* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ent153_tutorial1
Pseudo Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Viscoplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Work hardening wikipedia , lookup
Strengthening mechanisms of materials wikipedia , lookup
Cauchy stress tensor wikipedia , lookup
Stress (mechanics) wikipedia , lookup
Viscoelasticity wikipedia , lookup
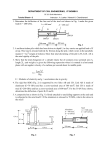
ENT 153 TUTORIAL 1 Problem 1: The bar in Fig. 1 (a) has a constant width of 35 mm and a thickness of 10 mm. Determine the maximum average normal stress in the bar when it is subjected to the loading shown. Note: Fig. 1 (b) shows the internal loadings of the members which are sectioned. Fig. 1 (c) shows the normal force diagram representing the above results graphically. These figures are not given in test or examination. Problem 2: The 80-kg lamp is supported by two rods AB and BC as shown in Figure 2 (a). If AB has a diameter of 10 mm and BC has a diameter of 8 mm, determine the average normal stress in each rod. Fig. 2 Problem 3: The casting shown in Figure 3 (a) is made of steel having a specific weight of γst = 80 kN/m3. Determine the average compressive stress acting at points A and B. Fig. 3 Problem 4: Member AC shown in Fig. 4 (a) is subjected to a vertical force of 3 kN. Determine the position x of this force so that the average compressive stress at the smooth support C is equal to the average tensile stress in the tie rod AB. The rod has a cross-sectional area of 400 mm2 and the contact area at C is 650 mm2. Fig. 4 Problem 5: The bar shown in Fig. 5 (a) has a square cross section for which the depth and thickness are 40 mm. If an axial force of 800 N is applied along the centroidal axis of the bar’s cross-sectional area, determine the average normal stress and average shear stress acting on the material along (a) section plane a-a and (b) section plane b-b. Fig. 5 • Problem 6. • Problem 7: • The small block (Fig. 1) has a thickness of 5 mm. If the stress distribution at the support developed by the load varies as shown, determine – the force F applied to the block, and – the distance d to where it is applied. • • Fig. 1