* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Justinian and Theodora
Monothelitism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Emirate of Crete wikipedia , lookup
History of Eastern Orthodox theology wikipedia , lookup
East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine–Arab wars (780–1180) wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine dress wikipedia , lookup
History of the East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
State church of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
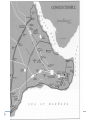
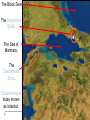
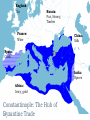
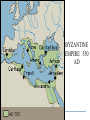
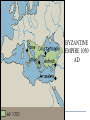
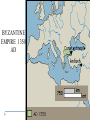
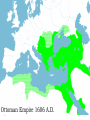
Byzantine Empire Main Idea After the fall of the Roman Empire in the West, the Byzantine Empire emerged as the dominant eastern power, with Constantinople as its political, economic, and religious center. The empire lasted over 1,000 years. Background: 1. Western half of the Roman Empire fell in 476 A.D. 2. Byzantium had already been rebuilt by Emperor Constantine, who then renamed the city Constantinople. Geography and Cityscape of Constantinople 1. Built on seven hills and divided into 14 districts, like Rome. 2. Protected by 13 miles of walls, watchtowers, and gates. 3. Easily fortified site surrounded on three sides by water, bordering a natural harbor. Its location combined with its control of the Bosporus Strait made the city a hub for trade and shipping between Europe, Africa, and Asia. Walls of Constantinople A satellite view of the area. Can you see the remarkable location of Constantinople at the center of the ‘X’ of land Europe Black Sea & sea trade routes? Asia Aegean Sea The Black Sea. The Bosphorus Strait. The Sea of Marmara. The Dardanelles Strait. Constantinople today known as Istanbul. A great view of the Bosphorus from space. Can you see the point that is Byzantium? And can you see the narrow bay to the north of Byzantium that is called the Golden Horn? A satellite view of Istanbul today. There used to be a chain stretched across the Golden Horn for protection. Geography and Cityscape of Constantinople 4. Adequate distance from Germanic invasions of the western empire. 5. Good location to protect Europe’s eastern frontier. 6. Seized by Turks in 1435 and renamed Istanbul; today it is a major city in modern Turkey. Role of Constantinople: 1. True center or seat of Byzantine power until the Ottoman conquest 2. Important in preserving classical Greco-Roman culture Justinian and Theodora How Justinian Was Described While alive Justinian was described as devout, determined, and energetic. Why? After His Death, the historian Procopius referred to Justinian as two-faced and cruel in a “Secret History” Achievements of Byzantine Emperor Justinian: 1. Justinian Code (Corpus Juris Civilis) – sorted through old Roman laws and established a new code of law for the Byzantine Empire. It lasted for 900 years! - included laws concerning marriage, slavery, property, inheritance, and women’s rights - Significance – had a significant impact on European legal code Achievements of Byzantine Emperor Justinian: 2. Re-conquered former Roman territories but not Rome 3. Significantly expanded trade Achievements of Byzantine Emperor Justinian: 4. Acted as head of church and state (2seated Chair) 5. Placed a heavy emphasis on church building, which displayed his leadership of both the government and the church. - Hagia Sophia – Constantinople’s masterpiece of architecture and faith One of Justinian’s greatest accomplishments - the construction of the beautiful Cathedral of the Holy Wisdom ~ The Hagia Sophia And more achievements! 6. Came to throne at age 45! Considered Byzantium's most ambitious ruler. 7. Drove barbarians out of North Africa, Spain, and Italy 8. Built bridges, churches, hospitals, libraries, and last but not least parks. THEODORA!?!?!? Born into lower class, worked as an actress and dancer as a teenager. Loved adventure, new friendships and travel Married Justinian while in her 20’s, sometimes equaled or surpassed husbands wisdom and skills. Convinced her husband to crush Nika rebellion Established Social Welfare programs for the poor Worked for the rights of women Theodora Engineering an Empire Video- Justinian & Theodora In the bubble heads, write 5 statements about Theodora from the points of view of: The poor Women Nika rebels Justinian Her friends Hagia Sophia HAGIA SOPHIA Key Points in the History of the Hagia Sophia Built during Justinian’s reign. Took 5-6 years to build Known as the “Church of Holy Wisdom” When Constantinople fell to the Turks, Hagia Sophia became a mosque; now it is a museum HAGIA SOPHIA Important concepts found in the Hagia Sophia’s Architecture Plain exterior symbolizes earthly life Ornate interior symbolizes spiritual universe Cathedral’s size, thick pillars, and enclosed space show Roman influence. Intricate and ornate design shows Eastern influences 1. Byzantine architects invented the pendentives which connected the round base of a dome to a square building. 