* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Beginning Proofs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
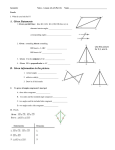
Beginning Proofs Lesson 1.4 Two column proofs and theorems Theorem: A mathematical statement that can be proven. We prove theorem(s) We shall omit the proofs of certain theorems, even though all have proofs We use theorems to help prove sample problems You are then given the challenge of using the theorems to prove homework problems. Theorems will save you much time if you learn them and then use them! You use theorems to prove others, Do not use proffs of theorems as a guide. Use sample problems as a guide. You use deductive reasoning to prove theorems. (Basically you create a chain of logical steps that move from the hypothesis to the concusion of the conjecture you are proving Theorem 1: If two angles are right angles, then they are congruent Given: <A is a right < <B is a right < Prove: <A <B Proof: Statements Reasons 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Given 2. Right angles = 90 3. Given 4. Right angles = 90 5. Two angles of the same measure are congruent <A is a right angle M<A = 90 <B is a right angle M<B = 90 <A <B Theorem 2: If two angles are straight angles, then they are congruent. Given: Diagram Prove: <ABC <FBD Given: <ABC = 115 <XYZ = 115 Prove: <ABC <XYZ Statements 1. <ABC = 115 2. <XYZ = 115 3. <ABC <XYZ Reasons 1. Given 2. Given 3. Def of angles Try This: