* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download stoma
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Indigenous horticulture wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Hydroponics wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
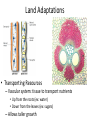
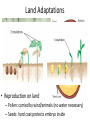
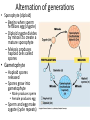
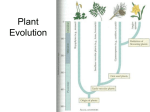
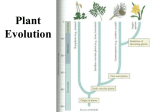
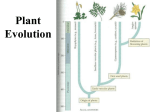
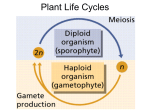
PLANT EVOLUTION KEY CONCEPT Plant life began in the water and became adapted to land. Plant Evolution • Evolved from green algae (450 mya) – Both have chlorophyll, store energy as starch, DNA similarities • Green algae ancestor – Multicellular body – Cells w/ channels to communicate – Reproduce w/ sperm & egg • Early plants – Low growth • True plants evolved through natural selection. – Ancestral charophyceans lived in areas of shallow water. – Those that could survive longer dry periods were favored. – First true plants probably grew at edges of water. – True plants have embryos that develop while attached to female parent. Land Adaptations stoma • Retain Moisture – Early plants grew near waters edge – Cuticle: waxy coating – Stomata: pores to allow gas exchange Land Adaptations • Transporting Resources – Vascular system: tissue to transport nutrients • Up from the roots (ex: water) • Down from the leaves (ex: sugars) – Allows taller growth Land Adaptations • Growing upright – Large plants need to support own weight – Lignin: hardens cell wall; gives wood strength Land Adaptations • Reproduction on land – Pollen: carried by wind/animals (no water necessary) – Seeds: hard coat protects embryo inside Alternation of generations • Sporophyte (diploid) – Begins when sperm fertilizes egg (zygote) – Diploid zygote divides by mitosis to create a mature sporophyte – Meiosis produces haploid cells called spores • Gametophyte – Haploid spores released – Spores grow into gametophyte • Male produces sperm • Female produces egg – Sperm and egg make zygote (cycle repeats) Plant Ecology • Mutualistic relationships – Type of symbiosis where both organisms benefit – Ex: Plants (provides living space)/Bacteria (create nutrients) – Ex: Plants (provide food)/Insects (help pollinate) • Herbivore interactions – Defense adaptations – Spines, thorns, chemicals,