2. The combination of Greco-Roman and Middle Eastern influence are evident in the intricate decoration on this column. Mosaics with gold-covered stones added more light to the huge interior of Hagia Sofia. Byzantine Achievements in Art and Architecture: 3. art and architecture inspired by two things: Christian religion and imperial power 4. Icons – definition – religious images 5. Elaborate mosaics in public and religious structures Icon/Mosaic in Hagia Sophia Byzantine Achievements in Art and Architecture: 4. Hagia Sophia – most beautiful architectural achievement 5. Hippodrome – entertainment venue for chariot races and circuses Hippodrome Engineering and Empire Video Byzantine Culture: 1. Greek and Roman knowledge preserved in Byzantine libraries 2. Greek – primary language (as opposed to Latin in the West) 3. Church – Greek Orthodox Christianity The Division of the Christian Church: Background: Distance and lack of contact slowly caused the doctrines and rituals of Western and Eastern th Christianity to split in the 11 Century. The Great Schism Icons – Pictures of important Christians or sacred events. Can be mosaics, murals, wooden panels. Those who did not believe in them were called Iconoclasts (Eastern Christians) This was one of the breaking points for the split. East vs. West : A Religious Dispute •Patriarch- head bishop of the east (Constantinople) •Conflict about power of Pope (in west) and Emperor (in east) •Regional differences made more conflicts arise The Western ChurchRoman Catholic 1. Centered in Rome 2. Far from the seat of government power once the capital moved to Constantinople 3. Services conducted in Latin The Western ChurchRoman Catholic 4. The pope had authority over all other bishops 5. The pope had authority over all kings and emperors 6. Priests cannot marry and must remain celibate 7. Divorce is not permitted The Eastern Church – Greek/Eastern Orthodox 1. Centered in Constantinople 2. Close to seat of government power once capital moved to Constantinople 3. Services conducted in Greek or local languages The Eastern Church – Eastern Orthodox 4. The patriarch and other bishops head the church as a group 5. The emperor claimed authority over the patriarch and other bishops of the Byzantine Empire 6. Priests may be married 7. Divorce is allowed under certain conditions The Great Schism In 1054, the split between the Eastern and Western Churches was made permanent when the Pope (in the West) and the Patriarch (in the East) excommunicated each other. Excommunication – definition: cast out from the church This permanent split was called the schism Service are conducted in Latin The pope has authority over all other bishops The pope claims authority over all kings and emperors Priests may not marry Divorce is not permitted Roman Catholic They base their faith on the gospel of Jesus and the Bible They use sacraments such as baptism Their religious leaders are priests and bishops They seek to convert people Service are conducted in Greek or local languages The patriarch and other bishops head the Church as a group The emperor claims authority over the patriarch and other bishops of the empire Priests may be married Divorce is permitted under certain conditions Eastern Orthodox England Tin Russia: Fur, Honey, Timber France: Wine China: Silk Spain: Cork India: Spices Africa: Ivory, gold Constantinople: The Hub of Byzantine Trade Plague of Justinian that crippled Empire In 542, 10,000 people were dying every day! Attacks from East, West, and North Slavs, Persians, Turks, and Russian invasions Attempt to maintain power Through political marriages, bribes and diplomacy Walls kept the peninsula strong until 1453 when it fell to the Ottoman Turks Split of the Church What goes up… … Must come down Decline of Empire BYZANTINE EMPIRE 550 AD BYZANTINE EMPIRE 1050 AD BYZANTINE EMPIRE 1350 AD Ottoman Empire 1606 A.D. Influence of Byzantine Culture on Eastern Europe and Russia: 1. Trade routes between the Black Sea and the Baltic Sea led to exchange of ideas and culture 2. Eastern Orthodox missionaries spread their faith to the Slavic people of Russia and Eastern Europe Influence of Byzantine Culture on Eastern Europe and Russia: 3. Cyril invented an alphabet for the Slavic languages so that the Slavs could read the Bible in their own tongue. This was called the Cyrillic alphabet 4. Church architecture and religious art A Russian Orthodox Church in the Ukraine ~ very similar to the Hagia Sophia.