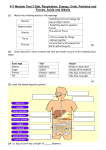
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solutions
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ionic compound wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Solutions Solutions • A solution is a homogeneous mixture where all particles exist as individual molecules or ions. • Mixtures in chemistry are combinations of different substances where each substance retains its chemical properties. A solution is a homogeneous mixture. • Homogeneous means that the mixture is the same all the way through. • You could take two same-sized samples: one from the bottom and one from the top and they would be identical. • Homogeneous mixtures do not settle out if left to sit undisturbed. A solution has two components: the solute and the solvent. • The solvent is the substance in greater amount. It does the dissolving. • It is usually a liquid, but it doesn’t have to be. (It is usually water) • The solute is the substance in lesser amount. It get dissolved. • It is usually a solid, but it doesn’t have to be. Like dissolves Like • A polar solute dissolves in a polar solvent. • A non-polar solute dissolves in a nonpolar solvent. • Other chemical properties also decide whether a solute will dissolve or not. Saturation • Saturated solution: contains the maximum amount of solute in a solvent. • Unsaturated solution: contains less than the maximum amount of solute in a solution. • Supersaturated solution: contains more than the maximum amount of solute in a solvent (this occurs when a solution is heated, solute added, then gradually cooled). Factors affecting Solubility PRESSURE : only gases can be affected by pressure. TEMPERATURE : gaseous solutes require a cooler temperatures to increase solubility. : liquid and solid solute will dissolve more readily in hot solvents. Factors affecting rate of dissolving • Heating • Stirring or Shaking • Increasing surface area • These processes all increase the number of interactions between solute and solvent. The word concentration refers to how much solute is dissolved. • It is a quantity. • Dilute means that only a little solute is dissolved in a lot of solvent(20.0g or less per 100ml solvent). • Concentrated means a great deal of solute is dissolved in a little solvent(20.0g or more per 100ml of solvent). • For example, 100.0g HCl in a little water is concentrated, while 100.0g HCl in a lot of water is dilute. Molarity measures concentration. Molarity = moles of solute litres of solution Ex: What is the Molarity of 53.5grams of calcium chloride dissolved in 362ml of solution? • Change grams of solute to moles of solute. • Divide moles of solute by litres of solvent. 1 mole CaCl2 = 111.0g CaCl2 x 53.5g CaCl2 x = 0.482 mol CaCl2 Molarity = moles of solute litres of solute M = 0.482 moles 0.362 litres M = 1.33M Suppose you had 58.44 grams of NaCl and you dissolved it in exactly 2.00 L of solution. What would be the molarity of the solution? 58.44g is 1 .000 moles of NaCl Molarity = moles of solute litres of solution M = 1.000 mol 2.00 L M = 0.500 M How many litres is needed to prepare a 0.876M solution of potassium nitrate that contains 12.0g of solute? 1 mole KNO3 = 101.1g x = 0.119 mol x 12.0g M = Moles Litres 0.876M = 0.119 moles x litres x = 0.136 litres (or 136ml or 136 cm3)