* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparing Monocot and Dicot Pants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Lilioid monocots wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
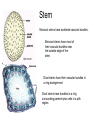
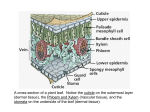
Comparing Monocot and Dicot Pants Objective: 1. To explain what a monocot and dicot plant is 1. To describe the differences between monocots and dicots in terms of their structures 2. To explain how one plant type evolved from the other Classifying Plants • Kingdom Plantae can be classified into two major divisions: 1.Vascular Plants (ie: Ferns, Trees) 2.Nonvascular Plants (ie: Mosses) In this unit we will be learning about vascular plants: their structure and how they function. TYPES OF PLANTS Kingdom Plantae non-vascular mosses vascular plants have specialized organs: roots, stems, leaves seedless ferns seed - bearing gymnosperms cone bearing pine, spruce, cedar angiosperms flowering plants monocot grasses, tulips We will focus on these guys dicot carrots, maples, tomatoes • Angiosperms can be divided into two classes: • Monocotyledons (monocots) and Dicotyledons (dicots) • Cotyledon: A seed leaf that stores carbohydrates (food) for the seedling (baby plant). • Is often the first photosynthetic organ of a young seedling. Go Discover… • Find out what a monocot plant and a dicot plant is. • Create a table to compare the structures of these two classes of plant. • In your table you should compare seeds (cotyledons), stem (vascular bundles), flower, leaf (vein pattern) and root. • Page 282, 296, 301 and 310 in your text book will help you. • The micro-slide-viewer contains a slides with some great images of monocot and dicot structures. Seeds Dicots are seeds that have two parts The two large parts of the seeds are called cotyledons. They supply the food for the young plant when it's growing. Monocots are seeds that only have one cotyledon Leaves Dicot leaves are usually net-veined Notice how the larger veins are thicker and straighter, but as veins get smaller and smaller, they tend to snake around. Monocots typically possess parallel-veined leaves Flower Monocots have their flower parts in threes or multiples of three; example the tulip and lily (Lilium ). Dicots have their flower parts in fours (or multiples) or fives (or multiples). Examples of some common dicot flowers include the geranium and snapdragon. Stem Monocot stems have scattered vascular bundles. Monocot stems have most of their vascular bundles near the outside edge of the stem. Dicot stems have their vascular bundles in a ring arrangement. Dicot stems have bundles in a ring surrounding parenchyma cells in a pith region. Root Dicot roots have their xylem in the center of the root and phloem outside the xylem. The roots of dicots are usually short and stringy. Monocot roots have their vascular bundles arranged in a ring. The root is often a single long tap root with smaller roots growing from it. Plenary 1. What is a cotyledon? 2. How many cotyledons do monocots have? How many do dicots have? 3. What is different about the arrangement of the vascular bundles in monocot and dicot stems? 4. What is different about the arrangement of the veins in monocot and dicot leaves? 5. How is the seed different in a monocot and dicot plant? H/W… 1) Review water and sugar transport in plants. 1) What transports water? 2) What transports sugars? 2) Read through the hand out and answer the questions provided.