Period – 84 years Rotational Period = 17 hours 14 minutes Tilt – Rolling ball (not top) Low internal heat Uranus’s Atmosphere Atmosphere Coldest Atomosphere in the solar system Belt -Zone Circulation Belt – Dark colored band Zone – Light colored band Belts and zones flow in opposite directions Storms occur in between belts Heat produced in the center feeds the storms Uranus’s ring system - FEATURES Made out of rock particles Thirteen narrow rings Roche Limit: where are the rings? Moons 27 moons Named from the works of Shakespeare and Alexander Pope Largest moon –Titania (less than half the size of the moon) Visited by Voyager 2 Uranus’s Moons Roche limit If moons are to close: The gravity of planet will break them up (maybe becoming rings) If moons are too far away: They orbit will not be held in Roche Limit (Notes) Distance within 2.5 radii of the center of a planet Moons cannot form/moons are torn apart RINGS ARE FOUND INSIDE THE ROCHE LIMIT MOONS ARE FOUND OUTSIDE THE ROCHE LIMIT Roche Limit Missions to the outer solar system Pioneer 10 and 11 Voyager 1 and 2 Galileo (Jupiter) Cassini (Saturn) Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Ganymede, Io, europa, Callisto, Titan, tritan, titania Neptune! Neptune Facts Mythology – Named after the roman god of the sea 8th planet from the sun 17 times the mass of the earth Ice Giant Neptune Statistics Orbital Period – 164 years Rotational period – 16.11 hours Neptune’s Great Dark Spot Strongest sustained winds win the solar system 2100 km per hour Neptune’s ring system - FEATURES Made out of rock particles Very fragmented Very Faint Moons 13 moons Triton: moves in the opposite direction of its planets Most likely used to be a dwarf planet Spiraling inward (will eventually be torn apart)