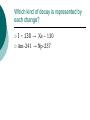* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nuclear Decay (Radioactivity)
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
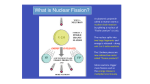
Nuclear Decay (Radioactivity) Subatomic particles Electron -negatively charged particle found outside the nucleus. Proton – positively charged subatomic particle found inside the nucleus. Neutron – Neutrally charged (no charge) subatomic particle found inside the nucleus. Some Surprises A neutron is a proton with a captured electron. A neutron can become a proton by losing that electron. That electron, when it comes flying out of the nucleus, will be called a beta particle. It’s symbol is the Greek letter β. Beta radiation What would happen to the nuclear make-up as a result of beta radiation? Consider: carbon – 14. -+ = neutron + +-+ + -+ -+ +-++ + -+ + -+ -+ = proton Beta radiation What would happen to the nuclear make-up as a result of beta radiation? Consider: carbon – 14. -+ = neutron + +-+ + -+ -+ +-++ + -+ + -+ - + = proton Beta radiation How many protons does it have now? What is its mass number? -+ = neutron + +-+ + -+ -+ +-++ + -+ + -+ + = proton Alpha Radiation An alpha (α) particle is the same as a helium nucleus and is therefore symbolized by: 42 He -+ = neutron + = proton -+ -+ + + -+ + -+ + + -+ +-+ + -+ -+ -+ + -+ -+ + -+ -+ + ++ + + ++ -+ -+ + -+ + -+ -+ +-+-+ -+ + + -+ ++ + -+ -+ Alpha Decay When an alpha particle is emitted from a nucleus, what is left? Consider Uranium – 238. 238 92 U XTh 234 90 + 4 2 He Which kind of decay is represented by each change? I – 130 → Xe – 130 Am-241 → Np-237 Three Kinds of Decay Alpha – a helium nucleus, cannot penetrate paper. Beta - an electron which is emitted from the nucleus. Can penetrate paper, but cannot penetrate aluminum foil. Gamma ray – not a particle. 50% emitted will penetrate 1cm of lead.