* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
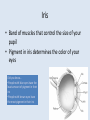
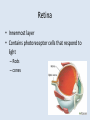
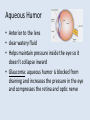
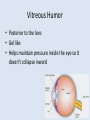
The Eye Chapter 8 Sclera • Thick, white tissue that covers the outermost part of the eyeball – The “white of the eye” • Central, anterior portion is clear Cornea • Transparent window through which light enters the eye Did you know… •The cornea is the only tissue in the body that can be transplanted without the worry of rejection •Since no blood vessels can reach the cornea, it is out of the reach of the immune system Choroid • Middle coat of the eyeball • Prevents light from scattering inside the eye Iris • Band of muscles that control the size of your pupil • Pigment in iris determines the color of your eyes Did you know… •People with blue eyes have the least amount of pigment in their iris •People with brown eyes have the most pigment in their iris Pupil • Opening in the iris that regulates the amount of light that passes into the eye – Constricts: close vision & bright light – Dilates: far vision & dim light Lens • Focuses light entering the eye on the retina • Cataracts: – Lens gets hard and opaque causing it to not be able to focus light as well resulting in hazy vision and eventually blindness Nearsighted vs. Farsighted • Lens doesn’t focus light correctly on retina • Nearsighted (myopia) – Distance objects appear blurry – Point of focus before retina • Farsighted – Near objects appear blurry – Point of focus behind retina Retina • Innermost layer • Contains photoreceptor cells that respond to light – Rods – cones Photoreceptors • Rods – Allow us to see gray tones – Provide for peripheral vision Did you know… •Colorblindness is more frequent in men than women…it is a sex linked trait • Cones – 3 varieties (red, green, blue) – Allow us to see colors – Color blindness: caused by lack of cone type Optic Nerve • Photoreceptors transfer message they receive from light to the optic nerve • Optic nerve sends message to brain – Result is vision. • Blind spot: – Location where optic nerve leaves eyeball (optic disk) – no photoreceptors Aqueous Humor • Anterior to the lens • clear watery fluid • Helps maintain pressure inside the eye so it doesn’t collapse inward • Glaucoma: aqueous humor is blocked from draining and increases the pressure in the eye and compresses the retina and optic nerve Vitreous Humor • Posterior to the lens • Gel like • Helps maintain pressure inside the eye so it doesn’t collapse inward